JAVA 泛型
泛型
泛型概述
泛型:是JDK5中引入的特性,它提供了编译时类型安全检测机制,该机制允许在编译时检测到非法的类型
它的本质是参数化类型,也就是说所操作的数据类型被指定为一个参数
一提到参数,最熟悉的就是定义方法时有形参,然后调用此方法时传递实参。那么参数化类型如何理解?
顾名思义,就是将类型由原来的具体的类型参数化,然后在使用/调用时传入具体的类型
这种参数类型可以用在类、方法和接口中,分别被称为泛型类、泛型方法、泛型接口
泛型定义格式:
-
- <类型>: 指定一种类型的格式。这里的类型可以看成是形参
- <类型1,类型2…> 指定多种类型的格式,多种类型之间用逗号隔开。这里的类型可以看成是形参
- 将来具体调用时候给定的类型可以看成是实参,并且实参的类型只能是引用数据类型
泛型的好处:
-
- 把运行时问题提前到了编译期间
- 避免了强制类型转换
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 5 /* 6 泛型 7 8 需求:Collection集合存储字符串并遍历 9 */ 10 public class GenericDemo { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 //创建集合对象 13 // Collection c=new ArrayList(); 14 Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>(); 15 16 //添加元素 17 c.add("hello"); 18 c.add("world"); 19 c.add("java"); 20 // c.add(100);//运行时期问题改为编译期问题 21 22 //遍历集合 23 // Iterator it = c.iterator(); 24 Iterator<String> it = c.iterator(); 25 while (it.hasNext()) { 26 // Object obj = it.next(); 27 // System.out.println(obj); 28 29 //向下转型 30 // String s=(String)it.next();//运行时问题:ClassCastException 31 String s = it.next();//不需要强制类型转换 32 System.out.println(s); 33 } 34 35 }
泛型类
- 格式:修饰符 class 类名<类型> {}
<>中表示泛型的参数可以是任意标识,常见的如T、E、K、V等
1 //学生类 2 public class Student { 3 private String name; 4 5 public String getName() { 6 return name; 7 } 8 9 public void setName(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 13 }
1 //老师类 2 public class Teacher { 3 private Integer age; 4 5 public Integer getAge() { 6 return age; 7 } 8 9 public void setAge(Integer age) { 10 this.age = age; 11 } 12 13 }
1 /* 2 泛型类的定义格式: 3 4 - 格式:修饰符 class 类名<类型>{} 5 - 范例:public class Generic<T>{} 6 此处**T**可以随便写为任意标识,常见的如**T、E、K、V**等形式的参数常用于表示泛型 7 */ 8 9 public class Generic<T> { 10 private T t; 11 12 public T getT() { 13 return t; 14 } 15 16 public void setT(T t) { 17 this.t = t; 18 } 19 20 }
1 //测试类 2 public class GenericDemo { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Student s = new Student(); 5 s.setName("小白"); 6 System.out.println(s.getName()); 7 8 Teacher t = new Teacher(); 9 t.setAge(23); 10 // t.setAge("34");//报错 11 System.out.println(t.getAge()); 12 System.out.println("--------"); 13 14 Generic<String> g1 = new Generic<String>(); 15 g1.setT("小黑"); 16 System.out.println(g1.getT()); 17 18 Generic<Integer> g2 = new Generic<Integer>(); 19 g2.setT(12); 20 System.out.println(g2.getT()); 21 22 Generic<Boolean> g3 = new Generic<Boolean>(); 23 g3.setT(true); 24 System.out.println(g3.getT()); 25 26 } 27 }
泛型方法
- 格式:修饰符 <类型> 返回值类型 方法名(类型 变量名) { }
1 /*泛型方法改进*/ 2 public class Generic { 3 public <T> void show(T t) { 4 System.out.println(t); 5 } 6 } 7 8 9 public class GenericDemo2 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 12 Generic g = new Generic(); 13 g.show("小白"); 14 g.show(24); 15 g.show(true); 16 g.show(12.34); 17 18 } 19 }
泛型接口
- 格式:修饰符 interface 接口名<类型> { }
1 //泛型接口 2 public interface Generic1<T> { 3 void show(T t); 4 }
1 //泛型类继承接口 2 public class Genriclmpl<T> implements Generic1<T> { 3 @Override 4 public void show(T t) { 5 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 6 System.out.println(t); 7 } 8 }
1 //测试类 2 public class GenericDemo3 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Generic1<String> g1 = new Genriclmpl<String>(); 5 g1.show("小白"); 6 7 Generic1<Integer> g2 = new Genriclmpl<Integer>(); 8 g2.show(23); 9 10 Generic1<Boolean> g3 = new Genriclmpl<Boolean>(); 11 g3.show(true); 12 13 } 14 }
类型通配符:<?>
- 使用类型通配符,可以用于表示各种泛型List的父类
- 若希望它代表某一类泛型List的父类,可以使用类型通配符的上限
- 若希望它代表某一类泛型List的子类,可以使用类型通配符的下限
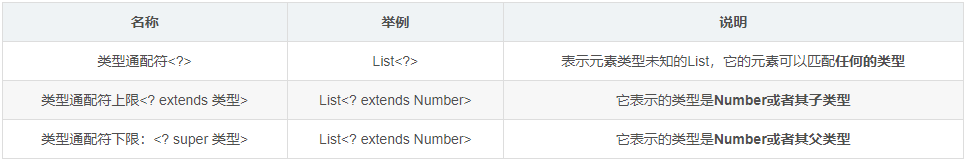
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 /* 5 **类型通配符** 6 7 为了表示各种泛型List的父类,可以使用类型通配符 8 9 - 类型通配符:**<?>** 10 - List<?>:表示元素类型未知的List,它的元素可以匹配**任何的类型** 11 - 这种带通配符的List仅表示它是各种泛型List的父类,并不能把元素添加到其中 12 13 如果说我们不希望List<?>是任何泛型List的父类,只希望它代表某一类泛型List的父类,可以使用类型通配符的上限 14 15 - 类型通配符上限:**<? extends 类型>** 16 - List<? extends Number>:它表示的类型是**Number或者其子类型** 17 18 除了可以指定类型通配符的上限,我们也可以指定类型通配符的下限 19 20 - 类型通配符下限:**<? super 类型>** 21 - List<? super Number>:它表示的类型是**Number或者其父类型** 22 */ 23 24 public class GenericDemo4 { 25 public static void main(String[] args) { 26 //类型通配符:<?> 27 List<?> list1 = new ArrayList<Object>(); 28 List<?> list2 = new ArrayList<Number>(); 29 List<?> list3 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 30 System.out.println("--------"); 31 32 // 类型通配符上限:<? extends 类型> 33 // List<? extends Number> list4=new ArrayList<Object>();//报错 34 List<? extends Number> list5 = new ArrayList<Number>(); 35 List<? extends Number> list6 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 36 System.out.println("--------"); 37 38 //类型通配符下限:<? super 类型> 39 List<? super Number> list7 = new ArrayList<Object>(); 40 List<? super Number> list8 = new ArrayList<Number>(); 41 // List<? super Number> list9=new ArrayList<Integer>();//报错 42 43 } 44 }
可变参数
可变参数又称参数个数可变,用作方法的形参出现,那么方法参数个数就是可变的了
-
- 格式:修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型… 变量名) { }
- 范例:public static int sum(int… a) { }
可变参数注意事项:
-
- 这里的变量其实是一个数组
- 如果一个方法有多个参数,包含可变参数,可变参数要放在最后
1 public class ArgsDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println(sum(1, 2)); 4 System.out.println(sum(1, 2, 3)); 5 System.out.println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4)); 6 7 System.out.println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); 8 System.out.println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)); 9 System.out.println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)); 10 11 } 12 13 // public static int sum(int... a,int b) {//报错 14 // return 0; 15 // } 16 17 // public static int sum(int b,int... a) {//可变参数要放在后面 18 // return 0; 19 // } 20 21 public static int sum(int... a) { 22 // System.out.println(a); 23 // return 0; 24 int sum = 0; 25 for (int i : a) { 26 sum += i; 27 } 28 return sum; 29 30 } 31 32 // public static int sum(int a,int b) { 33 // return a+b; 34 // } 35 // public static int sum(int a,int b,int c) { 36 // return a+b+c; 37 // } 38 // public static int sum(int a,int b,int c,int d) { 39 // return a+b+c+d; 40 // } 41 }
可变参数的使用
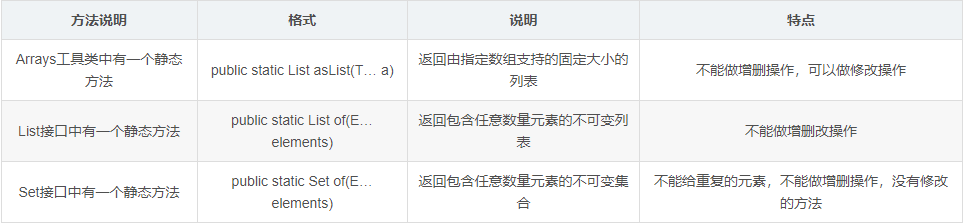
1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.Set; 4 5 /* 6 Arrays工具类中有一个静态方法: 7 8 - public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a):返回由指定数组支持的固定大小的列表 9 10 List接口中有一个静态方法: 11 12 - public static <E> List<E> of(E... elements):返回包含任意数量元素的不可变列表 13 14 Set接口中有一个静态方法: 15 16 - public static <E> Set<E> of(E... elements):返回包含任意数量元素的不可变集合 17 */ 18 19 public class ArgsDemo2 { 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 22 //public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a):返回由指定数组支持的固定大小的列表 23 List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello","world","java"); 24 25 // list.add("javaee");//UnsupportedOperationException:不支持请求操作 26 // list.remove("world");//UnsupportedOperationException 27 list.set(1,"javaee");//添加和删除都会修改List的大小,所以不可以用,修改不会改变大小,可以用 28 System.out.println(list); 29 30 31 32 //public static <E> List<E> of(E... elements):返回包含任意数量元素的不可变列表 33 List<String> list = List.of("hello","world","java","world"); 34 35 // list.add("javaee");//UnsupportedOperationException 36 // list.remove("world");//UnsupportedOperationException 37 // list.set(1,"javaee");//UnsupportedOperationException 38 //增删改都不可以 39 System.out.println(list); 40 41 42 43 //public static <E> Set<E> of(E... elements):返回包含任意数量元素的不可变集合 44 Set<String> set = Set.of("hello","world","java"); 45 // Set<String> set = Set.of("hello","world","java","world");//IllegalArgumentException:非法或不正确的参数 46 //因为set不能有重复元素 47 48 // set.add("javaee");//UnsupportedOperationException 49 // set.remove("world");//UnsupportedOperationException 50 System.out.println(set); 51 52 } 53 }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY