import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #使用numpy生成200个随机点 x_data = np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)[:,np.newaxis] noise = np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data) + noise #定义两个placeholder x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) #定义神经网络中间层 Weights_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1,10])) biases_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10])) Wx_plus_b_L1 = tf.matmul(x,Weights_L1) + biases_L1 L1 = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L1) #定义神经网络输出层 Weights_L2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10,1])) biases_L2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,1])) Wx_plus_b_L2 = tf.matmul(L1,Weights_L2) + biases_L2 prediction = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L2) #二次代价函数 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - prediction)) #使用梯度下降法 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess: #变量初始化 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for _ in range(2000): sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:x_data,y:y_data}) #获得预测值 prediction_value = sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={x:x_data}) #画图 plt.figure() plt.scatter(x_data,y_data) plt.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw = 5) plt.show()
得到结果:
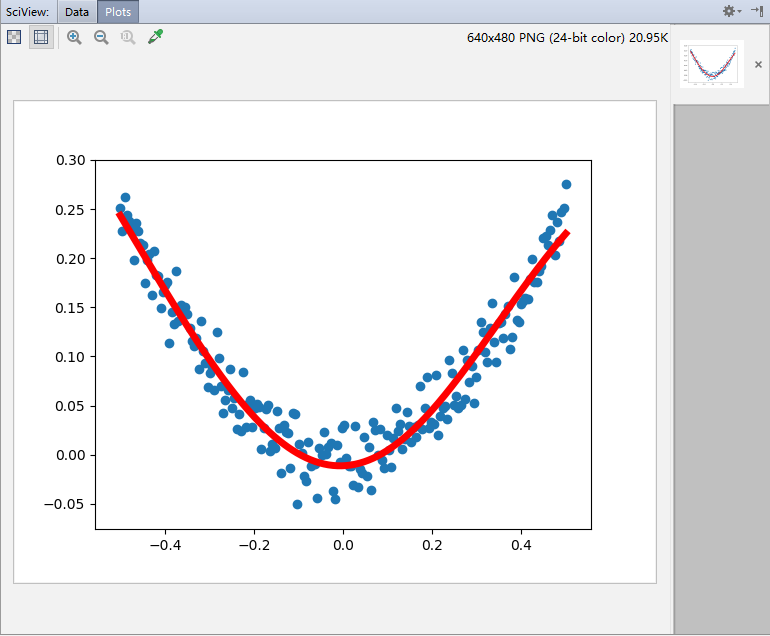
——
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #载入数据集 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data",one_hot=True) #每个批次的大小 batch_size = 100 #计算一共有多少个批次 n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size #定义两个placeholder x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784]) #图片 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10]) #标签 #创建一个简单的神经网络 w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,w)+b) #二次代价函数 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction)) #梯度下降算法 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss) #初始化变量 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() #结果存放在一个bool类型的列表中,argmax()返回一维张量中最大值所在的位置,equal函数判断两者是否相等 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1)) #求准确率,cast:将bool型转换为0,1然后求平均正好算到是准确率 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32)) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) for epoch in range(21): for batch in range(batch_size):#next_batch:不断获取下一组数据 batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys}) acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels}) print("Iter "+str(epoch)+",Testing Accuracy "+str(acc))
训练结果:
Iter 0,Testing Accuracy 0.657 Iter 1,Testing Accuracy 0.7063 Iter 2,Testing Accuracy 0.7458 Iter 3,Testing Accuracy 0.7876 Iter 4,Testing Accuracy 0.8203 Iter 5,Testing Accuracy 0.8406 Iter 6,Testing Accuracy 0.8492 Iter 7,Testing Accuracy 0.8586 Iter 8,Testing Accuracy 0.8642 Iter 9,Testing Accuracy 0.8678 Iter 10,Testing Accuracy 0.8709 Iter 11,Testing Accuracy 0.8736 Iter 12,Testing Accuracy 0.8751 Iter 13,Testing Accuracy 0.8784 Iter 14,Testing Accuracy 0.88 Iter 15,Testing Accuracy 0.8816 Iter 16,Testing Accuracy 0.883 Iter 17,Testing Accuracy 0.8841 Iter 18,Testing Accuracy 0.8847 Iter 19,Testing Accuracy 0.8855 Iter 20,Testing Accuracy 0.8878
可见,通过多次的训练,识别的准确值不断提高
——


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号