【sping揭秘】8、容器内部事件发布(一)
容器内部事件发布
Spring的applicationContext容器提供的容器内事件发布功能,是通过java提供的自定义事件实现的
事件类型:eventObject 类继承
事件监听:eventListener 接口实现
定义事件类型
package event; import java.util.EventObject; /** * * Title: MethodExecutionEvent.java * Description: 定义一个自定义的事件对象 * @author xiaof * @date 2018年3月28日 * @version 1.0 * */ public class MethodExecutionEvent extends EventObject { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -2324856893034735293L; private String methodName; /** * 构造函数是,继承的类实现的 * @param source */ public MethodExecutionEvent(Object source) { super(source); } public MethodExecutionEvent(Object source, String methodName) { super(source); this.methodName = methodName; } public String getMethodName() { return methodName; } public void setMethodName(String methodName) { this.methodName = methodName; } }
创建自定义事件类的监听接口
package event; import java.util.EventListener; public interface MethodExecutionEventListener extends EventListener { /** * 处理方法开始执行的时候发布的methodexecutionevent事件 * @param evt */ void onMethodBegin(MethodExecutionEvent evt); /** * 处理方法开结束执行的时候发布的methodexecutionevent事件 * @param evt */ void onMethodEnd(MethodExecutionEvent evt); }
发布事件
package event; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * * Title: MethodExeuctionEventPublisher.java * Description: 事件发布 * @author xiaof * @date 2018年3月28日 * @version 1.0 * */ public class MethodExeuctionEventPublisher { private List<MethodExecutionEventListener> listeners = new ArrayList<MethodExecutionEventListener>(); public void methodToMonitor() { MethodExecutionEvent event2Publish = new MethodExecutionEvent(this, "methodToMonitor"); this.publishEvent(MethodExecutionStatus.BEGIN, event2Publish); //实际其他方法逻辑 this.publishEvent(MethodExecutionStatus.END, event2Publish); } protected void publishEvent(MethodExecutionStatus status, MethodExecutionEvent methodExecutionEvent) { List<MethodExecutionEventListener> copyListeners = new ArrayList<MethodExecutionEventListener>(listeners); //循环发布 for(MethodExecutionEventListener listener : copyListeners) { if(MethodExecutionStatus.BEGIN.equals(status)) { listener.onMethodBegin(methodExecutionEvent); } else { listener.onMethodEnd(methodExecutionEvent); } } } public void addMethodExecutionListener(MethodExecutionEventListener listener) { this.listeners.add(listener); } public void removeListener(MethodExecutionEventListener listener) { if(this.listeners.contains(listener)) { this.listeners.remove(listener); } } public void removeAllListeners() { this.listeners.clear(); } public static void main(String[] args) { MethodExeuctionEventPublisher eventPublisher = new MethodExeuctionEventPublisher(); eventPublisher.addMethodExecutionListener(new SimpleMethodExecutionEventListener()); eventPublisher.methodToMonitor(); } }
那么spring的容器内事件的发布类结构是什么样的呢?
Spring的事件类型分一下三种
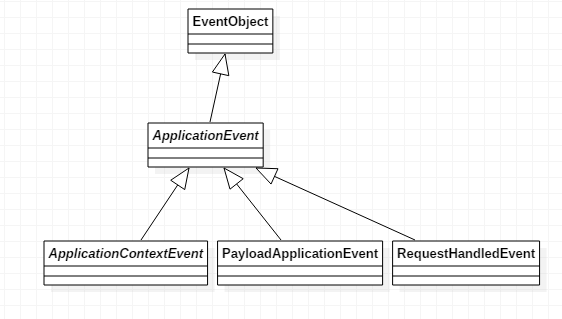
我们主要使用一下几个
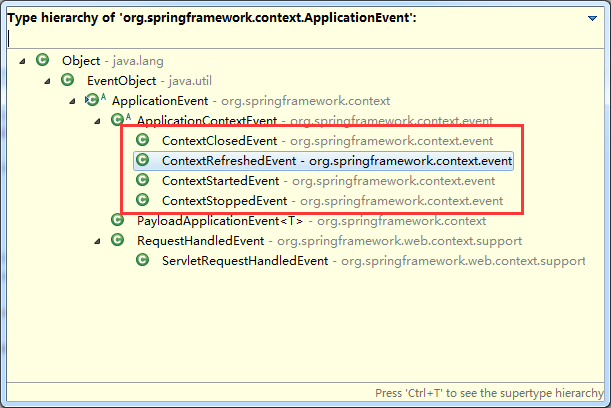
在spring容器中,这四个重上到下,分别是:
容器关闭的时候发布的事件类型
容器在初始化的时候或者刷新的时候发布
当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 start() 方法启动 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布
当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 stop() 方法停止 ApplicationContext 时,发布这个事件。你可以在接受到这个事件后做必要的清理的工作。
RequestHandledEvent web请求处理后发布的事件
spring监听事件
application在启动的时候,会自动识别并加载eventlistner类型bean定义。
一旦容器内有事件发布,将通知这些注册到容器的eventlistener
ApplicationListener
Spring发布事件
ApplicationEventPublisher 接口 实现对象 ApplicationContext 也是一个事件发布对象
这里做一个小测试:
package cn.cutter.start.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStartedEvent; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyStartEventHandler implements ApplicationListener<ContextStartedEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextStartedEvent event) { System.out.println("cutter_point 启动application容器"); } }
package cn.cutter.start.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyStopEventHandler implements ApplicationListener<ContextStoppedEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextStoppedEvent event) { System.out.println("cutter_point 停止application容器"); } }
package cn.cutter.start.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyStopEventHandler2 implements ApplicationListener<ContextStoppedEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextStoppedEvent event) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("cutter_point 停止application容器 222"); } }
package cn.cutter.start.resourceloader; import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; public class FooBar implements ResourceLoaderAware { //资源加载器 private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; public void foo(String location) { //这里有没有很熟悉 // ResourceDemo.class.getResource(location).getClass() System.out.println(this.getResourceLoader().getResource(location).getClass()); } @Override public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { //这里进行resourceloader的注入 this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; } public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() { return resourceLoader; } public void sayFoo() { System.out.println("hi foo!"); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.cutter" /> <!-- 国际化配置 --> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basenames"> <list> <value>i18/users</value> <value>i18/errormsg</value> </list> </property> </bean> <bean id="ttmRateService" class="cn.cutter.simplefx.service.impl.MockTTMRateServiceImpl"></bean> <bean id="fooBar" class="cn.cutter.start.resourceloader.FooBar" /> <bean id="fooBar2" class="cn.cutter.start.resourceloader.FooBar2" /> <bean id="resourceDemo" class="cn.cutter.start.resourceloader.ResourceDemo"> <property name="resource"> <value>classpath:applicationContext-bean.xml</value> </property> </bean> <!-- <bean id="myObject" class="cn.cutter.start.bean.MyObject"></bean> --> <!-- <alias name="FXNewsProvider" alias="provideralias"/> --> <!-- <bean id="test4key2" ></bean> <bean id="" class="..." lazy-init="true"> <constructor-arg> <ref bean="" parent=""/> </constructor-arg> <property name="test1"> <value>ttttt1</value> <idref bean="ttttt1"/> </property> <property name="test2"> <list> <value>test2value</value> <ref bean="test2222"/> <idref bean="test22222"/> <bean class="..."></bean> </list> </property> <property name="test3"> <set> <value>test2value</value> <ref bean="test2222"/> <idref bean="test22222"/> <bean class="..."></bean> </set> </property> <property name="test4"> <map> <entry key="test4key1"> <value>something</value> </entry> <entry key-ref="test5key2"> <list> <value>test2value</value> <ref bean="test2222"/> <idref bean="test22222"/> <bean class="..."></bean> </list> </entry> </map> </property> </bean> --> </beans>
启动测试案例
@Test public void testEvent() { //这里出发start事件和stop事件,就是使用ConfigurableApplicationContext的start和stop事件 ConfigurableApplicationContext cac = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) before(); cac.start(); FooBar fooBar = (FooBar) cac.getBean("fooBar"); fooBar.sayFoo(); cac.stop(); }
运行截图



