我的python渗透测试工具箱之自制netcat
此工具的目的是实现在目标主机上的文件传输,控制命令行的功能,主要逻辑依靠python的subprocess模块、`sys`模块和`getopt`模块。
知识准备
studin和studut
studin和studout是用来获取标准输入输出的,它们是sys模块下的方法。
标准输入输出就是包括/n/t等特殊字符的输出,可以用来作为拆分的条件。
在python中调用print时,事实上调用了sys.stdout.write(obj+'\n'),调用input时则是调用了sys.studin.readline().strip('\n')
subprocess模块
subprocess模块主要是用来执行外部命令的模块,
1,subprocess.call(),执行命令,并返回执行状态,其中shell参数为False时,命令需要通过列表的方式传入,当shell为True时,可直接传入命令。
2,subprocess.check_call(),增加当返回值不为0时,直接抛出异常。。
3,在此脚本中,主要使用subprocess.check_output(),它会做两件事:
· 检查返回值,如果不为0则代表当前进程执行失败。
· 返回标准输出结果。
sys模块
sys模块是python和解释器交互的模块,较为容易理解,在这个脚本中我们主要用的是它的`sys.argv`。
sys.argv,它的作用是返回将执行脚本的路径和命令参数整合到一个list中返回,list的第一项是当前脚本的路径。
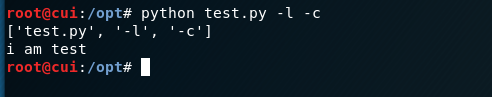
大家看到这可能会有疑问,sys.argv返回值的第一项确实是路径,这里显示文件名是因为我是在文件同级目录下运行的。
getopt模块
getopt模块大家可能见到的比较少,在网上各式各样的解释也让人眼花缭乱,这里说一下我的理解。
getopt模块有两个方法,这里主要介绍getopt.getopt()。它的作用其实两个字就能说明:匹配。
getopt.getopt会返回匹配到的命令行参数和参数值组成的元组。
有三个参数:
1,命令行参数,我们可以通过sys.argv[1:]来获取,把路径元素跳过。
2,短参数的匹配规则。短参数就是 -h,-l,-v这种的,加上 `:`就代表":"左右两边的参数有值。
3,长参数的匹配规则,长参数就是-help,-version,-command这种,加上`=`就代表该参数有值。
有两个返回值:
1,匹配到的命令行参数及其值 组成的元组 构成的列表。
2,未匹配到的命令行参数。
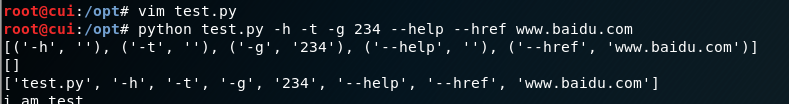
示例代码:

运行结果:
程序代码及讲解
import sys import getopt import socket import subprocess import threading #设置全局变量 listen = False command = False upload = False execute = "" host = "" upload_path = "" port = 0 def help(): ''' 这里就是一些注释及使用方法说明,如果用中文怕不支持,英文我还不会 :param:null :return: none ''' print("knife tools") print("-l --listen ") print("-t --host ") print("-c --command ") print("-u --upload ") sys.exit(0) #退出命令 #命令执行,通过suprocess.checkoutout def run_command(command): command = command.strip() try: output = subprocess.check_output(command, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, shell=True) except: output = "Failed to execute command.\r\n" return output def client_handler(client_socket): ''' 通过不同参数的长度来决定处理什么事务 :param client_socket:也就是服务端的我们习惯的conn :return: ''' #定义全局变量 global upload global command #上传文件功能 if len(upload_path): file_buffer = "" while True: data = client_socket.recv(1024) if not data: break else: file_buffer += data #简单的文件操作 try: with open(upload_path, "wb") as f: f.write(file_buffer) client_socket.send("Successfully saved file to %s\r\n" % upload_path) except: client_socket.send("Failed to save file to %s\r\n" % upload_path) #执行命令 if command: while True: #会夯住,客户端会模拟命令行输入 client_socket.send("<command:#> ") cmd_buffer = "" while "\n" not in cmd_buffer: cmd_buffer += client_socket.recv(1024) #返回命令执行结果 response = run_command(cmd_buffer) client_socket.send(response) def client_sender(buffer): client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) try: client.connect((host, port)) if len(buffer): client.send(buffer) #接收数据并回传,以字符串大的形式储存到response中 while True: recv_len = 1 response = "" while recv_len: data = client.recv(4096) recv_len = len(data) response += data if recv_len < 4096: break print(response) #夯住,继续获取命令行输入并继续传输 buffer = input("") buffer += "\n" client.send(buffer) except: client.close() #通过socket创建服务端 def server_loop(): global host global port if not len(host): host = "0.0.0.0" server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) server.bind((host, port)) server.listen(5) #建立多线程处理 while True: client_socket, addr = server.accept() client_thread = threading.Thread(target=client_handler, args=(client_socket,)) client_thread.start() def main(): ''' 主函数 :param:null ''' global listen global port global command global upload_path global host #判断命令行参数,如果个数为零,那么就输出错误信息并且退出 if not len(sys.argv[1:]): help() try: opts,args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],"hl:t:p:cu",["help","listen","execute","host","port","command","upload"]) except getopt.GetoptError as err: print(str(err)) #输出错误信息 help() #通过if..else..来判断执行什么动作 for o, a in opts: if o in ("-h", "--help"): help() elif o in ("-l", "--listen"): listen = True elif o in ("-c", "--commandshell"): command = True elif o in ("-u", "--upload"): upload_destination = a elif o in ("-t", "--host"): host = a elif o in ("-p", "--port"): port = int(a) else: assert False, "Unhandled Option" if not listen and len(host) and port > 0: #获取标准输入 buffer = sys.stdin.read() client_sender(buffer) #listen为True则创建监听 if listen: server_loop() main()



