拓扑排序入门
最长路
给你一个有向无环图,N个点M条边
求最长路
Format
Input
第一行给出N,M,代表点数与边数
接下M行,每行3个数字a,b,c代表从a到b有边权为1
N,M<=1e5
Output
如题 ,如果没有的话,输出0.
否则输出结果%10^9+7
Samples
输入数据 1
4 5
1 2
1 3
3 2
2 4
3 4
输出数据 1
3
这个权值在边上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 | #include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int mod=1e9+7;int n,m;int x,y;int dep[100010];int son[2000010],now[2000010],pre[2000010],val[2000010],tot;queue<int> q;int ans;void put(int x, int y) { pre[++tot] = now[x]; now[x] = tot; son[tot] = y;}int main() { cin>>n>>m; //n个点,m条边 for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) { cin>>x>>y; put(x,y); dep[y]++; //y的入度加1 } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(dep[i]==0) //将入度为0的点加入队列 q.push(i); tot=0; while(!q.empty()) //当队列不为空 { int noww=q.front(); //取出头结点 q.pop(); tot++; for(int i=now[noww]; i; i=pre[i]) //遍历与noww相连的边,找出这条边上的另一个点 { dep[son[i]]--; //son[i]这个点的入度要减少1 if(dep[son[i]]==0) q.push(son[i]); val[son[i]]=max(val[son[i]],val[noww]+1); } } if(tot!=n) cout<<0<<endl; else { for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) ans=max(ans,val[i]); cout<<ans%mod<<endl; } return 0;} |
Test for Job
Mr.dog被他原来的公司炒了。现在为了养家糊口的他,要尽快找到一个工作。现在有一个工作,但是这年头失业的人很多啊,因此公司不得不使用一个测试来选择自己需要的职工。
这个测试是这样的:从一个起始的城市出发,通过单向的路径来到其他的城市,并且经过每个城市可能会赚到一定的利润,或者交纳一定的费用,这样不断的行动,直到到达一个终点的城市。你的老板会在终点处等你,他会总结出你一路上花费的费用,或者是得到的利润,来决定你是否能够被雇佣。
为了更好的得到这份工作,Mr.dog设法得到了所有城市经过的纯利润Vi(如果是负数表示到这个城市不但得不到利润,还要花费),以及城市与城市的连通关系。假设一个城市没有能够从其他城市到达的道路,那么这个城市被看作起始的城市之一;假设一个城市没有能够到达其他城市的道路,那么这个城市被看作终点的城市之一;而Mr.dog的任务是将选择一个起始的结点出发,走出一条路径,这条路径在一个终点的城市结束,且这条路径包含的城市的总利润最大。
Input
包含若干个数据。
每个数据的第一行有2个整数n,m(1 < = n < = 100000,1 < =m < = 1000000)
后面紧接着n行,其中第i行描述Vi
再后面紧接m行,第i行2个整数x,y,表示有一条从x到y的单向道路。
数据保证没有点对(x,y)重复出现,并且保证无法从一个城市出发经过若干条路径后再回到这个城市。
Output
只有一行,一个整数表示dog这次测试最多可以得到多少利润(或者说最少使用多少花费)
Samples
输入数据 1
6 5
1
2
5
2
1
1
1 2
1 3
2 4
3 4
5 6
输出数据 1
8
Hint
请用 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)进行读入
这个权值在点上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | #include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int n,m;int x,y;int dep[2000010],out[2000010],val[2000010],ans[2000010];int son[2000010],now[2000010],pre[2000010],tot;queue<int> q;int max1;void put(int x, int y) { pre[++tot] = now[x]; now[x] = tot; son[tot] = y;}int main() { while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF) { memset(dep,0,sizeof dep); memset(son,0,sizeof son); memset(now,0,sizeof now); memset(pre,0,sizeof pre); memset(val,0,sizeof val); memset(ans,0,sizeof ans); memset(out,0,sizeof out); tot=0; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>val[i],ans[i]=-INT_MAX; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) { cin>>x>>y; put(x,y); dep[y]++; out[x]++; } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(dep[i]==0) q.push(i),ans[i]=val[i]; while(!q.empty()) { int noww=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i=now[noww]; i; i=pre[i]) { dep[son[i]]--; if(dep[son[i]]==0) q.push(son[i]); ans[son[i]]=max(ans[son[i]],ans[noww]+val[son[i]]); //已找到一条路径了,于是更新下最值优 //这个与是否入度为0,是没有关系的 } } max1=-INT_MAX; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(out[i]==0) //找到出度为0的点,其代表终点 max1=max(max1,ans[i]); cout<<max1<<endl; } return 0;} |
有限制的全排列
给你一个数字N,及另一个数字M
代表希望你找出N的某个全排列出来,其满足M个条件
每个条件会给出两个数字a,b
代表在目标全排列中,数字a在数字b前面
Format
Input
第一行两个整数n,m
接下来M行,每行两个数字
Output
输出目标全排列,找不到输出-1
如果存在多个解则输出字典序最小的那个
Samples
输入数据 1
4 3
2 1
3 4
2 4
输出数据 1
2 1 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | #include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int n,m;int x,y;int dep[2000010];int son[2000010],now[2000010],pre[2000010],tot;priority_queue<int, vector<int> , greater<int> > q;queue<int> ans;void put(int x, int y) { pre[++tot] = now[x]; now[x] = tot; son[tot] = y;}int main() { cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) { cin>>x>>y; put(x,y); dep[y]++; } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(dep[i]==0) q.push(i); while(!q.empty()) { int noww=q.top(); q.pop(); ans.push(noww); for(int i=now[noww]; i; i=pre[i]) { dep[son[i]]--; if(dep[son[i]]==0) q.push(son[i]); } } if(ans.size()!=n) cout<<-1<<endl; else { while(!ans.empty()) cout<<ans.front()<<" ",ans.pop(); cout<<endl; } return 0;} |
有限制的全排列
给你一个数字N,及另一个数字M
代表希望你找出N的某个全排列出来,其满足M个条件
每个条件会给出两个数字a,b
代表在目标全排列中,数字a在数字b前面
Format
Input
第一行两个整数n,m
接下来M行,每行两个数字
Output
输出目标全排列,找不到输出-1
如果存在多个解则输出字典序最小的那个
Samples
输入数据 1
4 3
2 1
3 4
2 4
输出数据 1
2 1 3 4
sol:
针对形如
a要放在b的前面的表述,建立一条有向表从a指向b
然后找出所有入度的0的点,放入一个小根堆中(注意不是一般的队列)
然后不断从堆中弹出堆顶元素x,其权值最小,并且是比所有数字小的。
然后将所有与x相连的边所指向的另一个点的入度减少1,如果入度为0,则又放到小堆根中,最终得到答案
针对样例来说:
2 1
3 4
2 4
建立的图形如下:
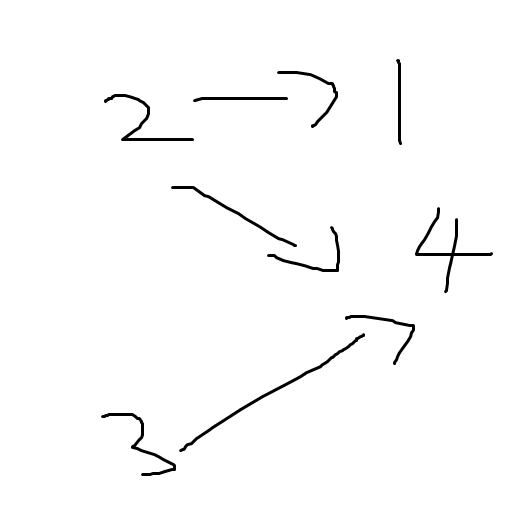
首先将入度为0的点2,3入堆中
然后弹出2出,并将1与4的入度分别减少1。发现1的入度为0,于是1进入堆中
然后弹出1,1没有相连的边,无后续操作
然后弹出3,将4的入度减少1,发现4的入度为0,加入堆中
最后弹出4
最终结果为2,1,3,4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | #include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int n,m;int x,y;int dep[2000010];int son[2000010],now[2000010],pre[2000010],tot;priority_queue<int, vector<int> , greater<int> > q;queue<int> ans;void put(int x, int y) { pre[++tot] = now[x]; now[x] = tot; son[tot] = y;}int main() { cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) { cin>>x>>y; put(x,y); dep[y]++; } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(dep[i]==0) q.push(i); while(!q.empty()) { int noww=q.top(); q.pop(); ans.push(noww); for(int i=now[noww]; i; i=pre[i]) { dep[son[i]]--; if(dep[son[i]]==0) q.push(son[i]); } } if(ans.size()!=n) cout<<-1<<endl; else { while(!ans.empty()) cout<<ans.front()<<" ",ans.pop(); cout<<endl; } return 0;} |
小球的标签
有N个球,重量从1到N,各不相同,每个球有个编号也是从1到N,各不相同。现在给你一些约束条件, 每个约束条件给出数字A,B,表示A号球轻于B号球。请你求出满足约束条件的某个球的重量的全排列, 注意如果有多个排列满足条件,我们希望1号球的重量越小越好;当1号球的重量一样时,希望2号球的重量越小越好 当2号球的重量一样时,希望3号球的重量越小越好
Input
第一行给出一个数字N,代表有N组数据
每个数据给出数字N,M,代表有N个球,
M个约束条件N (1 ≤ N ≤ 200) , M (0 ≤ M ≤ 40,000).
下面将有M行每行两个数字A,B,(1 ≤ a, b ≤ N)表示A号球轻于B号球.
Output
依次输出从1号球到N号球的重量,任两个数字之间以一个空格格开
无解输出-1
Sol:
本题要求最终结果字典序最小,有两种策略
1:将较轻的重量给数字编号较小的球
2:将较重的重量给数字编号较大的球
发现策略2优于策略1,例如下面这组数据
4 2
3 1
2 4
我们建立有向边a-->b,代表a重于b,上图形如下
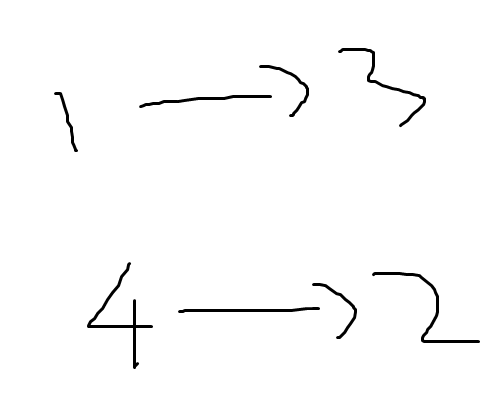
将1与4进大根堆
弹出4,将最大的重量4给它,然后将2加入堆
弹出2,将重量3给它
弹出1,将重量2给它,然后3加入堆
最后弹出3,将重量1给它。
最终1,2,3,4这四个球的重量分别为2 3 1 4
大家可试用着策略1来做一下,发现结果并不优于这种
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | #include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<algorithm>#include<queue>using namespace std;int head[500],degree[500],result[450],m,n,t;struct node { int to,next;}s[400000];void add(int x,int y){ s[t].to=y; s[t].next=head[x]; head[x]=t++;}int topo(){ int i,j,p; priority_queue<int >Q; for(i=1;i<=m;i++) if(degree[i]==0) Q.push(i); p=m; while(!Q.empty()) { int w=Q.top(); Q.pop(); result[w]=p--; for(int k=head[w];k!=-1;k=s[k].next) { int e=s[k].to; degree[e]--; if(!degree[e]) Q.push(e); } } if(p==0) return 1; return 0;}int main(){ int N,a,b,i,j; scanf("%d",&N); while(N--) { t=0; memset(degree,0,sizeof(degree)); memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); add(b,a); degree[a]++; } int qw=topo(); if(qw) { for(i=1;i<m;i++) printf("%d ",result[i]); printf("%d\n",result[i]); } else printf("-1\n"); } return 0;} |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现