g2o优化库实现曲线拟合
g2o优化库实现曲线拟合
最近学习了一下g2o优化库的基本使用,尝试着自己写了一个曲线拟合的函数,也就是下面这个多项式函数:
我们以 为例,拟合出的图像大概长这样。
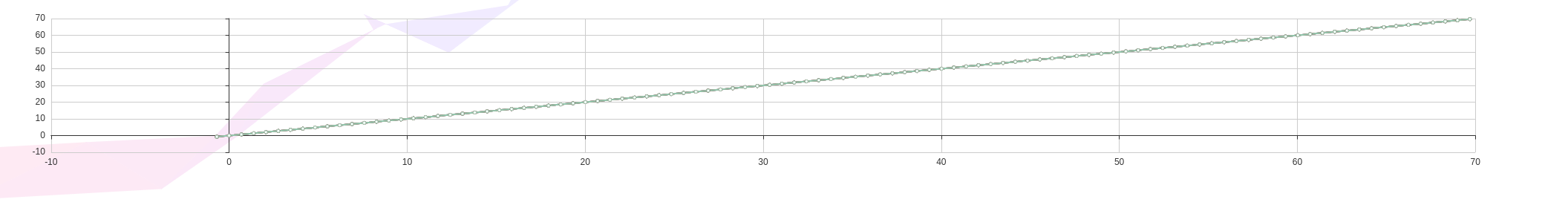
下面简单记录一下思路:
目标函数:
目标就是求解出一组 使得观测值和估计值的误差最小化。
-
高斯牛顿法
推导出每个误差项关于优化变量的导数:
于是 , 高斯牛顿法的增量方程为:
代码在附录里,假设要估计的 ,大概只需要三次迭代就能得到估计的结果。
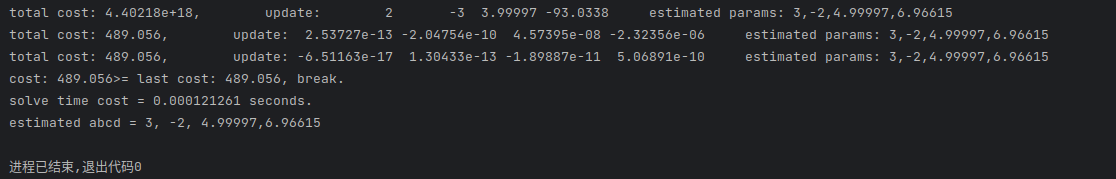
-
g2o
优化变量构成一个顶点,每个误差项构成一条边。
顶点类需要重写变量的重置,更新函数;
边类需要设置关联的顶点,重写误差计算函数,必要时也可以给出解析导数。
下面我们主要测试一下是否给出误差项关于优化变量的解析导数对g2o求解次数的影响(对应的就是g2o_curve.cpp中雅各比矩阵是否注释)
| 不提供解析导数 | 提供解析导数 |
|---|---|
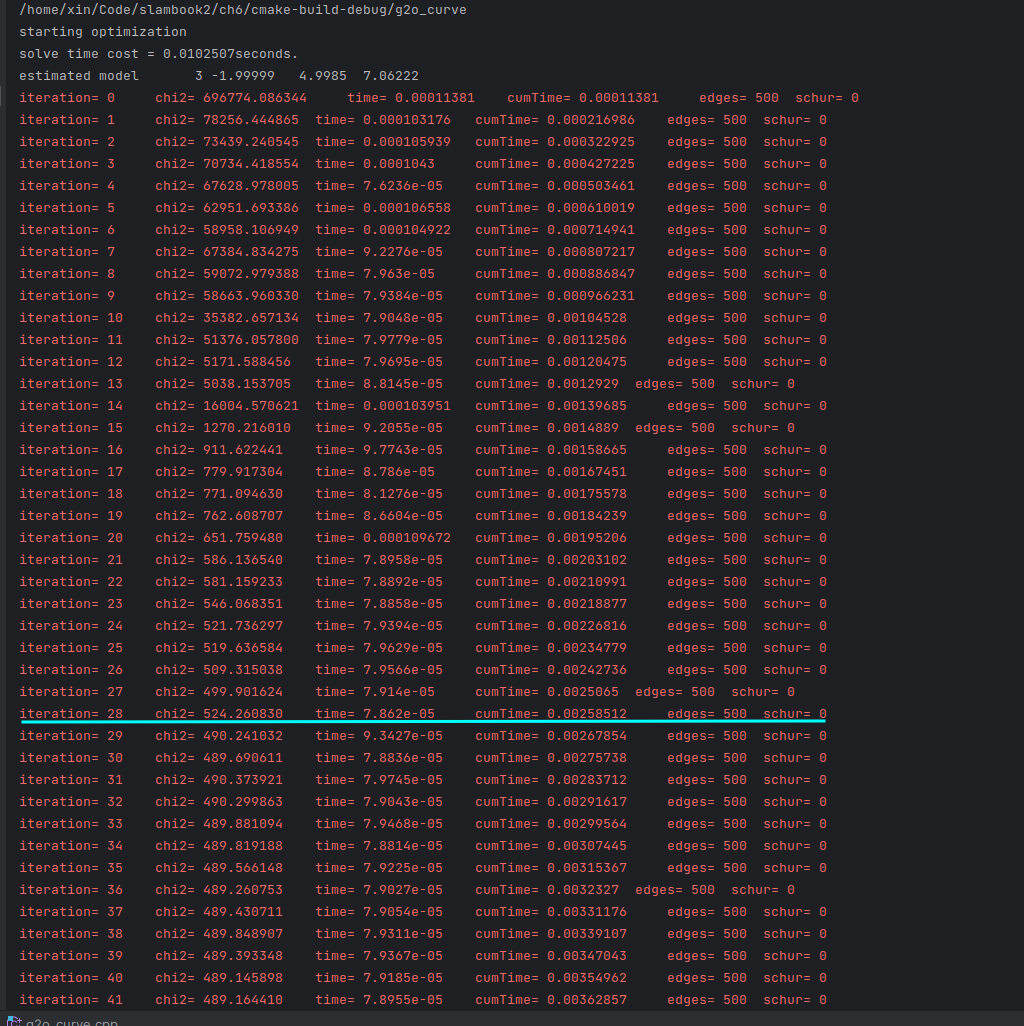 |
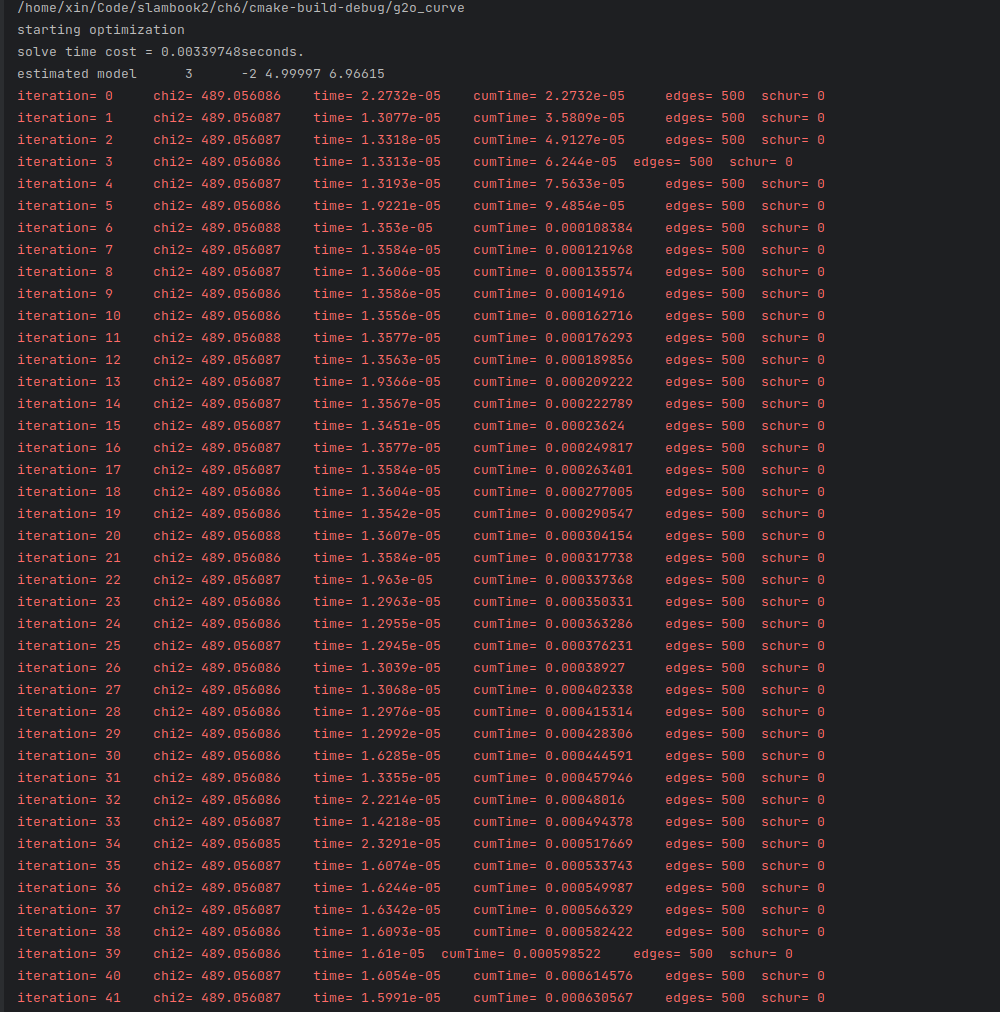 |
| 0.01s | 0.003s |
我们可以看到速度差别还挺大的。
附录
gaussNewton.cpp
//
// Created by xin on 23-6-6.
// use g2o curve fitting y = a*x_3 + b*x_2 + c*x + d
//
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double a = 3.0, b = -2.0, c = 5.0, d = 7; // 真实参数值
double ae = 1, be = 1, ce = 1, de = 100; // 初始参数值
int N = 500; //数据点个数
double w_sigma = 1.0;
double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma;
cv::RNG rng;
vector<double> x_data, y_data;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double x = double(i);
x_data.push_back(x);
y_data.push_back(a * pow(x, 3) + b * pow(x, 2) + c*x + d + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma));
//std::cout << x << "," << a * pow(x, 3) + b * pow(x, 2) + c * x + d + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma) << endl;
}
// 开始Gauss-Newton迭代
int iterations = 1000; // 迭代次数
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; // 本次迭代的cost和上一次迭代的cost
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
Eigen::Matrix4d H = Eigen::Matrix4d::Zero(); // Hessian = J^T W^{-1} J in Gauss-Newton
Eigen::Vector4d b = Eigen::Vector4d::Zero(); // bias
cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { //求每一个数据点的 J 矩阵
double xi = x_data[i], yi = y_data[i]; // 第i个数据点
double error = yi - (ae*pow(xi, 3) + be*pow(xi, 2) + ce*xi + de);
Eigen::Vector4d J; // 雅可比矩阵
J[0] = -pow(xi, 3);
J[1] = -pow(xi, 2);
J[2] = -xi;
J[3] = -1;
H += inv_sigma * inv_sigma * J * J.transpose();
b += -inv_sigma * inv_sigma * error * J;
cost += error * error;
}
// 求解线性方程 Hx=b
Eigen::Vector4d dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (isnan(dx[0])) {
cout << "result is nan!" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {
cout << "cost: " << cost << ">= last cost: " << lastCost << ", break." << endl;
break;
}
ae += dx[0];
be += dx[1];
ce += dx[2];
de += dx[3];
lastCost = cost;
cout << "total cost: " << cost << ", \t\tupdate: " << dx.transpose() <<
"\t\testimated params: " << ae << "," << be << "," << ce << "," << de << endl;
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl;
cout << "estimated abcd = " << ae << ", " << be << ", " << ce << "," << de << endl;
return 0;
return 0;
}
g2o_curve.cpp
//
// Created by xin on 23-6-6.
// use g2o curve fitting y = a*x_3 + b*x_2 + c*x + d
//
#include <iostream>
#include <g2o/core/g2o_core_api.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_dogleg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <cmath>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
/// 自定义图优化的顶点 以及 边
class CurveFittingVertex : public g2o::BaseVertex<4, Eigen::Vector4d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
// 重置
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate << 0, 0, 0, 0;
}
// 更新
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate += Eigen::Vector4d(update);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
class CurveFittingEdge : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1, double, CurveFittingVertex> { // 误差项的维度, 类型, 关联的顶点
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
CurveFittingEdge(double x) : BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {}
// 误差函数
virtual void computeError() override {
const CurveFittingVertex *v = static_cast<const CurveFittingVertex *> (_vertices[0]); //此处拿到关联的顶点
Eigen::Vector4d abcd = v->estimate();
_error(0, 0) =
_measurement - (abcd[0] * pow(_x, 3) + abcd[1] * pow(_x, 2) + abcd[2] * _x + abcd[3]);
}
// 雅各比矩阵,可以注释掉对比一下求解速度
virtual void linearizeOplus() override {
_jacobianOplusXi[0] = -_x * _x * _x;
_jacobianOplusXi[1] = -_x * _x;
_jacobianOplusXi[2] = -_x;
_jacobianOplusXi[3] = -1;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
public:
double _x; // 这个误差项对应的自变量x
};
int main() {
double a = 3.0, b = -2.0, c = 5.0, d = 7; // 真实参数值
double ae = 1, be = 1, ce = 1, de = 100; // 初始参数值
int N = 500; //数据点个数
double w_sigma = 1.0;
double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma;
cv::RNG rng;
vector<double> x_data, y_data;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double x = double(i);
x_data.push_back(x);
y_data.push_back(a * pow(x, 3) + b * pow(x, 2) + c*x + d + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma));
std::cout << x << "," << a * pow(x, 3) + b * pow(x, 2) + c * x + d + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma) << endl;
}
// 构建图优化
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<4, 1>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 线性求解器类型 dense CSparse
//梯度下降方法
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>())
);
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
//往图中加入顶点
CurveFittingVertex *v = new CurveFittingVertex();
v->setId(0);
v->setEstimate(Eigen::Vector4d(ae, be, ce, de));
optimizer.addVertex(v);
//往图中加入边(误差项)
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
CurveFittingEdge *edge = new CurveFittingEdge(x_data[i]);
edge->setId(i);
edge->setVertex(0, v);
edge->setMeasurement(y_data[i]);
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity() * 1 / (w_sigma * w_sigma));
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
cout << "starting optimization" << endl;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(100);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << "seconds." << endl;
// output 结果
Eigen::Vector4d abcd_estimate = v->estimate();
cout << "estimated model" << abcd_estimate.transpose() << endl;
return 0;
}
本文来自博客园,作者:CuriosityWang,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/curiositywang/p/17461105.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
2022-06-06 The surprising impact of mask-head architecture on novel class segmentation精讲