软件杯第二阶段
使用YOLO及Opencv实现目标检测
目录:
D:.
├─.idea
│ └─inspectionProfiles
├─darknet
│ ├─cfg
│ ├─data
│ │ └─labels
│ ├─examples
│ ├─include
│ ├─python
│ ├─scripts
│ └─src
├─images
├─output
├─videos
└─yolo-coco

# !/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2020/5/20 20:00 # @Author : CuiDog # @File : yolo.py #yolo.py该脚本用于图像处理 # import the necessary packages import numpy as np import argparse import time import cv2 import os #construct the argument parse and parse the arguments ap = argparse.ArgumentParser() ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True, help="path to input image") ap.add_argument("-y", "--yolo", required=True, help="base path to YOLO directory") ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5, help="minimum probability to filter weak detections") ap.add_argument("-t", "--threshold", type=float, default=0.3, help="threshold when applying non-maxima suppression") args = vars(ap.parse_args()) # class args: # image = 'test1.jpg'#自行替换文件 # config = 'yolov3.cfg' # weights = 'yolo-coco/yolov3.weights' # classes = 'yolov3.txt' #解析之后,args变量是一个包含命令行参数的键值对的字典。下面为每个标签设置随机颜色: # load the COCO class labels our YOLO model was trained on labelsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["yolo"], "coco.names"]) LABELS = open(labelsPath).read().strip().split("\n") # initialize a list of colors to represent each possible class label np.random.seed(42) COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(len(LABELS), 3),dtype="uint8") #上述加载所有类 LABELS,其类型是列表,保存的是类别名称,然后将随机颜色分配给每个标签 。下面设置YOLO权重和配置文件的路径,然后从磁盘加载YOLO文件: # derive the paths to the YOLO weights and model configuration weightsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["yolo"], "yolov3.weights"]) configPath = os.path.sep.join([args["yolo"], "yolov3.cfg"]) # load our YOLO object detector trained on COCO dataset (80 classes) print("[INFO] loading YOLO from disk...") net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(configPath, weightsPath) #从磁盘加载YOLO文件后,并利用OpenCV中的cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet函数从中读取网络文件及权重参数,此函数需要两个参数configPath 和 weightsPath,这里再次强调:OpenCV 的版本至少是3.4.2及以上才能运行此代码,因为它需要加载YOLO所需的更新的dnn模块。下面加载图像并处理: # load our input image and grab its spatial dimensions image = cv2.imread(args["image"]) (H, W) = image.shape[:2] # determine only the *output* layer names that we need from YOLO ln = net.getLayerNames() ln = [ln[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()] # construct a blob from the input image and then perform a forward # pass of the YOLO object detector, giving us our bounding boxes and # associated probabilities blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1 / 255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False) net.setInput(blob) start = time.time() layerOutputs = net.forward(ln) end = time.time() # show timing information on YOLO print("[INFO] YOLO took {:.6f} seconds".format(end - start)) #当blob准备好了后,我们就会通过YOLO网络进行前向传递; #显示YOLO的推理时间; #现在采取措施来过滤和可视化最终的结果。首先,让我们初步化一些处理过程中需要的列表: # initialize our lists of detected bounding boxes, confidences, and # class IDs, respectively boxes = [] confidences = [] classIDs = [] #下面用YOLO layerOutputs中的数据填充这些列表 : # loop over each of the layer outputs for output in layerOutputs: # loop over each of the detections for detection in output: # extract the class ID and confidence (i.e., probability) of # the current object detection scores = detection[5:] classID = np.argmax(scores) confidence = scores[classID] # filter out weak predictions by ensuring the detected # probability is greater than the minimum probability if confidence > args["confidence"]: # scale the bounding box coordinates back relative to the # size of the image, keeping in mind that YOLO actually # returns the center (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding # box followed by the boxes' width and height box = detection[0:4] * np.array([W, H, W, H]) (centerX, centerY, width, height) = box.astype("int") # use the center (x, y)-coordinates to derive the top and # and left corner of the bounding box x = int(centerX - (width / 2)) y = int(centerY - (height / 2)) # update our list of bounding box coordinates, confidences, # and class IDs boxes.append([x, y, int(width), int(height)]) confidences.append(float(confidence)) classIDs.append(classID) #过滤掉了不需要的检测结果后,我们将: #缩放边界框坐标,以便我们可以在原始图像上正确显示它们; #提取边界框的坐标和尺寸,YOLO返回边界框坐标形式: (centerX ,centerY ,width,height); #使用此信息导出边界框的左上角(x,y)坐标; #更新boxes, confidences ,classIDs列表。 #有了这些数据后,将应用“非最大值抑制”(non-maxima suppression,nms): # apply non-maxima suppression to suppress weak, overlapping bounding # boxes idxs = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, args["confidence"], args["threshold"]) #最后在图像上绘制检测框和类文本: # ensure at least one detection exists if len(idxs) > 0: # loop over the indexes we are keeping for i in idxs.flatten(): # extract the bounding box coordinates (x, y) = (boxes[i][0], boxes[i][1]) (w, h) = (boxes[i][2], boxes[i][3]) # draw a bounding box rectangle and label on the image color = [int(c) for c in COLORS[classIDs[i]]] cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2) text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(LABELS[classIDs[i]], confidences[i]) cv2.putText(image, text, (x, y - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2) # show the output image cv2.imshow("Image", image) cv2.waitKey(0)
截图:


# !/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2020/5/20 20:01 # @Author : CuiDog # @File : yolo_video.py #yolo_video.py该脚本用于视频处理 # import the necessary packages import numpy as np import argparse import imutils import time import cv2 import os # construct the argument parse and parse the arguments ap = argparse.ArgumentParser() ap.add_argument("-i", "--input", required=True, help="path to input video") ap.add_argument("-o", "--output", required=True, help="path to output video") ap.add_argument("-y", "--yolo", required=True, help="base path to YOLO directory") ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5, help="minimum probability to filter weak detections") ap.add_argument("-t", "--threshold", type=float, default=0.3, help="threshold when applyong non-maxima suppression") args = vars(ap.parse_args()) # load the COCO class labels our YOLO model was trained on labelsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["yolo"], "coco.names"]) LABELS = open(labelsPath).read().strip().split("\n") # initialize a list of colors to represent each possible class label np.random.seed(42) COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(len(LABELS), 3), dtype="uint8") # derive the paths to the YOLO weights and model configuration weightsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["yolo"], "yolov3.weights"]) configPath = os.path.sep.join([args["yolo"], "yolov3.cfg"]) # load our YOLO object detector trained on COCO dataset (80 classes) # and determine only the *output* layer names that we need from YOLO print("[INFO] loading YOLO from disk...") net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(configPath, weightsPath) ln = net.getLayerNames() ln = [ln[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()] # initialize the video stream, pointer to output video file, and # frame dimensions vs = cv2.VideoCapture(args["input"]) writer = None (W, H) = (None, None) # try to determine the total number of frames in the video file try: prop = cv2.cv.CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT if imutils.is_cv2() \ else cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT total = int(vs.get(prop)) print("[INFO] {} total frames in video".format(total)) # an error occurred while trying to determine the total # number of frames in the video file except: print("[INFO] could not determine # of frames in video") print("[INFO] no approx. completion time can be provided") total = -1 #逐帧处理 # loop over frames from the video file stream while True: # read the next frame from the file (grabbed, frame) = vs.read() # if the frame was not grabbed, then we have reached the end # of the stream if not grabbed: break # if the frame dimensions are empty, grab them if W is None or H is None: (H, W) = frame.shape[:2] ect Detection with OpenCVPython # construct a blob from the input frame and then perform a forward # pass of the YOLO object detector, giving us our bounding boxes # and associated probabilities blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False) net.setInput(blob) start = time.time() layerOutputs = net.forward(ln) end = time.time() # initialize our lists of detected bounding boxes, confidences, # and class IDs, respectively boxes = [] confidences = [] classIDs = [] # loop over each of the layer outputs for output in layerOutputs: # loop over each of the detections for detection in output: # extract the class ID and confidence (i.e., probability) # of the current object detection scores = detection[5:] classID = np.argmax(scores) confidence = scores[classID] # filter out weak predictions by ensuring the detected # probability is greater than the minimum probability if confidence > args["confidence"]: # scale the bounding box coordinates back relative to # the size of the image, keeping in mind that YOLO # actually returns the center (x, y)-coordinates of # the bounding box followed by the boxes' width and # height box = detection[0:4] * np.array([W, H, W, H]) (centerX, centerY, width, height) = box.astype("int") # use the center (x, y)-coordinates to derive the top # and and left corner of the bounding box x = int(centerX - (width / 2)) y = int(centerY - (height / 2)) # update our list of bounding box coordinates, # confidences, and class IDs boxes.append([x, y, int(width), int(height)]) confidences.append(float(confidence)) classIDs.append(classID) # apply non-maxima suppression to suppress weak, overlapping # bounding boxes idxs = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, args["confidence"], args["threshold"]) # ensure at least one detection exists if len(idxs) > 0: # loop over the indexes we are keeping for i in idxs.flatten(): # extract the bounding box coordinates (x, y) = (boxes[i][0], boxes[i][1]) (w, h) = (boxes[i][2], boxes[i][3]) # draw a bounding box rectangle and label on the frame color = [int(c) for c in COLORS[classIDs[i]]] cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2) text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(LABELS[classIDs[i]], confidences[i]) cv2.putText(frame, text, (x, y - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2) # check if the video writer is None if writer is None: # initialize our video writer fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG") writer = cv2.VideoWriter(args["output"], fourcc, 30, (frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0]), True) # some information on processing single frame if total > 0: elap = (end - start) print("[INFO] single frame took {:.4f} seconds".format(elap)) print("[INFO] estimated total time to finish: {:.4f}".format( elap * total)) # write the output frame to disk writer.write(frame) # release the file pointers print("[INFO] cleaning up...") writer.release() vs.release()
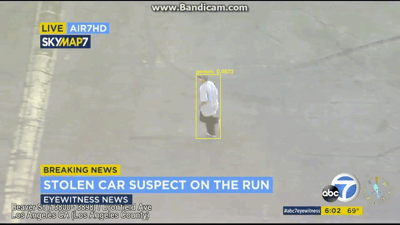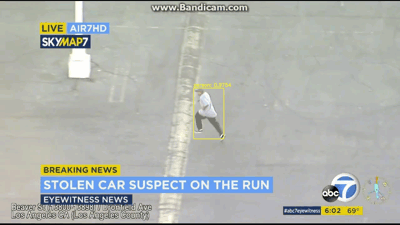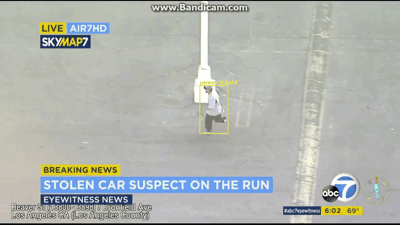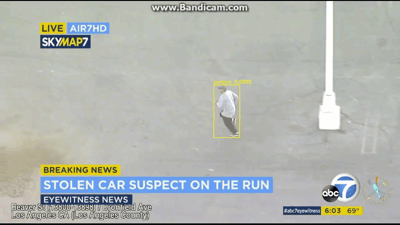
视频展示
最后就是说,把这个识别出来的视频再分割成几帧,然后需要哪帧看哪帧,界面展示出来,等于识别+动态跟踪,然后昨天视频直播,说要对识别数统计+同类物体分类,就是说人1人2人3,这个感觉有点难,网上也找不到相关代码,但计数功能可以实现,最后显示每帧的检测数多少。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号