《视觉SLAM十四讲》第13讲 设计SLAM系统 回环检测线程的实现
《视觉SLAM十四讲》第13讲 设计SLAM系统 回环检测线程的实现
这个学期看完了高翔老师的《视觉SLAM十四讲》,学到了很多,首先是对计算机视觉的基本知识有了一个更加全面系统的理解,其次是动手去做实验的过程中,也更加理解了很多有关g2o,opencv,sophus等等工具的使用。
在第13讲的实践部分,高翔老师已经写好了一个基本SLAM框架的前端,后端部分,因此本篇博文主要记录第三个线程回环检测的实现。
先简单介绍一下三个线程的功能:
-
前端(Frontend)线程: 前端线程负责处理相机图像流并提取特征点对应关系,然后使用这些对应关系来跟踪相机的运动。该线程负责实时地定位相机并估计其在三维空间中的轨迹。前端的主要任务包括:
-
特征提取和匹配:从相机图像中提取特征点,通常使用角点检测器或特征描述子来找到关键点,并将它们与先前帧中的特征点进行匹配。
-
运动估计:使用特征点的匹配信息来估计相机的运动,例如使用视觉里程计(Visual Odometry)技术来估计相机的位姿变化。
-
姿态跟踪:将估计的相机运动与地图中的特征点进行匹配,从而跟踪相机的姿态并实时更新相机的位姿。
-
-
后端(Backend)线程: 后端线程负责对前端估计的相机轨迹和地图进行优化,以获得更准确和一致的估计。该线程处理由前端产生的轨迹误差,并通过最小化重投影误差或其他优化准则来优化相机的位姿和地图点。后端的主要任务包括:
- 图优化:建立一个图结构,其中相机位姿和地图点是图的节点,一般优化loss使用重投影误差是,然后通过图优化算法(例如g2o)来最小化误差并优化位姿和地图点。
-
回环检测(Loop Closure)线程: 回环检测线程负责检测相机是否再次经过先前经过的地点。当检测到回环时,回环检测会触发回环优化过程,以修正先前轨迹的漂移和误差,从而提高整个系统的一致性和精度。回环检测的主要任务包括:
-
回环检测:使用特征点的描述子或其他特征匹配技术来检测先前访问过的地标或地图点。
-
回环优化:当检测到回环时,执行回环优化算法来修正先前轨迹的误差,以获得一致和精确的轨迹和地图。
-
下面是回环检测的相关代码:
KeyframeDatabase
KeyframeDatabase主要实现保存关键帧,以及关键帧对应的特征描述子,可以用来查询。
KeyframeDatabase.h
//
// Created by xin on 23-6-21.
//
#ifndef MYSLAM_KEYFRAMEDATABASE_H
#define MYSLAM_KEYFRAMEDATABASE_H
#include "common_include.h"
#include "frame.h"
#include "DBoW3/DBoW3.h"
namespace myslam {
class Frame;
class KeyframeDatabase {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
typedef std::shared_ptr<KeyframeDatabase> Ptr;
typedef std::unordered_map<unsigned long, Frame::Ptr> KeyframesType;
KeyframeDatabase() : keyframe_database_(DBoW3::Vocabulary("../vocabulary.yml.gz"), false, 0) {};
void InsertKeyFrame(Frame::Ptr frame);
// 由于访问 database 和 insertKeyframe 可能还冲突,所以需要对 database需要加锁
DBoW3::Database& getDatabase();
KeyframesType GetAllKeyFrames();
public:
DBoW3::Database keyframe_database_;
std::mutex mutex_; // 定义一个互斥锁
KeyframesType keyframes_; // all key-frames
};
} // myslam
#endif //MYSLAM_KEYFRAMEDATABASE_H
KeyframeDatabase.cpp
//
// Created by xin on 23-6-21.
//
#include "myslam/keyframeDatabase.h"
#include "DBoW3/DBoW3.h"
namespace myslam {
DBoW3::Database &KeyframeDatabase::getDatabase() {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mutex_);
return keyframe_database_;
}
KeyframeDatabase::KeyframesType KeyframeDatabase::GetAllKeyFrames() {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mutex_);
return keyframes_;
}
void KeyframeDatabase::InsertKeyFrame(Frame::Ptr frame) {
// std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mutex_);
if (keyframes_.find(frame->keyframe_id_) == keyframes_.end()) {
keyframes_.insert(make_pair(frame->keyframe_id_, frame));
} else {
keyframes_[frame->keyframe_id_] = frame;
}
keyframe_database_.add(frame->descriptors_);
}
} // myslam
loop_closure
回环检测线程主要实现当一个关键帧插入时,启动回环检测,检查当前插入的关键帧是否与之前的关键帧形成回环,如果存在,则根据查询到的关键帧id以及当前帧的id,按照顺序取出这些帧对应的地图点和位姿并执行优化函数。
由于第一次回环检测优化之后,由于还是在相同的地点,所以后续还会检测到回环,但这些回环其实只有第一次就足够,所以实现了一个小trick,即第一次回环检测成功之后,后续的五次回环检测将不执行优化,这个在代码void LoopClosure::LoopClosureLoop()中有所体现。
loop_closure.h
//
// Created by xin on 23-6-21.
//
#ifndef MYSLAM_LOOP_CLOSURE_H
#define MYSLAM_LOOP_CLOSURE_H
#include "common_include.h"
#include "keyframeDatabase.h"
#include "frame.h"
#include "map.h"
/*
* 回环检测线程,在检测到回环时启动优化
* Map更新由前端触发
*/
namespace myslam {
class Map;
class LoopClosure {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
typedef std::shared_ptr<LoopClosure> Ptr;
/// 构造函数中启动回环检测优化线程并挂起
LoopClosure();
/// 设置左右目相机,用来获取相机内外参
void SetCameras(Camera::Ptr left, Camera::Ptr right) {
cam_left_ = left;
cam_right_ = right;
}
/// 设置地图
void SetMap(std::shared_ptr<Map> map) { map_ = map; }
void InsertKeyframe(Frame::Ptr frame);
/// 触发地图更新,启动优化
void UpdateMap();
/// 关闭回环检测线程
void Stop();
private:
/// 回环检测线程
void LoopClosureLoop();
int DetectLoop();
/// 对回环上的关键帧和路标点进行优化
void Optimize(Map::KeyframesType &keyframes, Map::LandmarksType &landmarks);
public:
private:
double min_loop_score = 0.4;
double max_loop_score = 0.9;
unsigned int frame_passed_ = 0;
std::thread loop_closure_thread_; // 建立一个回环检测线程
std::mutex data_mutex_; // 互斥锁,用于在多线程环境下对共享数据进行保护
std::condition_variable map_update_; // 用于通知闭环检测线程有新的地图数据可用,从而触发闭环检测的执行。
std::atomic<bool> loop_closure_running_; // 用来启动或停止闭环检测线程,以及检查线程是否正在运行。
std::shared_ptr<KeyframeDatabase> database_;
Camera::Ptr cam_left_ = nullptr, cam_right_ = nullptr;
std::shared_ptr<Map> map_;
std::shared_ptr<Frame> current_frame_;
};
} // myslam
#endif //MYSLAM_LOOP_CLOSURE_H
loop_closure.cpp
//
// Created by xin on 23-6-21.
//
#include "myslam/loop_closure.h"
#include "myslam/algorithm.h"
#include "myslam/feature.h"
#include "myslam/g2o_types.h"
#include "myslam/map.h"
#include "myslam/mappoint.h"
#include "DBoW3/DBoW3.h"
namespace myslam {
LoopClosure::LoopClosure() {
database_ = KeyframeDatabase::Ptr(new KeyframeDatabase);
loop_closure_running_.store(true);
loop_closure_thread_ = std::thread(std::bind(&LoopClosure::LoopClosureLoop, this));
}
void LoopClosure::Stop() {
loop_closure_running_.store(false);
map_update_.notify_one();
loop_closure_thread_.join();
}
void LoopClosure::UpdateMap() {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(data_mutex_);
map_update_.notify_one();
}
int LoopClosure::DetectLoop(){
DBoW3::Database &db = database_->getDatabase();
DBoW3::QueryResults ret;
db.query(current_frame_->descriptors_, ret, 4);
for (const auto& result : ret) {
unsigned int imageId = result.Id; // 获取图像ID
double score = result.Score; // 获取匹配分数
if(score > min_loop_score && score < max_loop_score ){
return imageId;
}
}
return -1;
}
void LoopClosure::InsertKeyframe(Frame::Ptr frame) {
current_frame_ = frame;
database_->InsertKeyFrame(frame);
}
void LoopClosure::LoopClosureLoop() {
while (loop_closure_running_.load()){
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(data_mutex_);
map_update_.wait(lock);
int loop_start_index = DetectLoop();
LOG(INFO) <<"Loop Detecting";
if(loop_start_index >= 0){
frame_passed_++;
//这里是由于重复的回环不会使得精度再有提升,因此一次回环检测之后的后五次检测不执行更新
if(frame_passed_ == 1){
int loop_end_index = current_frame_->keyframe_id_;
LOG(INFO) << "\n\n\n\n\n" <<"Loop Detected at" << loop_start_index << "--------" << loop_end_index << "\n\n\n\n";
Map::KeyframesType loop_kfs = map_->GetLoopKeyFrames(loop_start_index, loop_end_index);
Map::LandmarksType loop_landmarks = map_->GetLoopMapPoints(loop_start_index, loop_end_index);
/// 回环检测线程优化 回环上的 frames 和 landmarks
Optimize(loop_kfs, loop_landmarks);
}
else if (frame_passed_ > 5)
frame_passed_ = 0;
else {
frame_passed_++;
}
}
}
}
void LoopClosure::Optimize(Map::KeyframesType &keyframes, Map::LandmarksType &landmarks) {
// setup g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver_6_3 BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType>
LinearSolverType;
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(
g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
// pose 顶点,使用Keyframe id
std::map<unsigned long, VertexPose *> vertices;
unsigned long max_kf_id = 0;
for (auto &keyframe : keyframes) {
auto kf = keyframe.second;
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose
vertex_pose->setId(kf->keyframe_id_);
vertex_pose->setEstimate(kf->Pose());
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
if (kf->keyframe_id_ > max_kf_id) {
max_kf_id = kf->keyframe_id_;
}
vertices.insert({kf->keyframe_id_, vertex_pose});
}
// 路标顶点,使用路标id索引
std::map<unsigned long, VertexXYZ *> vertices_landmarks;
// K 和左右外参
Mat33 K = cam_left_->K();
SE3 left_ext = cam_left_->pose();
SE3 right_ext = cam_right_->pose();
// edges
int index = 1;
double chi2_th = 5.991; // robust kernel 阈值
std::map<EdgeProjection *, Feature::Ptr> edges_and_features;
for (auto &landmark : landmarks) {
if (landmark.second->is_outlier_) continue;
unsigned long landmark_id = landmark.second->id_;
auto observations = landmark.second->GetObs();
for (auto &obs : observations) {
if (obs.lock() == nullptr) continue;
auto feat = obs.lock();
if (feat->is_outlier_ || feat->frame_.lock() == nullptr) continue;
auto frame = feat->frame_.lock();
EdgeProjection *edge = nullptr;
if (feat->is_on_left_image_) {
edge = new EdgeProjection(K, left_ext);
} else {
edge = new EdgeProjection(K, right_ext);
}
// 如果landmark还没有被加入优化,则新加一个顶点
if (vertices_landmarks.find(landmark_id) ==
vertices_landmarks.end()) {
VertexXYZ *v = new VertexXYZ;
v->setEstimate(landmark.second->Pos());
v->setId(landmark_id + max_kf_id + 1);
v->setMarginalized(true);
vertices_landmarks.insert({landmark_id, v});
optimizer.addVertex(v);
}
edge->setId(index);
edge->setVertex(0, vertices.at(frame->keyframe_id_)); // pose
edge->setVertex(1, vertices_landmarks.at(landmark_id)); // landmark
edge->setMeasurement(toVec2(feat->position_.pt));
edge->setInformation(Mat22::Identity());
auto rk = new g2o::RobustKernelHuber();
rk->setDelta(chi2_th);
edge->setRobustKernel(rk);
edges_and_features.insert({edge, feat});
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
}
// do optimization and eliminate the outliers
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
int cnt_outlier = 0, cnt_inlier = 0;
int iteration = 0;
while (iteration < 5) {
cnt_outlier = 0;
cnt_inlier = 0;
// determine if we want to adjust the outlier threshold
for (auto &ef : edges_and_features) {
if (ef.first->chi2() > chi2_th) {
cnt_outlier++;
} else {
cnt_inlier++;
}
}
double inlier_ratio = cnt_inlier / double(cnt_inlier + cnt_outlier);
if (inlier_ratio > 0.5) {
break;
} else {
chi2_th *= 2;
iteration++;
}
}
for (auto &ef : edges_and_features) {
if (ef.first->chi2() > chi2_th) {
ef.second->is_outlier_ = true;
// remove the observation
ef.second->map_point_.lock()->RemoveObservation(ef.second);
} else {
ef.second->is_outlier_ = false;
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "Outlier/Inlier in optimization: " << cnt_outlier << "/"
<< cnt_inlier;
// Set pose and lanrmark position
for (auto &v : vertices) {
keyframes.at(v.first)->SetPose(v.second->estimate());
}
for (auto &v : vertices_landmarks) {
landmarks.at(v.first)->SetPos(v.second->estimate());
}
}
} // myslam
备注
值得注意的是,由于高翔老师使用的是光流法进行前端的运动估计,我把系统修改为ORB特征点匹配的方法进行前端运动估计和回环检测。
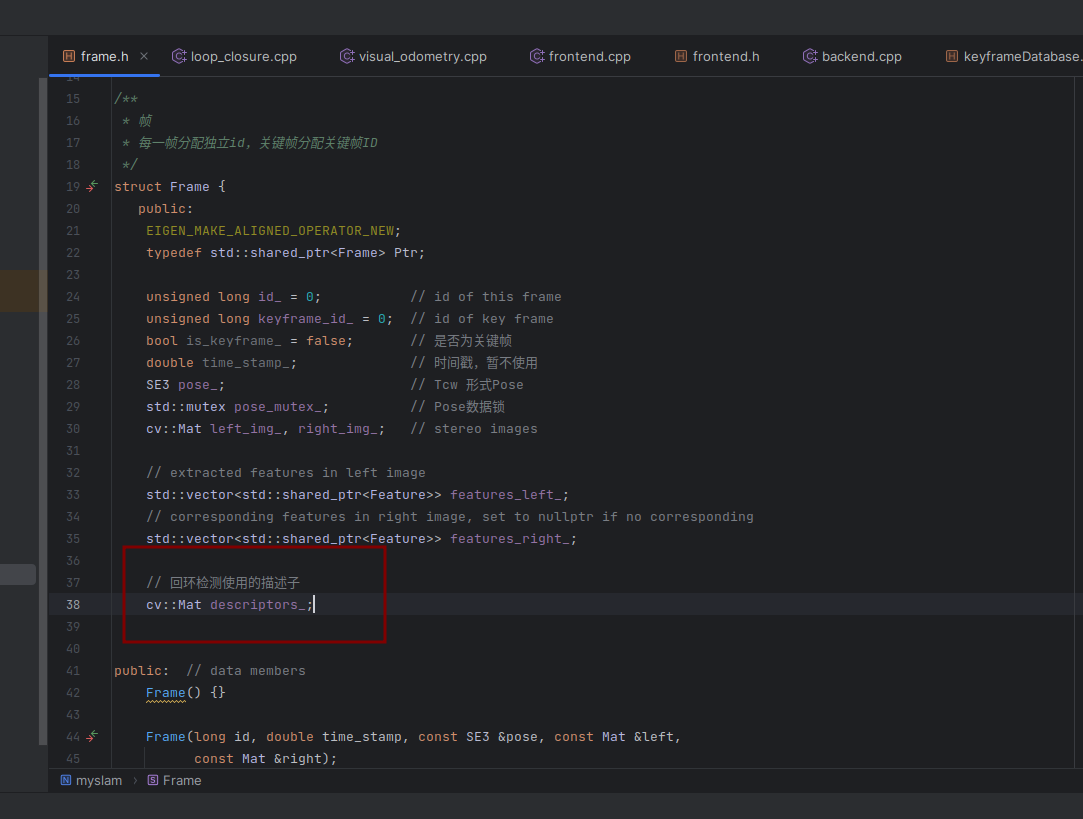
frame类里面添加一个 descriptors_ 成员变量。
frontend.cpp
int Frontend::DetectFeatures() {
cv::Mat mask(current_frame_->left_img_.size(), CV_8UC1, 255);
for (auto &feat : current_frame_->features_left_) {
cv::rectangle(mask, feat->position_.pt - cv::Point2f(10, 10),
feat->position_.pt + cv::Point2f(10, 10), 0, CV_FILLED);
}
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypoints;
// 修改为orb特征
orb_detector_->detectAndCompute(current_frame_->left_img_, mask, keypoints, current_frame_->descriptors_);
// gftt_->detect(current_frame_->left_img_, keypoints, mask);
int cnt_detected = 0;
for (auto &kp : keypoints) {
current_frame_->features_left_.push_back(
Feature::Ptr(new Feature(current_frame_, kp)));
cnt_detected++;
}
LOG(INFO) << "Detect " << cnt_detected << " new features";
return cnt_detected;
}
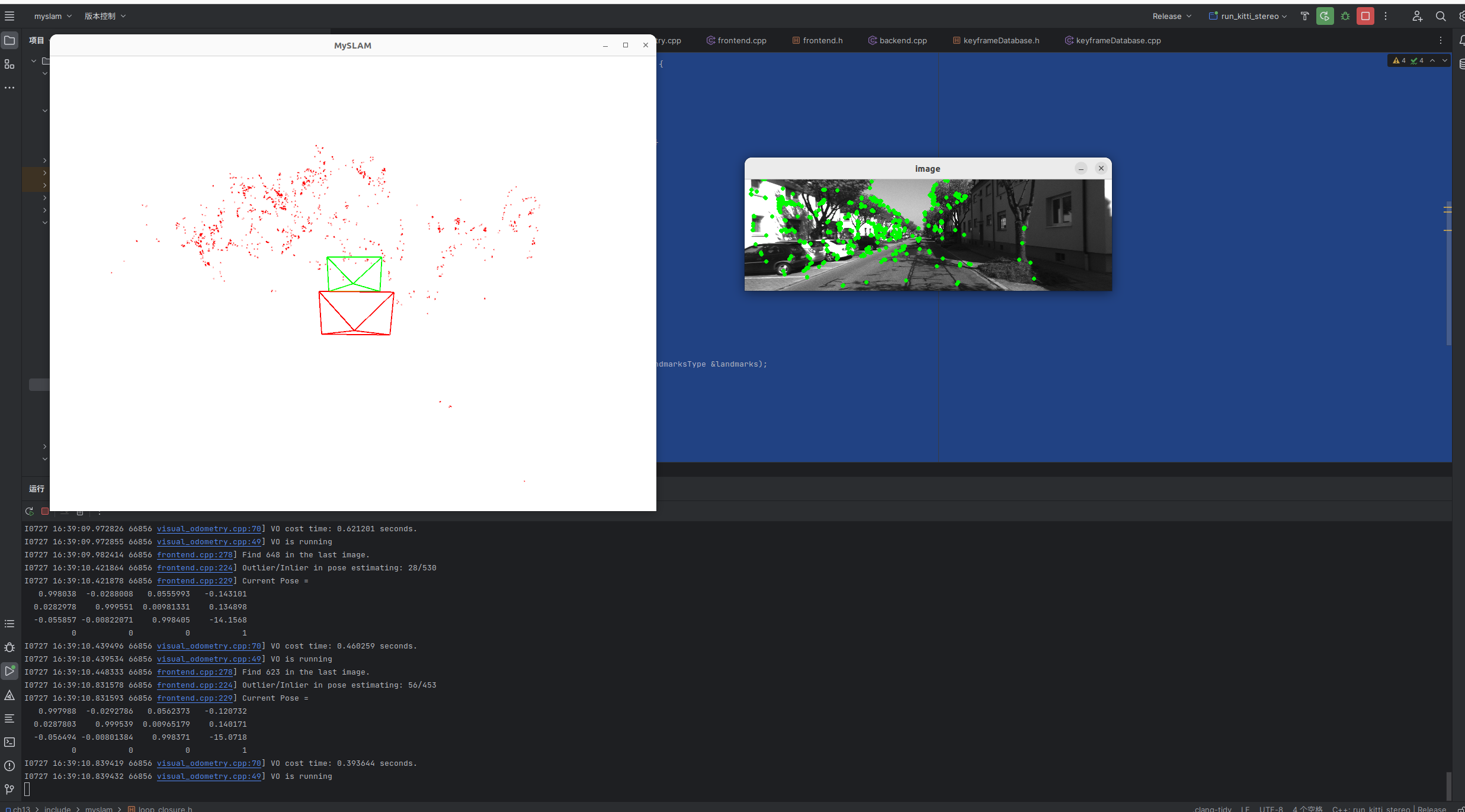
最后的运行效果:
本文来自博客园,作者:CuriosityWang,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/curiositywang/p/17585372.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号