使用Canny+hough实现钱币检测
这个是北京邮电大学《计算机视觉》的一门作业:


Canny边缘提取算法实现
首先定义一个Canny类
其init函数是:
class Canny:
def __init__(self, Guassian_kernal_size, img, HT_high_threshold, HT_low_threshold):
'''
:param Guassian_kernal_size: 高斯滤波器尺寸
:param img: 输入的图片(灰度图),在算法过程中改变
:param HT_high_threshold: 滞后阈值法中的高阈值
:param HT_low_threshold: 滞后阈值法中的低阈值
'''
self.Guassian_kernal_size = Guassian_kernal_size
self.img = img
self.y, self.x = img.shape[0:2]
self.angle = np.zeros([self.y, self.x]) # 图片的梯度方向
self.img_origin = None
self.x_kernal = np.array([[-1, 1]])
self.y_kernal = np.array([[-1], [1]])
self.HT_high_threshold = HT_high_threshold
self.HT_low_threshold = HT_low_threshold
-
计算图像的梯度图并获得梯度方向(Canny类的方法,下同)
def Get_gradient_img(self): ''' 计算梯度图和梯度方向矩阵。 :return: 生成的梯度图 ''' print ('Get_gradient_img') # ------------- write your code bellow ---------------- new_img_x = np.zeros([self.y, self.x], dtype=np.float) new_img_y = np.zeros([self.y, self.x], dtype=np.float) for i in range(0, self.x): for j in range(0, self.y): if j == 0: new_img_y[j][i] = 1 else: new_img_y[j][i] = np.sum(np.array([[self.img[j - 1][i]], [self.img[j][i]]]) * self.y_kernal) if i == 0: new_img_x[j][i] = 1 else: new_img_x[j][i] = np.sum(np.array([self.img[j][i - 1], self.img[j][i]]) * self.x_kernal) gradient_img, self.angle = cv2.cartToPolar(new_img_x, new_img_y) #返回下图中的两个值 self.angle = np.tan(self.angle) self.img = gradient_img.astype(np.uint8) return self.img # ------------- write your code above ----------------
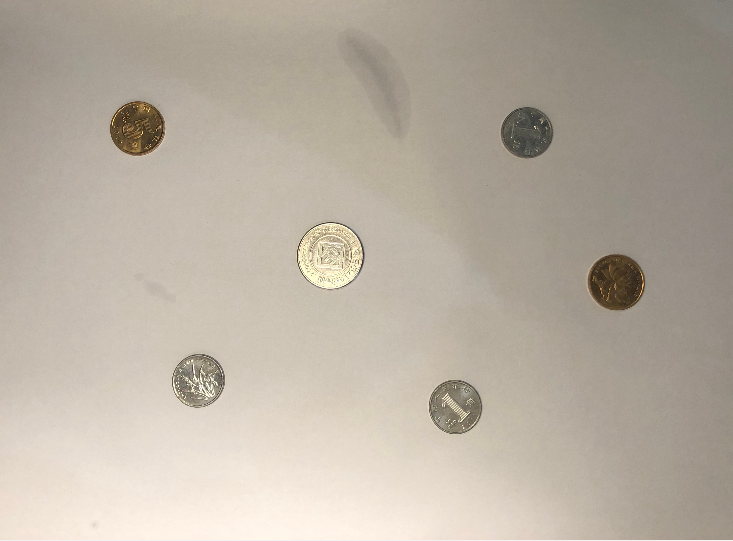
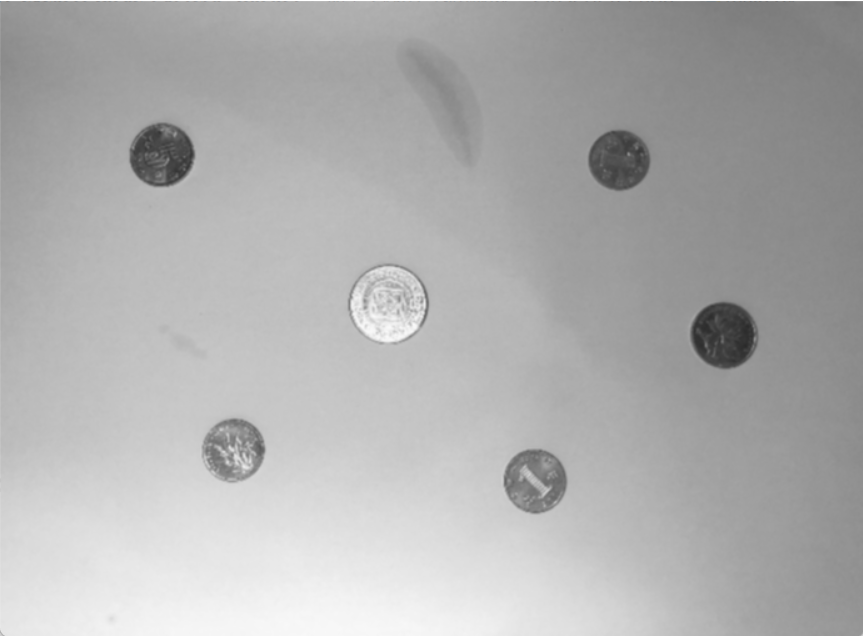
result
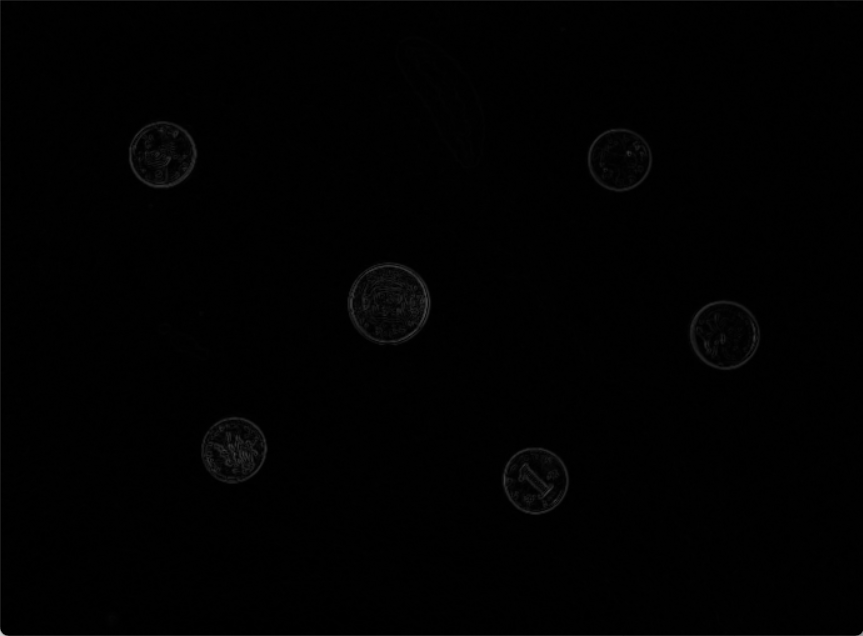
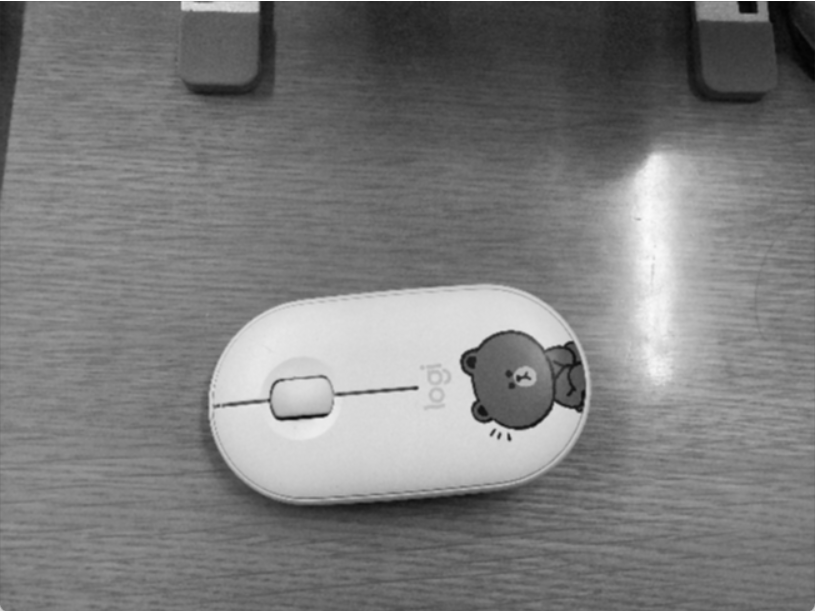
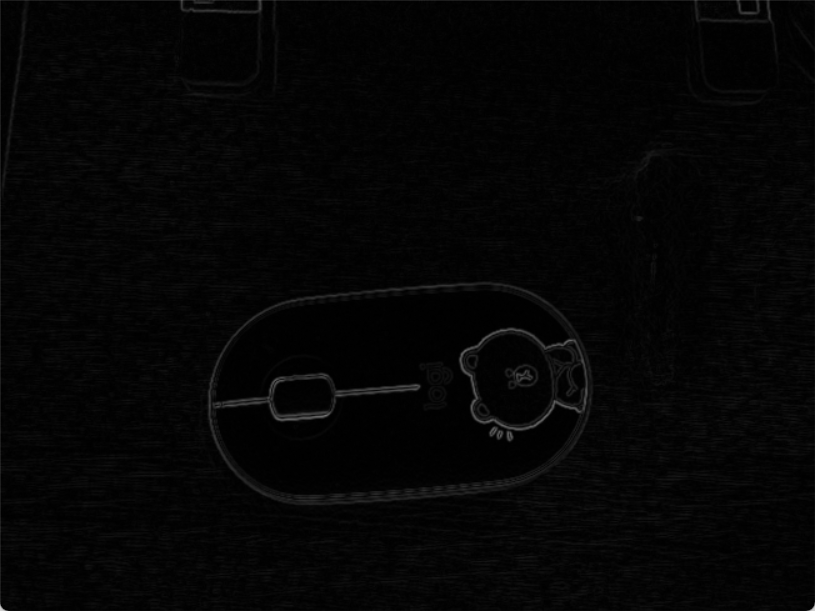
| image | image2(灰度图,高斯滤波) | 梯度 | image2+梯度 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
梯度值经过等比放缩,image2+梯度 图像不明显是因为梯度值普遍较小,未经过非最大值抑制的梯度图像线条较粗
-
非极大化抑制
在梯度矩阵B上进行非极大值运算处理,可以直接比较中心点0,90,45,135四个方向的梯度值,若该点是最大值,则保留。否则为0,即假设在梯度矩阵中的某点为中心点C(i,j),则该点的取值为C(i,j) 是否满足在(C(i,j), C(i,j+1), C(i+1,j), C(i+1, j+1))为最大值,若是保留,否则为0。
但由于实际图像中的像素点是离散的二维矩阵,处于真正中心位置C出的梯度方向的两侧的点不一定存在,或者说存在一个亚像素点,而这个不存在的点以及这个点的梯度值就必须通过两侧的点插值得到。 这句话我的理解是,以中心点C的梯度方向做一条斜线,用斜线与周围梯度值的交点 和 中心点C的梯度值比较判断其是否为最大值。
来个图说明一下: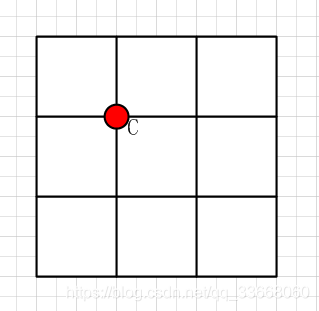
C 为中心点,梯度值为d(i,j);
在x方向的梯度为dx(i,j);
在y方向的梯度值为:dy(i,j);
则过C点的梯度方向线共有4中情况:
1) |dy|>|dx|,且dxdy>0; 2) |dy|>|dx|,且dxdy<0; 3) |dy|<|dx|,且dxdy>0; 4) |dy|<|dx|,且dxdy<0.
四种情况在图中显示如下所示:
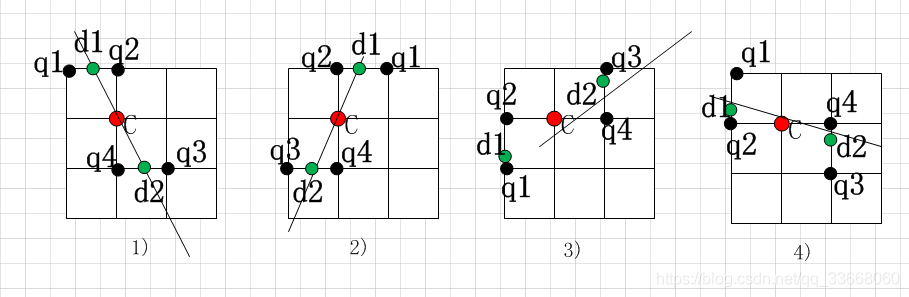
其中: q1,q2,q3,q4分别代表与在梯度矩阵中与C相关的相邻点。
当|dy|>|dx|时,共有2种情况:1)和2),此时weight=|dx|/|dy|.
由线与线之间的相交关系,结合三角形,即可求得:
d1 = weightq1+(1-weight)q2;
d2 = weightq3+(1-weight)q4;
当|dx|>|dy|时,共有2种情况:3)和4),此时weight=|dy|/|dx|.
同理,d1 = weightq1+(1-weight)q2; d2 = weightq3+(1-weight)q4;
然后,比较d(i,j)>=d1,且d(i,j)>=d2是否成立,若满足,保留d,否则d=0。[1]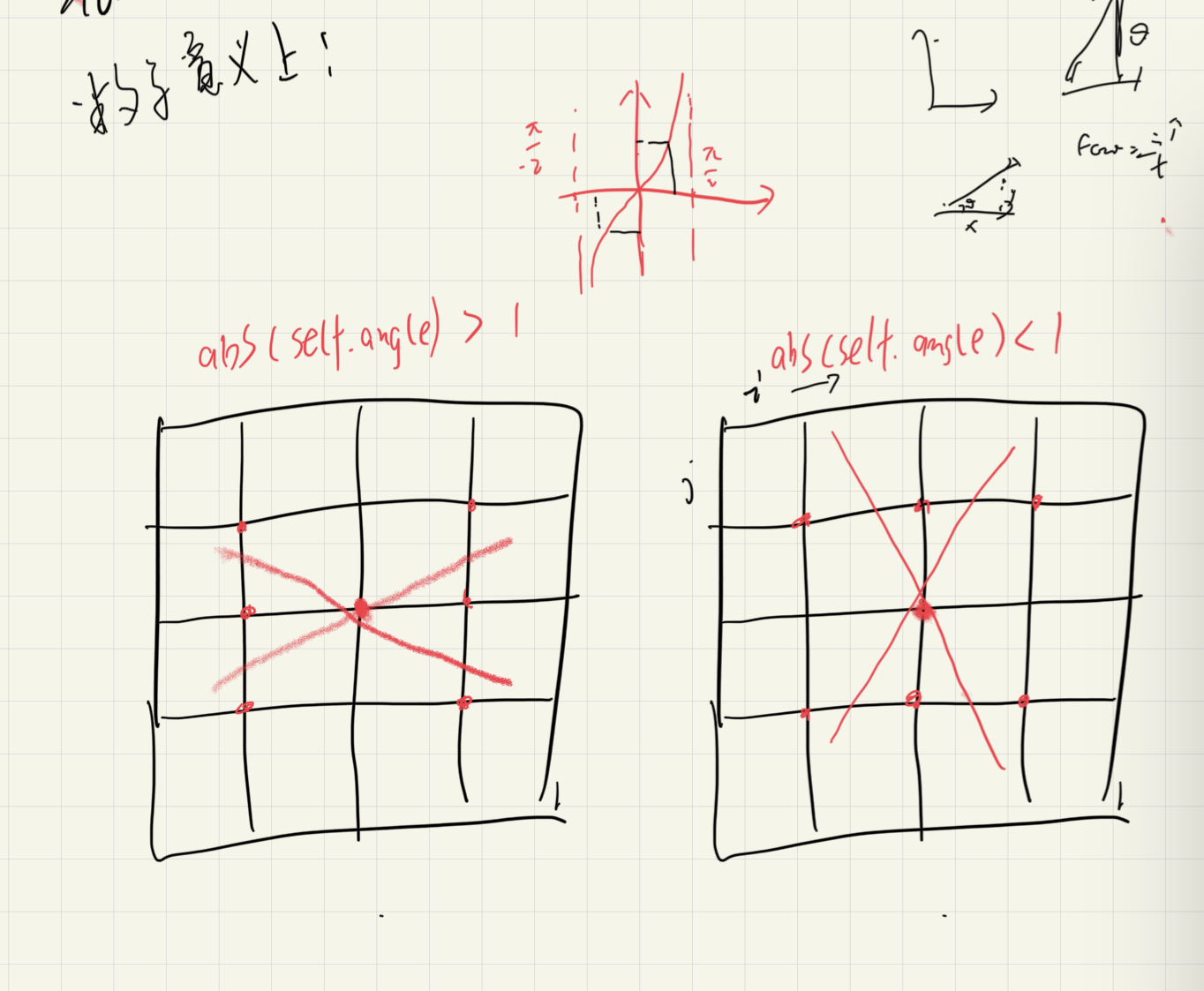
def Non_maximum_suppression(self): ''' 对生成的梯度图进行非极大化抑制,将tan值的大小与正负结合,确定离散中梯度的方向。 :return: 生成的非极大化抑制结果图 ''' print('Non_maximum_suppression') # ------------- write your code bellow ---------------- result = np.zeros([self.y, self.x]) for i in range(1, self.y - 1): for j in range(1, self.x - 1): # 对于梯度过小的值可以忽略 if abs(self.img[i][j]) < 6: result[i][j] = 0 continue elif abs(self.angle[i][j]) > 1: gradient2 = self.img[i - 1][j] gradient4 = self.img[i + 1][j] # g1 g2 # C # g4 g3 if self.angle[i][j] > 0: gradient1 = self.img[i - 1][j - 1] gradient3 = self.img[i + 1][j + 1] # g2 g1 # C # g3 g4 else: gradient1 = self.img[i - 1][j + 1] gradient3 = self.img[i + 1][j - 1] else: gradient2 = self.img[i][j - 1] gradient4 = self.img[i][j + 1] # g1 # g2 C g4 # g3 if self.angle[i][j] > 0: gradient1 = self.img[i - 1][j - 1] gradient3 = self.img[i + 1][j + 1] # g3 # g2 C g4 # g1 else: gradient3 = self.img[i - 1][j + 1] gradient1 = self.img[i + 1][j - 1] temp1 = abs(self.angle[i][j]) * gradient1 + (1 - abs(self.angle[i][j])) * gradient2 temp2 = abs(self.angle[i][j]) * gradient3 + (1 - abs(self.angle[i][j])) * gradient4 if self.img[i][j] >= temp1 and self.img[i][j] >= temp2: result[i][j] = self.img[i][j] else: result[i][j] = 0 self.img = result # ------------- write your code above ---------------- return self.img
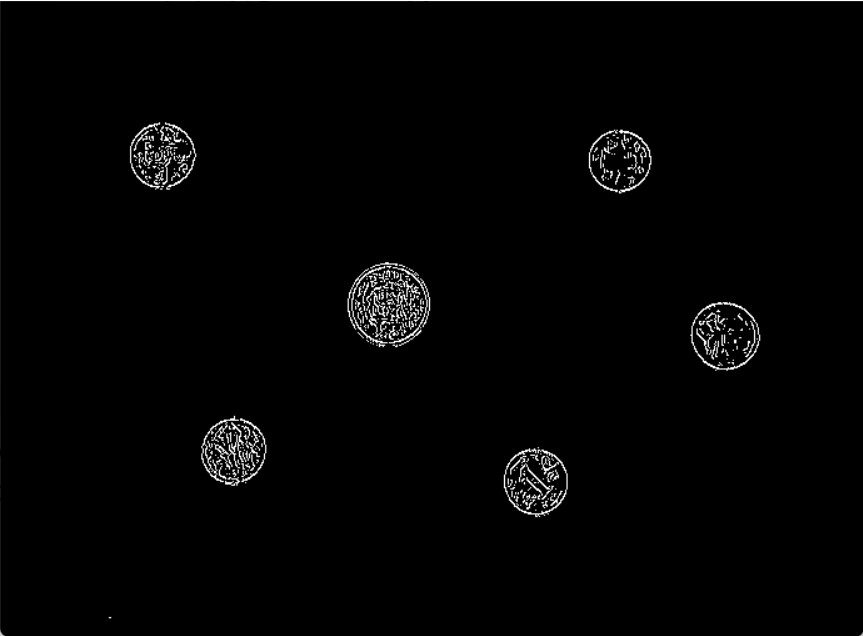
-
双阈值法
在施加非极大值抑制之后,剩余的像素可以更准确地表示图像中的实际边缘。然而,仍然存在由于噪声和颜色变化引起的一些边缘像素。为了解决这些杂散响应,必须用弱梯度值过滤边缘像素,并保留具有高梯度值的边缘像素,可以通过选择高低阈值来实现。如果边缘像素的梯度值高于高阈值,则将其标记为强边缘像素;如果边缘像素的梯度值小于高阈值并且大于低阈值,则将其标记为弱边缘像素;如果边缘像素的梯度值小于低阈值,则会被抑制。阈值的选择取决于给定输入图像的内容。
双阈值检测的伪代码描写如下:
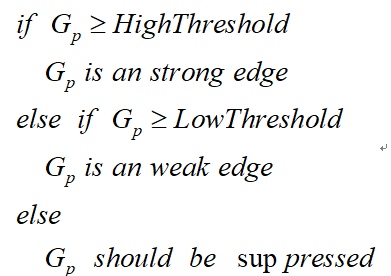 
抑制孤立低阈值点
到目前为止,被划分为强边缘的像素点已经被确定为边缘,因为它们是从图像中的真实边缘中提取出来的。然而,对于弱边缘像素,将会有一些争论,因为这些像素可以从真实边缘提取也可以是因噪声或颜色变化引起的。为了获得准确的结果,应该抑制由后者引起的弱边缘。通常,由真实边缘引起的弱边缘像素将连接到强边缘像素,而噪声响应未连接。为了跟踪边缘连接,通过查看弱边缘像素及其8个邻域像素,只要其中一个为强边缘像素,则该弱边缘点就可以保留为真实的边缘。
抑制孤立边缘点的伪代码描述如下:

[2]代码:
def Hysteresis_thresholding(self): ''' :return: 滞后阈值法结果图 ''' print('Hysteresis_thresholding') # ------------- write your code bellow ---------------- for i in range(1, self.y - 1): for j in range(1, self.x - 1): if self.img[i][j] >= self.HT_high_threshold: if abs(self.angle[i][j]) < 1: if self.img_origin[i - 1][j] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i - 1][j] = self.HT_high_threshold if self.img_origin[i + 1][j] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i + 1][j] = self.HT_high_threshold # g1 g2 # C # g4 g3 if self.angle[i][j] < 0: if self.img_origin[i - 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i - 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold if self.img_origin[i + 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i + 1][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold # g2 g1 # C # g3 g4 else: if self.img_origin[i - 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i - 1][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold if self.img_origin[i + 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i + 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold else: if self.img_origin[i][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold if self.img_origin[i][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold # g1 # g2 C g4 # g3 if self.angle[i][j] < 0: if self.img_origin[i - 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i - 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold if self.img_origin[i + 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i + 1][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold # g3 # g2 C g4 # g1 else: if self.img_origin[i - 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i + 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold if self.img_origin[i + 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold: self.img[i + 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold return self.img # ------------- write your code above ---------------- return self.img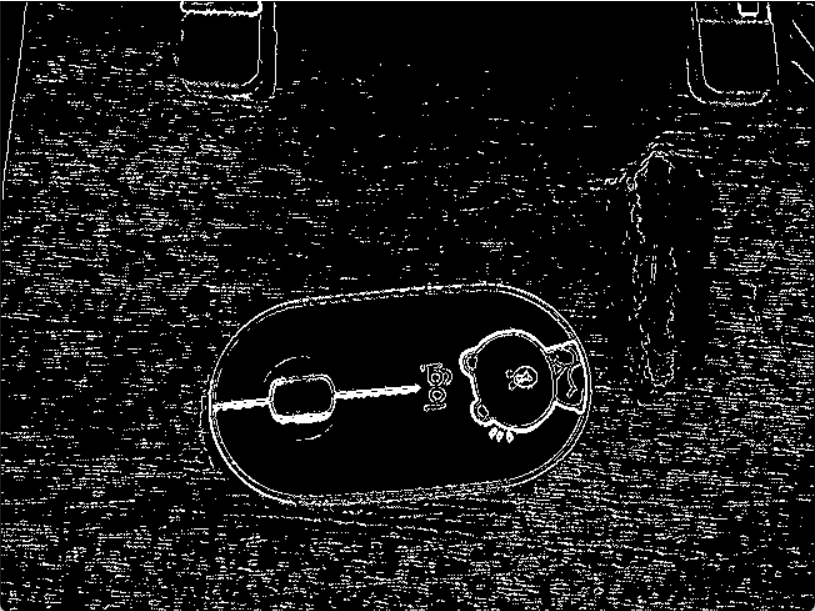
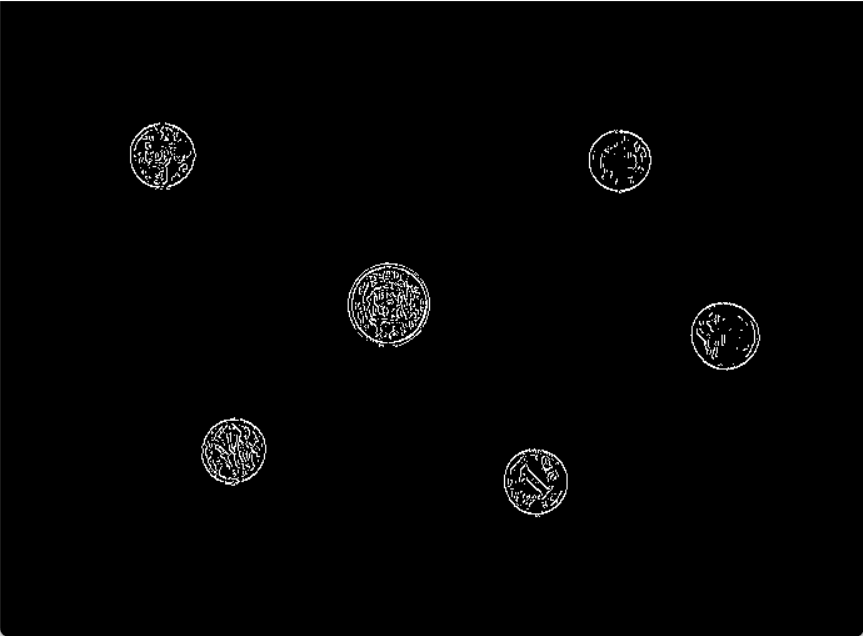
至此,利用Canny提取边缘算法完成。
霍夫变换实现
import numpy as np
import math
class Hough_transform:
def __init__(self, img, angle, step=5, threshold=135):
'''
:param img: 输入的图像
:param angle: 输入的梯度方向矩阵
:param step: Hough 变换步长大小
:param threshold: 筛选单元的阈值
'''
self.img = img
self.angle = angle
self.y, self.x = img.shape[0:2]
self.radius = math.ceil(math.sqrt(self.y**2 + self.x**2))
self.step = step
self.vote_matrix = np.zeros([math.ceil(self.y / self.step), math.ceil(self.x / self.step), math.ceil(self.radius / self.step)])
self.threshold = threshold
self.circles = []
def Hough_transform_algorithm(self):
'''
按照 x,y,radius 建立三维空间,根据图片中边上的点沿梯度方向对空间中的所有单
元进行投票。每个点投出来结果为一折线。
:return: 投票矩阵
'''
print ('Hough_transform_algorithm')
for i in range(1, self.y - 1):
for j in range(1, self.x - 1):
if self.img[i][j] > 0:
y = i
x = j
r = 0
while y < self.y and x < self.x and y >= 0 and x >= 0:
self.vote_matrix[math.floor(y / self.step)][math.floor(x / self.step)][math.floor(r / self.step)] += 1
y = y + self.step * self.angle[i][j]
x = x + self.step
r = r + math.sqrt((self.step * self.angle[i][j])**2 + self.step**2)
y = i - self.step * self.angle[i][j]
x = j - self.step
r = math.sqrt((self.step * self.angle[i][j])**2 + self.step**2)
while y < self.y and x < self.x and y >= 0 and x >= 0:
self.vote_matrix[math.floor(y / self.step)][math.floor(x / self.step)][math.floor(r / self.step)] += 1
y = y - self.step * self.angle[i][j]
x = x - self.step
r = r + math.sqrt((self.step * self.angle[i][j])**2 + self.step**2)
return self.vote_matrix
def Select_Circle(self):
'''
按照阈值从投票矩阵中筛选出合适的圆,并作极大化抑制,这里的非极大化抑制我采
用的是邻近点结果取平均值的方法,而非单纯的取极大值。
:return: None
'''
print ('Select_Circle')
houxuanyuan = []
for i in range(0, math.ceil(self.y / self.step)):
for j in range(0, math.ceil(self.x / self.step)):
for r in range(0, math.ceil(self.radius / self.step)):
if self.vote_matrix[i][j][r] >= self.threshold:
y = i * self.step + self.step / 2
x = j * self.step + self.step / 2
r = r * self.step + self.step / 2
houxuanyuan.append((math.ceil(x), math.ceil(y), math.ceil(r)))
if len(houxuanyuan) == 0:
print("No Circle in this threshold.")
return
x, y, r = houxuanyuan[0]
possible = []
middle = []
for circle in houxuanyuan:
if abs(x - circle[0]) <= 20 and abs(y - circle[1]) <= 20:
possible.append([circle[0], circle[1], circle[2]])
else:
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
middle.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
possible.clear()
x, y, r = circle
possible.append([x, y, r])
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
middle.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
def takeFirst(elem):
return elem[0]
middle.sort(key=takeFirst)
x, y, r = middle[0]
possible = []
for circle in middle:
if abs(x - circle[0]) <= 20 and abs(y - circle[1]) <= 20:
possible.append([circle[0], circle[1], circle[2]])
else:
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
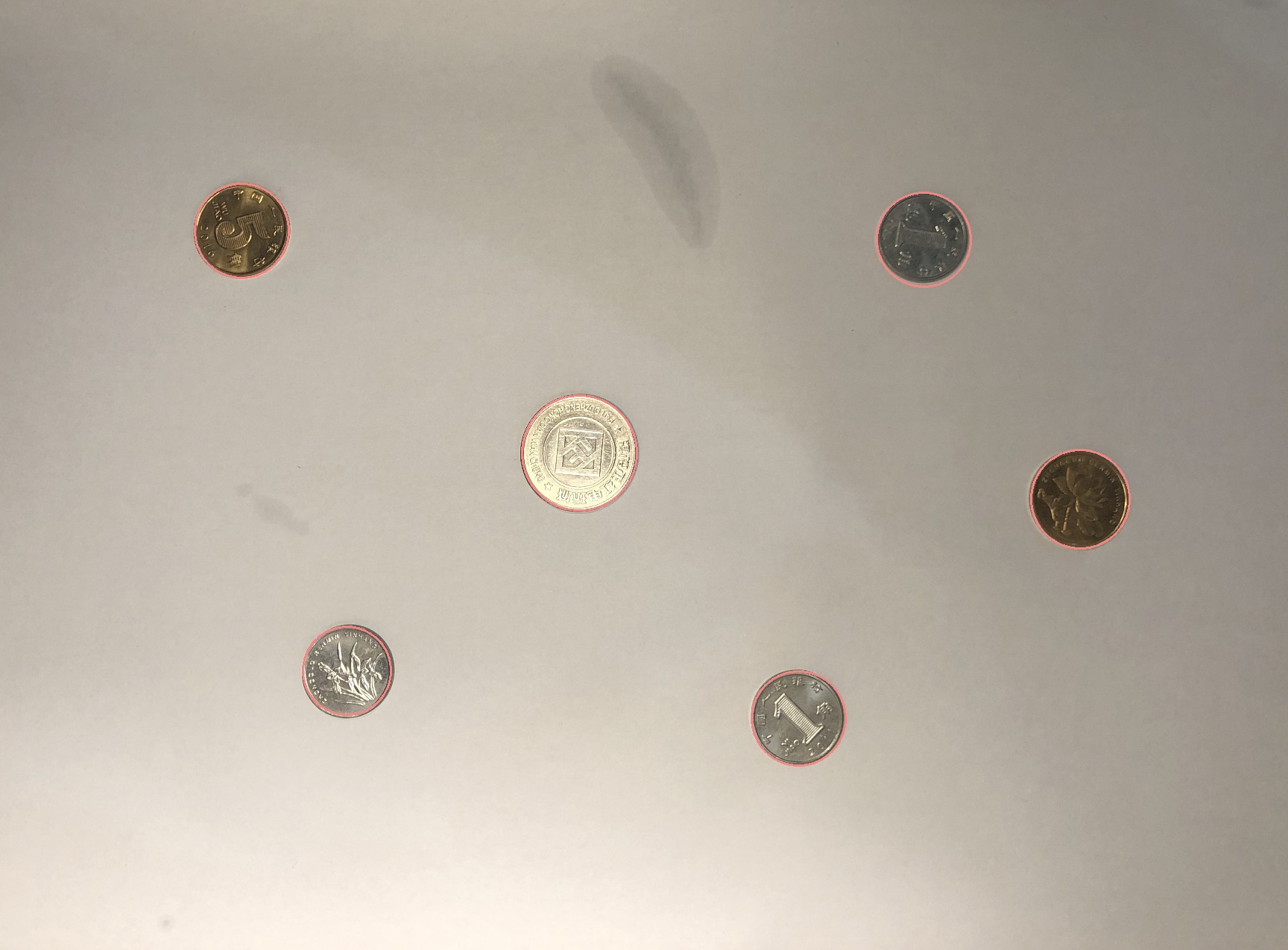
print("Circle core: (%f, %f) Radius: %f" % (result[0], result[1], result[2]))
self.circles.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
possible.clear()
x, y, r = circle
possible.append([x, y, r])
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
print("Circle core: (%f, %f) Radius: %f" % (result[0], result[1], result[2]))
self.circles.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
def Calculate(self):
'''
按照算法顺序调用以上成员函数
:return: 圆形拟合结果图,圆的坐标及半径集合
'''
self.Hough_transform_algorithm()
self.Select_Circle()
return self.circles
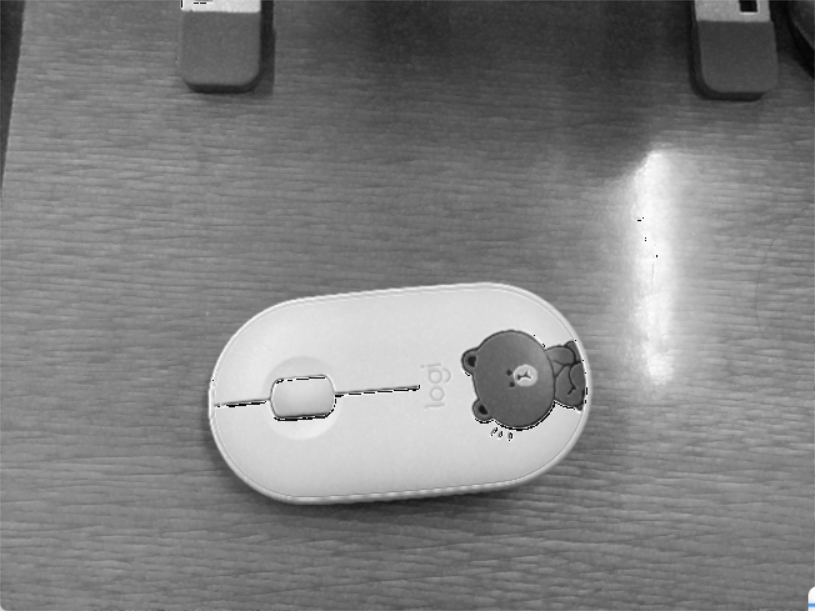
result:

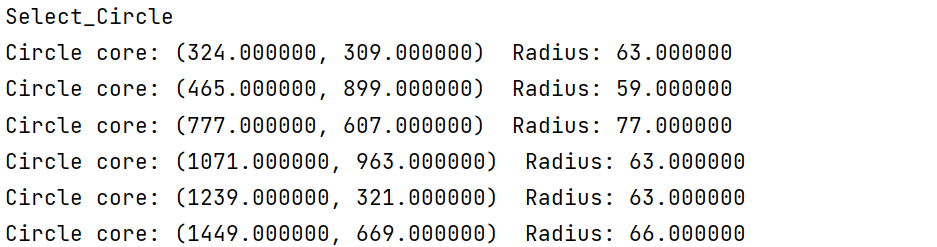
参考
- [1] Canny算子中的梯度求取及非最大值抑制(NMS)实现
- [2]nowgood:边缘检测之canny
本文来自博客园,作者:CuriosityWang,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/curiositywang/p/15638550.html


