splay的基本操作之点删除,区间提取
mid
维护一个集合,有2种操作:
1.每次可以插入一个元素。
2.找出当前集合中第(n+1)/2大的元素,把它输出,然后把它从集合中删除。
N<=100000
输入
第1行一个数N,表示由N次操作。接下来N行。每行第1个数C表示操作类型。
1.c=1,接下来还有一个数,表示要插入元素。
2.c=2,表示要进行第2种操作。
输出
一共m行。按顺序对应输入中的第2种情况。
样例输入 Copy
5
1 3
2
1 5
1 4
2
样例输出 Copy
3
5
查找:与二叉排序树查找类似,只是查找结束后要将找到的元素通过Splay操作旋转到根。
插入:用查找过程找到要插入的位置,进行插入。然后将新元素旋转到根。
删除:首先在树中找到要删除的元素x,将他转到根节点并删去,这样原来的树就分裂成了两棵树,然后将左子树中拥有最大关键字的那一个元素p转到根,由于它是左子树中的最大元素,所以他不存在右儿子,这样只要把原来x的右子树作为p的右子树,就重新合并成了一棵树。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fa[100010],son[100010][2],size[100010],val[100010],n,k,pps,root,tot;
int check(int x)
{
if(son[fa[x]][1]==x)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void down(int x)
{
size[x]=size[son[x][0]]+size[son[x][1]]+1;
}
int pre(int x)
{
int now=son[x][0];
while(son[now][1])now=son[now][1];
return now;
}
void move(int x)
{
int f=fa[x],s=son[x][check(x)^1],ret=check(x);
son[x][ret^1]=f,son[f][ret]=s;
if(s)fa[s]=f;fa[x]=fa[f];
if(fa[x])son[fa[x]][check(f)]=x;
fa[f]=x;
down(f);
down(x);
}
void splay(int x)
{
while(fa[x])
{
if(fa[fa[x]])
{
if(check(fa[x])==check(x))move(fa[x]);
else move(x);
}move(x);
}
root=x;
}
void insert(int x)
{
val[++tot]=x;int now=root;size[tot]=1;
if(!root){root=tot;return;}
while(true)
{
if(x<=val[now])
{
if(!son[now][0]){son[now][0]=tot,fa[tot]=now;down(now);break;}
now=son[now][0];
}
else
{
if(!son[now][1]){son[now][1]=tot,fa[tot]=now;down(now);break;}
now=son[now][1];
}
}
splay(tot);
}
void del(int x)
{
splay(x);
int p=pre(x);
//如果x的左子树中的最大点
if(!p)
//如果左子树为空
{
root=son[x][1];
//则右子树为根
fa[son[x][1]]=0;
return;
}
splay(p);
//root=p;这一句多余的吧。
//否则将p旋转至根
if(son[x][1])
//如果从前x有右子结点,则它做为P的右子结点
fa[son[x][1]]=p;
son[p][1]=son[x][1];
son[x][0]=son[x][1]=fa[x]=fa[p]=0;
down(p);
down(x);
}
void find(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(true)
{
if(size[son[now][0]]+1==x){printf("%d\n",val[now]),del(now);return;}
if(size[son[now][0]]+1>x&&son[now][0]>0)now=son[now][0];
else x=x-size[son[now][0]]-1,now=son[now][1];
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&k);
if(k==1)
{
scanf("%d",&pps);
insert(pps);
}
else find(size[root]-(size[root]+1)/2+1);
}
}
var
s:array[-10..500000,0..1]of longint;
v,f,c:array[-10..500000]of longint;
root,len:longint;
Function t(x:longint):longint; //求出x是其父亲的左儿子还是右儿子
begin
if s[f[x],1]=x then exit(1); exit(0);
end;
Procedure down(x:longint); //统计以x为根的树中有多少个结点,包括他自己
begin
if x=0 then exit;
c[x]:=c[s[x,1]]+c[s[x,0]]+1;
end;
Procedure move(x:longint); //一次的旋转操作
var
fa,son:longint;
begin
fa:=f[x];
son:=s[x,1-t(x)];
s[x,1-t(x)]:=fa;
s[fa,t(x)]:=son;
if son>0 then
f[son]:=fa;
f[x]:=f[fa];
if f[fa]>0 then
s[f[fa],t(fa)]:=x;
f[fa]:=x;
down(fa);
down(x);
end;
Procedure splay(x:longint);
begin
while f[x]>0 do
begin
if f[f[x]]>0 then //如果x的父亲,还有父亲的话
if t(x)=t(f[x]) then //如果x与x的父亲及其祖先点在一条直线上,而先旋转x的父亲
move(f[x])
else
move(x); //否则说明是个之字形结构,先旋转x本身
move(x);
end;
root:=x;
end;
Procedure join(x:longint);
var
i:longint;
begin
Inc(len);
v[len]:=x;
if root=0 then
begin
root:=len;
f[len]:=0;
s[len,1]:=0;
s[len,0]:=0;
exit;
end;
i:=root;
while true do
if x<=v[i] then
begin
Inc(c[i]);
if s[i,0]=0 then
begin
s[i,0]:=len;
f[len]:=i;
break;
end;
i:=s[i,0];
end
else
begin
Inc(c[i]);
if s[i,1]=0 then
begin
s[i,1]:=len;
f[len]:=i;
break;
end;
i:=s[i,1];
end;
splay(len);
end;
Procedure Del(x:longint);
var
i,son:longint;
begin
splay(x);
if (s[x,0]=0) and (s[x,1]=0) then
//如果左右儿子均为空,则删除当前点后,成为一个空树
begin
root:=0;
exit;
end;
for i:=0 to 1 do //看左右儿子哪个为空,则另一个儿子做根结点
if s[x,i]=0 then
begin
root:=s[x,1-i];
f[root]:=0;
exit;
end;
i:=s[x,0]; //取出x左儿子
while s[i,1]>0 do //不断去找右儿子
i:=s[i,1];
splay(i); //将这个点做为根
son:=s[x,1]; //取出从前那个点的右儿子
s[i,1]:=son; //将其做为i这个点的右儿子
f[son]:=i;
down(i);
end;
Function find(x:longint):longint;
var
i:longint;
begin
i:=root;
while true do
begin
if c[s[i,0]]+1=x then
exit(i);
if (c[s[i,0]]+1>x) and (s[i,0]>0) then
i:=s[i,0]
else
begin
x:=x-(c[s[i,0]]+1);
i:=s[i,1];
end;
end;
end;
Procedure main;
var
i,n,k,x,l:longint;
begin
readln(n);
root:=0; len:=0;
for i:=1 to n do
begin
read(k);
if k=1 then
begin
readln(x);
join(x);
continue;
end
else
begin
l:=c[root]-(c[root]+1) div 2+1;//转成求第l小的元素
l:=find(l);
writeln(v[l]);
Del(l);
end;
end;
end;
begin
main;
end.
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100050;
int n;
int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=getchar())if(ch=='-')f=-1;
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+ch-'0';
return x*f;
}
struct Splay
{
int tot,root;
int fa[maxn],son[maxn][2],val[maxn],siz[maxn];
bool t(int node)
{
return son[fa[node]][1]==node;
}
void updata(int node)
{
siz[node]=siz[son[node][0]]+1+siz[son[node][1]];
}
void move(int node)
{
int ret=t(node),f=fa[node],s=son[node][ret^1];
son[f][ret]=s;
if(s)
fa[s]=f;
son[node][ret^1]=f;
fa[node]=fa[f];
if(fa[f])
son[fa[f]][t(f)]=node;
fa[f]=node;
updata(f);
updata(node);
}
void splay(int node)
{
while(fa[node])
{
if(fa[fa[node]])
{
if(t(fa[node])==t(node))
move(fa[node]);
else
move(node);
}
move(node);
}
root=node;
}
void insert(int v)
{
val[++tot]=v;siz[tot]=1;
if(!root){root=tot;return;}
int node=root;
while(1){
if(val[node]>=v)
{
if(!son[node][0])
{
son[node][0]=tot;
fa[tot]=node;
break;
}
node=son[node][0];
}else{
if(!son[node][1]){son[node][1]=tot;fa[tot]=node;break;}
node=son[node][1];
}
}
splay(tot);
}
void destroy(int u)
{
val[u]=son[u][0]=son[u][1]=siz[u]=fa[u]=0;
}
void del(int node)
{
splay(node);
if(!son[node][0]&&!son[node][1])
{
destroy(node);
root=0;
return;
}
if(!son[node][0]) //如果左结点为空
{
root=son[node][1],fa[root]=0;
//则右结点为根
updata(root);
destroy(node);
return;
}
if(!son[node][1])
{
root=son[node][0],fa[root]=0;
updata(root);destroy(node);
return;
}
fa[son[node][0]]=0;
int s=son[node][0];
//走到node的左结点
while(son[s][1])
//不断向右找
s=son[s][1];
splay(s);
//将s做为根
son[root][1]=son[node][1];
//将从前node的右结点做为新根的右结点
siz[root]+=siz[son[node][1]];
fa[son[root][1]]=root;
destroy(node);
}
void find(int rk)
{
int node=root;
while(1)
{
if(siz[son[node][1]]+1==rk)
{
printf("%d\n",val[node]);
del(node);
return;
}
if(siz[son[node][1]]+1>=rk)
node=son[node][1];
else
rk-=siz[son[node][1]]+1,node=son[node][0];
}
}
}T;
int main(){
n=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int mode=read()-1;
if(mode)T.find((T.siz[T.root]+1)/2);
else{int x=read();T.insert(x);}
}
return 0;
}
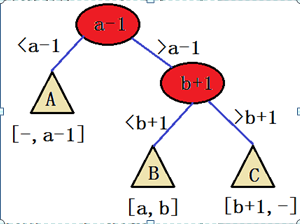
区间提取:
区间操作:
比如我们要提取区间[a,b],那么我们将a前面一个数对应的结点转到树根,将b 后面一个结点对应的结点转到树根的右边,那么根右边的左子树就对应了区间[a,b]。
原因很简单,将a 前面一个数对应的结点转到树根后, a 及a 后面的数就在根的右子树上,然后又将b后面一个结点对应的结点转到树根的右边,那么[a,b]这个区间就是下图中B所示的子树。