▶ 直接的矩阵加法,没有优化
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <malloc.h> 4 #include <time.h> 5 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 6 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 7 8 #define WIDTH (1024*1+19) 9 #define HEIGHT (1024*1+17) 10 #define THREAD_SIZE 16 11 #define BLOCK_SIZE 256 12 #define DIMENSION 1 //使用指定维数的跳转 13 #define SEED 1 //(unsigned int)time(MULL) 14 15 void checkNULL(void *input) 16 { 17 if (input == NULL) 18 { 19 printf("\n\tfind a NULL!"); 20 exit(1); 21 } 22 return; 23 } 24 25 void checkCudaError(cudaError input) 26 { 27 if (input != cudaSuccess) 28 { 29 printf("\n\tfind a cudaError!"); 30 exit(1); 31 } 32 return; 33 } 34 35 int checkResult(float * in1, float * in2, const int length) 36 // 注意返回值为0(两向量相等)或者“值不等的元素下标加一”(防止0号元素就不相等),返回后若想使用该下标则需要减1 37 { 38 int i; 39 for (i = 0; i < length; i++) 40 { 41 if (in1[i] != in2[i]) 42 return i + 1; 43 } 44 return 0; 45 } 46 47 // 采用一维跳转 48 __global__ void add1(const float *a, const float *b, float *c) 49 { 50 int id = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; 51 52 while (id < WIDTH * HEIGHT) 53 { 54 c[id] = a[id] + b[id]; 55 id += gridDim.x*blockDim.x; 56 } 57 return; 58 } 59 60 // 采用二维跳转 61 __global__ void add2(const float *a, const float *b, float *c) 62 { 63 int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; 64 int idy = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; 65 int id = idx + idy *blockDim.y *gridDim.y; 66 67 while (id < WIDTH * HEIGHT) 68 { 69 c[id] = a[id] + b[id]; 70 id += gridDim.x * blockDim.x * gridDim.y * blockDim.y; 71 } 72 return; 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 int i; 78 float *h_a, *h_b, *cpu_out, *gpu_out; 79 float *d_a, *d_b, *d_c; 80 clock_t timeCPU; 81 cudaEvent_t start, stop; 82 float timeGPU; 83 cudaEventCreate(&start); 84 cudaEventCreate(&stop); 85 86 printf("\n\tStart! Matrix dimension:\t%d × %d", WIDTH, HEIGHT); 87 88 checkNULL(h_a = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 89 checkNULL(h_b = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 90 checkNULL(cpu_out = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 91 checkNULL(gpu_out = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 92 checkCudaError(cudaMalloc((float **)&d_a, sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 93 checkCudaError(cudaMalloc((float **)&d_b, sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 94 checkCudaError(cudaMalloc((float **)&d_c, sizeof(float)*WIDTH*HEIGHT)); 95 96 // 初始化 97 timeCPU = clock(); 98 srand(SEED); 99 for (i = 0; i < WIDTH*HEIGHT; i++) 100 { 101 h_a[i] = (float)rand() / RAND_MAX; 102 h_b[i] = (float)rand() / RAND_MAX; 103 } 104 printf("\n\tInitialized! Time:\t\t%8.3f ms\n", (float)(clock() - timeCPU)); 105 106 timeCPU = clock(); 107 for (i = 0; i < WIDTH*HEIGHT; i++) 108 cpu_out[i] = h_a[i] + h_b[i]; 109 printf("\n\tCPU time:\t%8.3f ms\n", (float)(clock() - timeCPU)); 110 111 cudaMemset(d_c, 0, sizeof(float) * WIDTH * HEIGHT); 112 cudaEventRecord(start, 0); 113 cudaMemcpy(d_a, h_a, sizeof(float) * WIDTH * HEIGHT, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 114 cudaMemcpy(d_b, h_b, sizeof(float) * WIDTH * HEIGHT, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 115 if(DIMENSION == 1) 116 add1 << < BLOCK_SIZE * BLOCK_SIZE, THREAD_SIZE * THREAD_SIZE >> > (d_a, d_b, d_c); 117 else 118 add2 << < dim3(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE), dim3(THREAD_SIZE, THREAD_SIZE) >> > (d_a, d_b, d_c); 119 cudaMemcpy(gpu_out, d_c, sizeof(float) * WIDTH * HEIGHT, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 120 cudaDeviceSynchronize(); 121 cudaEventRecord(stop,0); 122 cudaEventSynchronize(stop); 123 cudaEventElapsedTime(&timeGPU, start, stop); 124 if (i = checkResult(cpu_out, gpu_out, WIDTH * HEIGHT)) 125 printf("\n\tCompute error at i = %d\n\tcpu_out[i] = %10d, gpu_out[i] = %10d\n", i - 1, cpu_out[i - 1], gpu_out[i - 1]); 126 else 127 printf("\n\tGPU Compute correctly!\n"); 128 printf("\n\tGPU Time:\t%8.3f ms\n", timeGPU); 129 130 free(h_a); 131 free(h_b); 132 free(cpu_out); 133 free(gpu_out); 134 cudaFree(d_a); 135 cudaFree(d_b); 136 cudaFree(d_c); 137 getchar(); 138 return 0; 139 }
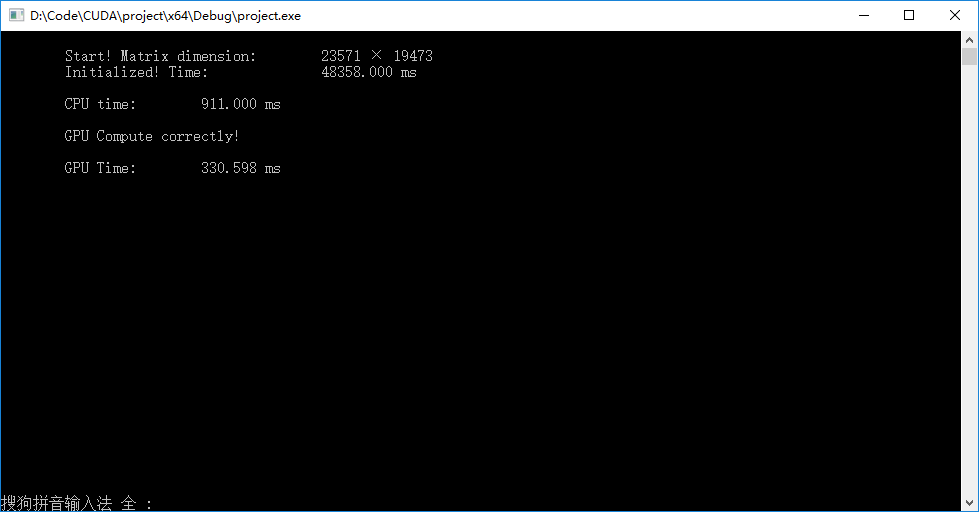
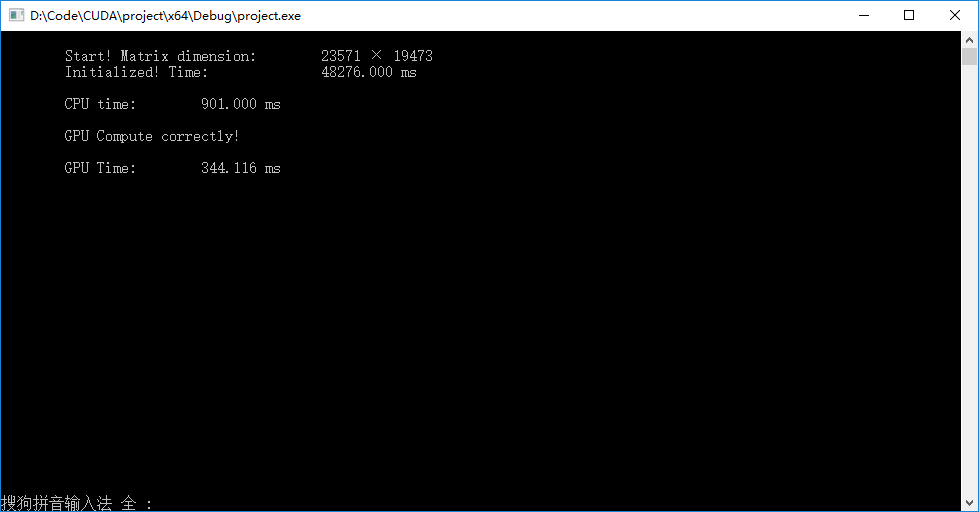
▶输出结果,对于超大型矩阵的加法计算,左下图为一维跳转,右下图为二维跳转。矩阵较大时初始化矩阵费时较多。超大矩阵的计算上GPU相对CPU产生了一定的优势,一维跳转比二维跳转稍快,因为省去了复杂的下标映射。
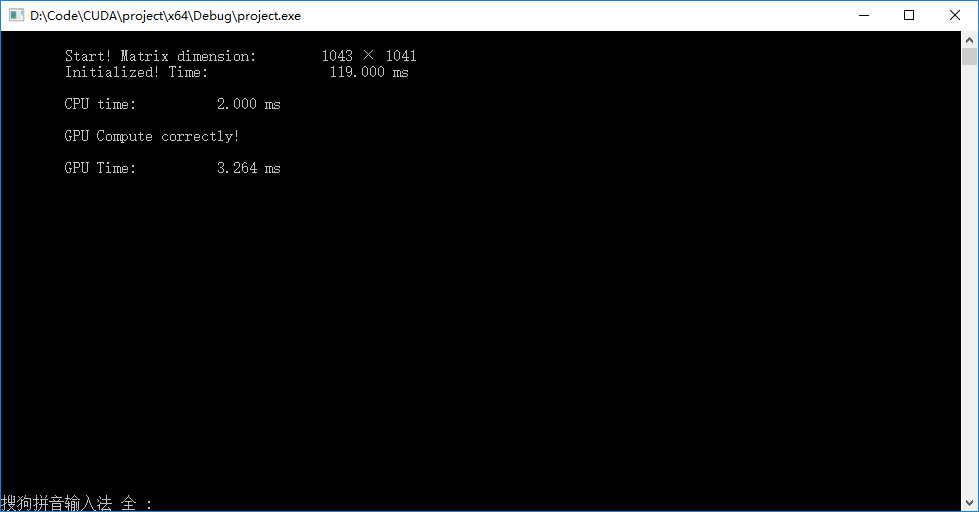
▶ 对于较小的矩阵,GPU没有发挥出优势, 因为内存拷贝等方面耗时明显。