typescript学习
1、unknown 和 any 区别
any 放弃了类型检查。 unknown 只是指明了类型还未确认,后续还需要你去断言
2、组合类型
联合: type MyBool = 'open' | 'closed' | 'minimized'
泛型
3、结构化的类型系统
TypeScript 的一个核心原则是类型检查基于对象的属性和行为(type checking focuses on the shape that values have)。这有时被叫做“鸭子类型”或“结构类型”(structural typing)。
在结构化的类型系统当中,如果两个对象具有相同的结构,则认为它们是相同类型的。
interface Point { x: number; y: number; } function logPoint(p: Point) { console.log(`${p.x}, ${p.y}`); } // 打印 "12, 26" const point = { x: 12, y: 26 }; logPoint(point);
// point 变量从未声明为 Point 类型。 但是,在类型检查中,TypeScript 将 point 的结构与 Point的结构进行比较。它们
// 的结构相同,所以代码通过了。
// 结构匹配只需要匹配对象字段的子集。
3、typescript类型
内置类型
number、string、bigint、boolean、symbol、null、undefined、object
其他重要类型
| Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
unknown |
the top type. |
never |
the bottom type. |
| object literal | eg { property: Type } |
void |
for functions with no documented return value |
T[] |
mutable arrays, also written Array<T> |
[T, T] |
tuples, which are fixed-length but mutable |
(t: T) => U |
functions |
函数定义:
let fst: (a: any, b: any) => any = (a, b) => a; // (a: any, b: any) => any 是typescript的断言
//更准确的说法:
let fst: <T, U>(a: T, b: U) => T = (a, b) => a;
4、 interface 接口
//允许加入任意值
interface User { name: string; age: number; like?: string; [propname: string]: any; //这个的意思是,属性的名字是字符串类型,属性的值可以是任何类型 }
5、类型保护-类型断言 as
class MathTeacher {
public compute(): void {
console.log('数学老师会计算')
}
}
class EnglishTeacher {
public say(): void {
console.log('英语老师说 Hello!')
}
}
function teacherTeach(teacher: MathTeacher|EnglishTeacher): void {
(teacher as EnglishTeacher).say();
(teacher as MathTeacher).compute();
}
const lucy=new MathTeacher()
teacherTeach(lucy)
6、类型保护 - in 语法
class MathTeacher { public compute(): void { console.log('数学老师会计算') } } class EnglishTeacher { public say(): void { console.log('英语老师说 Hello!') } } function teacherTeach(teacher: MathTeacher|EnglishTeacher): void { if ("compute" in teacher) { teacher.compute() } else { teacher.say() } } const lucy=new MathTeacher('Lucy', '乡村小学') teacherTeach(lucy)
7、类型保护- instaceof 语法
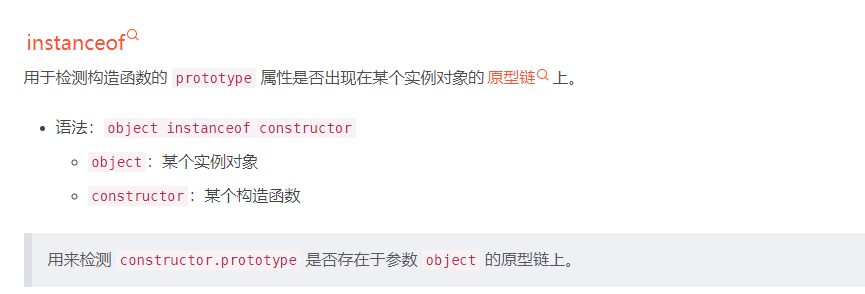
class MathTeacher { public compute(): void { console.log('数学老师会计算') } } class EnglishTeacher { public say(): void { console.log('英语老师说 Hello!') } } function teacherTeach(teacher: MathTeacher|EnglishTeacher): void { if (teacher instanceof MathTeacher) { teacher.compute() } else { teacher.say() } } const lucy=new MathTeacher('Lucy', '乡村小学') teacherTeach(lucy)
8、extends , implements 区别
1、在类的声明中,通过关键字extends来创建一个类的子类。
一个类通过关键字implements声明自己使用一个或者多个接口。
extends 是继承某个类, 继承之后可以使用父类的方法, 也可以重写父类的方法;
implements 是实现多个接口, 接口的方法一般为空的, 必须重写才能使用
2、extends是继承父类,子类除了不能继承父类的私有成员(方法和属性)和构造函数,其他的都可以继承。
TypeScript 一次只能继承一个类,不支持继承多个类,但 TypeScript 支持多重继承(A 继承 B,B 继承 C)。
但implements可以实现多个接口,用逗号分开就行了 比如 :
class A extends B implements C,D,E
接口实现的注意点:
a.实现一个接口就是要实现该接口的所有的方法(抽象类除外)。
b.接口中的方法都是抽象的。
c.多个无关的类可以实现同一个接口,一个类可以实现多个无关的接口。
//demo1
interface Alarm { name:string, alert(): void; } class Door { } class SecurityDoor extends Door implements Alarm { name!: string, alert() { console.log('SecurityDoor alert'); } }
//demo2 extends 用来 泛型约束
9、泛型
//泛型接口
interface GenericIdentityFn { <Type>(arg: Type): Type; } function identity<Type>(arg: Type): Type { return arg; } let myIdentity: GenericIdentityFn = identity;
》》》》》or《《《《《《《
10、 keyof (键类型操作符)
//keyof操作符接受一个对象类型,并产生其键的字符串或数字字面值联合。下面的类型P与类型P = "x" | "y"相同:
type Point = { x: number; y: number }; type P = keyof Point;
let p: P = 'x' // p值 只能为 'x' 或 'y'
//如果类型有字符串或数字索引签名,keyof将返回这些类型:
11、实用类 1> Awaited<Type> 该类型用于模拟async函数中的await操作,或者promise上的.then()方法——具体来说,就是它们递归展开promise的方式。 type A = Awaited<Promise<string>>; // type A = string type B = Awaited<Promise<Promise<number>>>; // type B = number type C = Awaited<boolean | Promise<number>>; // type C = number | boolean 2> Partial<Type> 构造一个将type的所有属性设置为可选的类型。此实用程序将返回表示给定类型的所有子集的类型。 interface Todo { title: string, desc: string } type A = Pratial<Todo> // 即 type A = { title?: string, desc?: string } 3> Required<Type> 构造由type set为required的所有属性组成的类型。Partial的反义词。 4> Readonly<Type> 构造一个将type的所有属性设置为只读的类型,这意味着不能重新分配构造类型的属性 interface Todo { title: string; } const todo: Readonly<Todo> = { title: "这是一个标题" } todo.title = "hello" // 此处会报错 5> Record<Keys, Type> 构造一个对象类型,其属性键为keys,属性值为type。此实用程序可用于将一个类型的属性映射到另一个类型。 interface CatInfo { age: number; breed: string } type CatName = 'miffy' | 'boris' | 'mrodred' const cats: Record<CatName, CatInfo> = { // cats 必须包含CatName中的所有属性 miffy: { age: 1, breed: '1' }, boris: { age: 2, breed: '2' }, mordred: { age: 3, breed: '3' } } 6> Pick<Type, keys> 通过从type中选取一组属性Keys(字符串字面值或字符串字面值的并集)来构造一个类型 interface Todo { title: string; desc: string; completed:boolean; } type TodoPreivew = Pick<Todo, 'title' | 'completed'> const todo: TodoPreview = { title:'1', completed: false } 7> Omit<Type, Keys> 通过从type中选取所有属性然后移除Keys(字符串字面值或字符串字面值的并集)来构造类型。Pick的反义词。 interface Todo { title: string; desc: string; completed: boolean; createAt: number; } type TodoPreview = Omit<Todo, 'desc'> const todo:TodoPreview = { title:'1', completed: false, createAt:111 } type TodoInfo = Omit<Todo, 'completed' | 'createAt'> const todoInfo: TodoInfo = { title:'1', desc:'222' } 8> Exclude<UnionType, ExcludedMembers> 通过从UnionType中排除可分配给ExcludedMembers的所有联合成员来构造类型 type T0 = Exclude<"a" | "b" | "c", "a">; // type T0 = "b" | "c" type T1 = Exclude<"a" | "b" | "c", "a" | "b">; // type T1 = "c" type T2 = Exclude<string | number | (() => void), Function>; // type T2 = string | number type Shape = { kind: "circle"; radius: number } | { kind: "square"; x: number } | { kind: "triangle"; x: number; y: number }; type T3 = Exclude<Shape, { kind: "circle" }> // type T3 = { kind: "square"; x: number; } | { kind: "triangle"; x: number; y: number; } 9> Extract<Type, Union> 通过从type中提取可分配给union的所有联合成员来构造类型(交集)。 type T0 = Extract<"a" | "b" | "c", "a" | "f">; // type T0 = "a" type T1 = Extract<string | number | (() => void), Function>; //type T1 = () => void type Shape = { kind: "circle"; radius: number } | { kind: "square"; x: number } | { kind: "triangle"; x: number; y: number }; type T2 = Extract<Shape, { kind: "circle" }> // type T2 = { kind: "circle"; radius: number; } 10> NonNullable<Type> 通过从type中排除null和undefined来构造一个类型 type T0 = NonNullable<string | number | undefined>; // type T0 = string | number type T1 = NonNullable<string[] | null | undefined>; // type T1 = string[]




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号