Mybatis 源码2——SqlSession,执行器和一级缓存
一丶 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,SqlSessionFactory,sqlSession
mybatis 获取sqlSession是通过SqlSessionFactory获取的,SqlSessionFactory又是由SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建出来的
1.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建SqlSessionFactory
//可选的参数是environment和properties。Environment决定加载哪种环境(开发环境/生产环境),包括数据源和事务管理器。
//如果使用properties,那么就会加载那些properties(属性配置文件),那些属性可以用${propName}语法形式多次用在配置文件中
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
//最后一个build方法使用了一个Configuration作为参数,并返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
2.SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
- SqlSessionFactory使用工厂模式创建SqlSession
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
//还有诸多SqlSession openSession的重载方法
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
//获取配置
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
-
DefaultSqlSessionFactory是默认使用的SqlSessionFactory
- 根据数据源创建SqlSession
// ExecutorType 执行器类型 //TransactionIsolationLevel 事务隔离级别 //是否自动提交 private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); //通过事务工厂来产生一个事务 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); //生成一个执行器(事务包含在执行器里) //根据执行器类型创建执行器 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); //然后产生一个DefaultSqlSession return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { //如果打开事务出错,则关闭它 closeTransaction(tx); throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { //最后清空错误上下文 ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } -
根据连接创建数据源
奇怪的是openSessionFromConnection在catch里面没有像openSessionFromDataSource一样在抛出异常后执行事务的close 为什么
private SqlSession openSessionFromConnection(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection) {
try {
boolean autoCommit;
try {
//根据连接获取是否支持自动提交
//连接关闭or 不支持自动提交将抛出SQLException
autoCommit = connection.getAutoCommit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Failover to true, as most poor drivers
// or databases won't support transactions
autoCommit = true;
}
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
final Transaction tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(connection);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
//为什么这里不关闭事务????
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
3.SqlSession
3.1SqlSession概述
SqlSession实际使用了一种设计模式,门面模式(将复杂的逻辑进行包装,如同医院有多个个科室,十分复杂,但是存在前台,前台就是门面模式,将复杂的就诊进行包赚简化)。SqlSession是一个接口,定义了很多方法供调用,其中很多方法都是重载的,参数不一样,满足了各种调用场景。SqlSession用来执行SQL,获取映射器,管理事务。
3.2SqlSession的实现
-
DefaultSqlSession 默认的SqlSession实现,持有一个执行器,实际方法的调用都依赖于Excutor的执行
-
SqlSessionManager
同时实现了SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession,具有创建和完成数据库操作的能力
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
private ThreadLocal<SqlSession> localSqlSession = new ThreadLocal<SqlSession>();
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
//动态代理
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
sqlSessionProxy使用了动态代理模式创建了SqlSession的代理对象。在以后操作CURD相关方法时候,都会委托给这个代理对象。最后一个属性localSqlSession由一个本地线程进行维护,这样保证了并发安全,如果调用了startManagedSession方法那么将使用sqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession并存入到localSqlSession中,SqlSessionInterceptor拦截了数据库crud的执行优先从localSqlSession中获取。
//SqlSessionManager 中数据库crud部分逻辑其实和DefaultSqlSession一样
//SqlSessionManager newInstance()调用了SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build 最后其实调用了
DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
//所以SqlSessionManager中被代理的SqlSessionProxy其实是DefaultSqlSessionFactory创建出来的,最后就是被代理的DefaultSqlSession
https://www.cfanz.cn/resource/detail/xQBWKQzljzxBn ThreadLocal内存泄漏及弱引用的理解
-
SqlSessionTemplate
mybatis-spring包中存在的,后续研究spring整合mybatis再详细学习
4.DefaultSqlSession详细学习
1.DefaultSqlSession的属性
/** 全局配置*/
private Configuration configuration;
/**持有 executor **/
private Executor executor;
/**是否自动提交*/
private boolean autoCommit;
/**是否脏数据 只 更新了数据库但是没有提交*/
private boolean dirty;
2.selectOne 和 selectList
- selectOne 最后调用的是selectList
//RowBounds是分页参数 指定当前页 和页面最大size
//statement 是statement id
//parameter查询参数
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//根据statement id找到对应的MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//转而用执行器来查询结果
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
-
SelectOne
- 没有数据 那么返回null,此时如果使用基本类型接受 那么拆箱将抛出NPE
- TooManyResultsException,数据库存在多条数据满足要求,但是返回是一个,抛出此
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) { //转而去调用selectList,很简单的,如果得到0条则返回null,得到1条则返回1条,得到多条报TooManyResultsException错 //特别需要主要的是当没有查询到结果的时候就会返回null。因此一般建议在mapper中编写resultType的时候使用包装类型 //而不是基本类型,比如推荐使用Integer而不是int。这样就可以避免NPE List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter); if (list.size() == 1) { return list.get(0); } else if (list.size() > 1) { throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size()); } else { return null; } }
3.新增,删除,更新
新增删除都是调用的更新方法
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
//每次要更新之前,dirty标志设为true
//因为这个时候还没有提交 or 回滚
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//转而用执行器来update结果
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
4.提交,回滚,关闭
提交和回滚都是调用了执行器对应的方法,如何判断是否需要提交,回滚,关闭
//检查是否需要强制commit或rollback
//force是否需要强制提交
private boolean isCommitOrRollbackRequired(boolean force是否需要强制提交) {
return (!autoCommit && dirty) || force;
}
5.其他有意思的
-
查询的参数如果是集合or数组将被StrictMap包装
//把参数包装成Collection private Object wrapCollection(final Object object) { if (object instanceof Collection) { //参数若是Collection型,做collection标记 StrictMap<Object> map = new StrictMap<Object>(); map.put("collection", object); if (object instanceof List) { //参数若是List型,做list标记 map.put("list", object); } return map; } else if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) { //参数若是数组型,,做array标记 StrictMap<Object> map = new StrictMap<Object>(); map.put("array", object); return map; } //参数若不是集合型,直接返回原来值 return object; }这或许就是mybatis <foreach > 中属性填写list 和 collection 以及array 可以进行元素便利的原因么??? -
为什么mybatis #{} 使用没有的参数 会抛出Parameter【a】not found,Available parameters are 【param1,param2】
//严格的Map,如果找不到对应的key,直接抛BindingException例外,而不是返回null public static class StrictMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = -5741767162221585340L; @Override public V get(Object key) { if (!super.containsKey(key)) { throw new BindingException("Parameter '" + key + "' not found. Available parameters are " + this.keySet()); } return super.get(key); } }或许这就是@Param注解绑定参数的作用???
二丶执行器和一级缓存逻辑

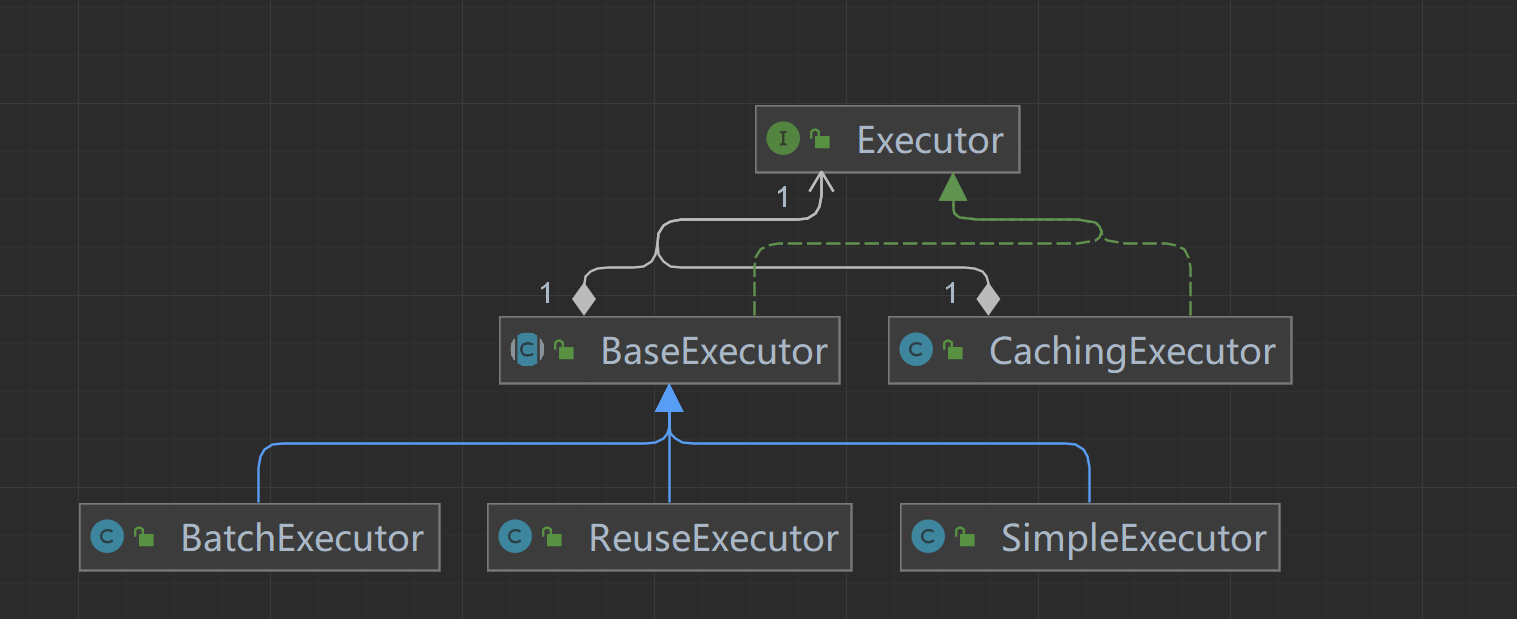
1.mybatis 是如何确定我们要使用的执行器类型的
//产生执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
//默认使用 SimpleExecutor
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//然后就是简单的3个分支,产生3种执行器BatchExecutor/ReuseExecutor/SimpleExecutor
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//如果要求缓存,生成另一种CachingExecutor(默认就是有缓存),装饰者模式,所以默认都是返回CachingExecutor
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//此处调用插件,通过插件可以改变Executor行为
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
可以在mapper.xml or 使用注解指定使用的执行器的类型 但是这种方式只能指定BatchExecutor/ReuseExecutor/SimpleExecutor
CachingExecutor 没有继承BaseExecutor 其负责二级缓存,逻辑位于CachingExecutor中
在全局开始二级缓存的时候的将使用CachingExecutor对 BatchExecutor/ReuseExecutor/SimpleExecutor进行一个包装,使用装饰器进行增强
还有那些使用装饰器的例子 Collections.synchronizedList() java1.5 中流等等
上述代码也展示了Mybatis是如何支持插件的(大概看了PageHelper的源码,惊奇发现作者是个中国人,中文注释YYDS,大概的逻辑是拦截sql,根据分页参数和所使用的数据库方言对执行的sql进行修改,对出参逻辑进行拦截,将当前页,total等等字段进行复制)(那么内存分页是不是也可以抽象成一个这样的拦截器,不拦截sql,只是在出餐进行list分割和当前页,total进行赋值)
2.Executor接口定义的方法
//更新
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
//查询,带分页,带缓存,BoundSql
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
//查询,带分页
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
//刷新批处理语句
//BacthExecutor是实现了方法,底层调用PreparedStatement的批处理提交方法
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
//提交和回滚,参数是是否要强制
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
//创建CacheKey
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
//判断是否缓存了
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
//清理Session缓存
void clearLocalCache();
//延迟加载 据说实现方式是代理了返回结果,在一对多,一对一查询是代理了get方法,在需要数据的时候再去查询,目前没看源码
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
//获取事务,回滚commit 依赖此
Transaction getTransaction();
//关闭sqlSession
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
//设置包装的对象
//此方法被CachingExecutor和BaseExecutor 实现,前者抛出异常 后者将改变持有executor的指向
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
3.查询调用链条
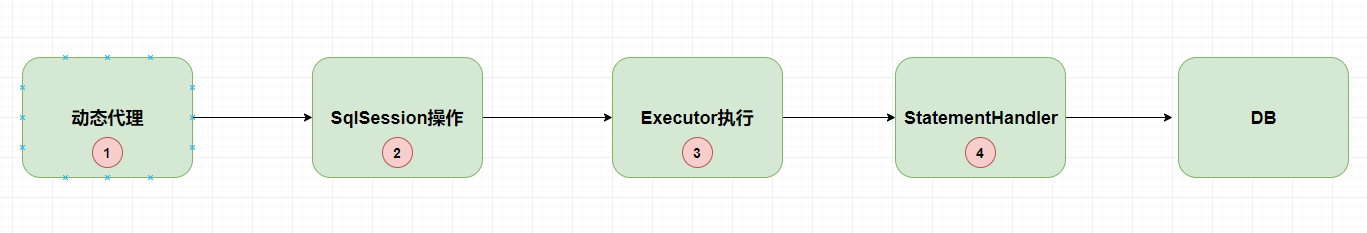
当SqlSession执行查询是其实调用到Executor的查询方法,如果启用了二级缓存了,会走CachingExcutor的二级缓存(见下一个笔记)如果二级缓存没有命中或者没有配置二级缓存,那么就会调用到SimpleExecutor,BatchExcutor 或者ResueExcutor,但是查询在父类的query中进行了统一的实现(模板方法(Template Method)模式的定义如下:定义一个操作中的算法骨架,而将算法的一些步骤延迟到子类中,使得子类可以不改变该算法结构的情况下重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。它是一种类行为型模式)
4.一级缓存的命中条件
//BaseExecutor中的持有一个localCache
//一级缓存载体
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
//PerpetualCache内部实际维护着一个HashMap
//BaseExecutor中的持有一个localCache 在构造方法进行了初始化,这意味着一级缓存和Exector是一对一的,不同执行器的一级缓存并不共享,之前的SqlSession部分代码说明了Mybatis的执行器和SqlSession都是一对一的关系,所以一级缓存和SqlSession是一对一的关系,是会话级别的缓存,也就是要命中一级缓存,必须是同一个SqlSession,而且未关闭
//且PerpetualCache没有做任何线程安全的措施,mybatis觉得执行器生命周期很短,不会存在多线程的调用
//如果存在业务场景:需要多线程分别查询,且存在重复查询和修改数据库操作,可能线程不安全问题
//查询入口逻辑
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//得到绑定sql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//创建缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
//查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//从这段代码我们可以知道,一级缓存是否命中和 MappedStatement,方法入参,分页信息,绑定sql相关
//而MappedStatement 是DefaultSqlSession根据StatementId从配置中获取了
//所以基本上可以说。相同的sql语句,相同参数,相同StatementId 相同的分页信息再同一个个SqlSession中才可以命中缓存
//createCacheKey 方法内部 还会根据当前使用的环境进行更新更新缓存key 防止不同环境的数据通过一级缓存混乱读取
5.查询逻辑
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
//如果已经关闭,报错
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//先清局部缓存,再查询.但仅查询堆栈为0,才清。为了处理递归调用
//查询堆栈queryStack是mybatis解决嵌套查询 的变量
//这里的嵌套查询是mybatis ResultMap colletion标签 associate标签定义的嵌套查询
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//先根据cachekey从localCache去查
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
//若查到localCache缓存,处理 localOutputParameterCache
//localOutputParameterCache 是针对存储过程,存储过程输出参数会加入到此缓存
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//从数据库查
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
//清空堆栈
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
//延迟加载队列中所有元素
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
//清空延迟加载队列
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT)
// issue #482
//如果是STATEMENT,清本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
//大体和从普通拿缓存相似,都是先再缓存拿,拿不到再查询数据库
//从数据库查
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//先向缓存中放入占位符号,这个也是为了嵌套查询的问题
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//doQuery方法由各子类实现 模板方法设计模式
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//最后删除占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//加入缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
//如果是存储过程,OUT参数也加入缓存
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
6.缓存刷新清除
-
update方法执行,mybatis视为其改变了数据,进行简单的全部清楚
-
commit rollback 执行时候,视为数据持久化到数据,当前缓存的时效性准确性无法保证直接清空
-
配置了缓存作用域是STATEMENT
若设置值为 STATEMENT,本地会话仅用在语句执行上,对相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据。 默认是SESSION级别 一级缓存是默认开启的,也无法关闭,但是我们可以调整它的作用域。一级缓存在BaseExecutor内,而Executor和SqlSession是一一对应的,所以一级缓存的作用域就是SqlSession。 -
配置了flushRequire为true 那么执行查询且查询堆栈为0的时候进行清楚
7.BatchExecutor,SimpleExecutor,ReuseExecutor有什么不同
-
查询
-
SimpleExecutor:直接获取StatementHandler和Statement后直接执行query
-
ReuseExecutor内部维护了一个map保存StatementId和Statement的关系
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; //得到绑定的SQL语句 BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); String sql = boundSql.getSql(); //如果缓存中已经有了,直接得到Statement if (hasStatementFor(sql)) { stmt = getStatement(sql); } else { //如果缓存没有找到,则和SimpleExecutor处理完全一样,然后加入缓存 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); putStatement(sql, stmt); } handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }-
BatchExecutor
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { //进行批量提交 那怕没有需要提交 flushStatements(); //获取 StatementHandler Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog()); //准备Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection); handler.parameterize(stmt); //StatementHandler 执行 return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
-
-
更新
-
BatchExecutor 支持批量提交
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException { final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); final StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); final BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); final String sql = boundSql.getSql(); final Statement stmt; //如果就是当要执行的sql 直接拿最后条执行结果 作为当前执行结果,避免同一个sql 重复执行 if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) { int last = statementList.size() - 1; stmt = statementList.get(last); BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(last); batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject); } else { Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog()); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); //缓存最后执行的sql currentSql = sql; currentStatement = ms; //记录需要执行的sql statementList.add(stmt); //记录对应的执行结果 batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject)); } handler.parameterize(stmt); //调用Statement的 addBatch 调用excuteBatch才会真正执行 // /并没有执行到数据库中,调用commit rollback 和此类的doQuery 会提交到数据库 or回滚 因为会这些方法都会调用doFlushStatements,BatchExector 在这里面循环遍历每一个Statement 的 executeBatch 并且更新BatchResult //批量提交是 BatchExecutor独有的功能 SimpleExecutor 是默认什么都不做的实现。ReuseExecutor会循环关闭每一个Statement 并且清空StatementId和Statement的缓存map handler.batch(stmt); return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE; } -
SimpleExecutor:直接获取StatementHandler和Statement后直接执行update
-
ReuseExecutor,支持Statement的复用
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; //得到绑定的SQL语句 BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); String sql = boundSql.getSql(); //如果缓存中已经有了,直接得到Statement if (hasStatementFor(sql)) { stmt = getStatement(sql); } else { //如果缓存没有找到,则和SimpleExecutor处理完全一样,然后加入缓存 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); putStatement(sql, stmt); } handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
-


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号