AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
一、概述
AQS的框架
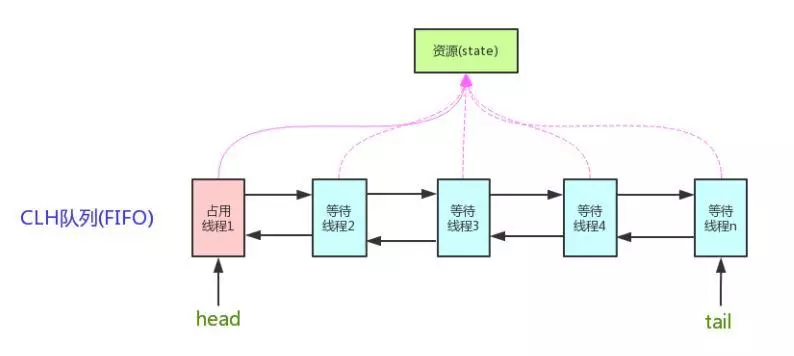
AQS维护了一个volatile的共享资源变量state和一个FIFO线程等待队列,双链表
资源的使用方式分为独占式和共享式2种
独占式:只有单个线程可以获取资源并执行,如ReentrantLock
共享式:多个线程可以获取资源并执行,如Semaphore、CountDownLatch
AQS将大部分的同步逻辑均已经实现好,继承的自定义同步器只需要实现state的获取(acquire)和释放(release)的逻辑代码就可以
核心方法:acquire()核心中的核心、addWaiter()、enq()、doReleaseShared()、doAcquireShared()、acquireQueued()
二、源码
1、父类
public abstract class AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3737899427754241961L;
protected AbstractOwnableSynchronizer() { }
//独占模式下的当前线程
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread thread) {
exclusiveOwnerThread = thread;
}
protected final Thread getExclusiveOwnerThread() {
return exclusiveOwnerThread;
}
}
2、内置Node
static final class Node {
//表示一个节点在共享模式下等待
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
//表示一个节点在排他模式下等待
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
//等待状态值,表示节点已取消调度,当timeout或中断后节点会变为此状态,之后状态不会再变化
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
//等待状态值,表示后继节点在等待当前节点唤醒,后继节点入队时会将前继节点更新为SIGNAL
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
//等待状态值,表示节点等待在Condition上,当其他线程调用了Condition的signal()后,CONDITION状态的节点将从等待队列转移到同步队列中,等待获取同步锁
static final int CONDITION = -2;
//等待状态值,表示在共享模式下,前继结点不仅会唤醒其后继结点,同时也可能会唤醒后继的后继结点
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
//状态字段,只可能是SIGNAL、CANCELLED、CONDITION、PROPAGATE、0(新节点入队时的默认状态)
volatile int waitStatus;
//上一个节点
volatile Node prev;
//下一个节点
volatile Node next;
//加入此节点的线程
volatile Thread thread;
//下一个等待的节点
Node nextWaiter;
//如果节点在共享模式下等待就返回true
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
//返回上一个节点
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() {
}
//被addWaiter使用
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) {
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
//被Condition使用
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) {
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
3、属性
//队列的节点头
private transient volatile Node head;
//队列的节点尾
private transient volatile Node tail;
//同步状态
private volatile int state;
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
3、方法
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
原子更新state的状态,类似于获得许可,如果成功就可以占有锁,如果失败说明锁已经被其他对象占用
unsafe.compareAndSwapInt是用CAS原理实现的,底层native的c代码是一个for循环,通过反射根据字段偏移去修改对象,之后会说Unsafe
static final long spinForTimeoutThreshold = 1000L;
作为自旋等待时间判断的忽略值,1000纳秒,当计算得出判断自旋等待还有不到1000纳秒就可以开始自旋的时候,直接进入自旋,因为1000纳秒已经非常小,非常短的时间等待无法做到十分精确,如果这时再进入等待反而会让自旋超时表现的不那么准确
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
将节点插入队列的末尾,如果是空队列就先创建队头然后再次循环,主要给后面的addWaiter使用
这里当前节点是通过node.prev=t先接到前继节点的,如果compareAndSetTail争用成功,就通过t.next=node让前继节点接到当前节点,如果不成功说明并发竞争失败,就进入下一次循环接到新的tail节点后面
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
用当前线程构建一个节点,节点类型是独占或者共享的,尝试加入队尾,如果非空队列添加失败说明有并发,再进入enq自旋修改
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
将节点设为队头,清空属性方便垃圾回收
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
唤醒后继节点的线程,将当前节点的状态置0,如果后继节点为空或者已取消,就从tail队尾开始遍历,找离当前节点最近的可唤醒节点
最后使用LockSupport唤醒线程,后面会说LockSupport
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue;
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue;
}
if (h == head)
break;
}
}
共享模式的核心唤醒函数,用来唤醒下个线程或者设置传播状态
主要给releaseShared使用,在最开始是直接使用unparkSuccessor的,存在问题,所以用这个doReleaseShared方法包了一层,也增加了PROPAGATE状态,以后细说
如果头结点的状态成功置0,就执行unparkSuccessor唤醒后继线程,如果头结点状态已经为0,就将头结点状态置为PROPAGATE,保证后继节点仍然可以被唤醒
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head;
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
这个类的作用是在共享锁获取成功后设置头节点,然后根据条件唤醒后继线程
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
Node predNext = pred.next;
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node;
}
}
取消某个节点获取锁,把当前节点状态置为CANCELLED,然后将节点移出队列,把后继和前继连接起来
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
根据前驱节点的状态判断是否要让当前线程进入waiting状态
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
让当前线程中断
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
让线程进入等待状态
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
在队列中等待获取锁,核心方法
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
和acquireQueued基本一样,增加了对中断异常的抛出
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
在doAcquireInterruptibly的基础上增加超时等待的功能
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
共享锁版在队列中等待获取锁
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
增加了异常抛出
private boolean doAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
再增加超时等待
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
分别是尝试获取独占锁、尝试释放独占锁、尝试获取共享锁、尝试释放共享锁、当前是否获得独占锁(只有用到condition才需要实现)
AQS实现了框架,并通过模板方法开放了以上方法,具体资源的获取释放方式需要自定义的同步器来重写完成,没有使用abstract是因为独占锁只需要实现tryAcquire和tryRelease,不用实现其它的,共享锁同理
如何实现之后看具体的同步器
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
独占模式下获取锁的顶层入口,线程如果取到资源就直接返回,如果没有取到就进入等待队列,直到取到资源,这就是lock()的语义
先通过tryAcquire去尝试获取资源,如果成功就返回,如果失败就通过addWaiter将独占状态的自身节点加入队列尾部,然后acquireQueued进入等待队列,如果等待过程中中断了,会执行selfInterrupt将线程中断
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
相应中断和相应中断+超时的acquire版本
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
释放资源的顶层入口,实现unlock的效果,当资源释放后会唤醒后继线程
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0 || doAcquireSharedNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
共享锁版本的一套
//是否有线程在等待锁
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return head != tail;
}
//是否有节点
public final boolean hasContended() {
return head != null;
}
//返回队列里第一个没有取到锁的线程
public final Thread getFirstQueuedThread() {
return (head == tail) ? null : fullGetFirstQueuedThread();
}
private Thread fullGetFirstQueuedThread() {
Node h, s;
Thread st;
if (((h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null &&
s.prev == head && (st = s.thread) != null) ||
((h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null &&
s.prev == head && (st = s.thread) != null))
return st;
Node t = tail;
Thread firstThread = null;
while (t != null && t != head) {
Thread tt = t.thread;
if (tt != null)
firstThread = tt;
t = t.prev;
}
return firstThread;
}
//判断线程是否在队列里
public final boolean isQueued(Thread thread) {
if (thread == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev)
if (p.thread == thread)
return true;
return false;
}
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {
Node h, s;
return (h = head) != null &&
(s = h.next) != null &&
!s.isShared() &&
s.thread != null;
}
//判断当前线程是否在队列的队首
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t && ((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
//返回等待这个锁的线程数量
public final int getQueueLength() {
int n = 0;
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread != null)
++n;
}
return n;
}
//返回队列里的线程
public final Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
return list;
}
//返回队列里独占模式的线程
public final Collection<Thread> getExclusiveQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (!p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
//返回队列里共享模式的线程
public final Collection<Thread> getSharedQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
public String toString() {
int s = getState();
String q = hasQueuedThreads() ? "non" : "";
return super.toString() +
"[State = " + s + ", " + q + "empty queue]";
}
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;
if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queue
return true;
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {
Node t = tail;
for (;;) {
if (t == node)
return true;
if (t == null)
return false;
t = t.prev;
}
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
final boolean transferAfterCancelledWait(Node node) {
if (compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0)) {
enq(node);
return true;
}
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node))
Thread.yield();
return false;
}
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
int savedState = getState();
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
public final boolean owns(ConditionObject condition) {
return condition.isOwnedBy(this);
}
public final boolean hasWaiters(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.hasWaiters();
}
public final int getWaitQueueLength(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitQueueLength();
}
public final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitingThreads();
}
AQS提供的一些辅助函数
5、内置ConditionObject
6、unsafe
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long headOffset;
private static final long tailOffset;
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail"));
waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus"));
nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update);
}
private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);
}
private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node, int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset, expect, update);
}
private static final boolean compareAndSetNext(Node node, Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(node, nextOffset, expect, update);
}
通过底层方法实现了对state、head、tail、waitStatus、next的原子操作方法,如果返回true则操作成功,如果返回false表示存在争用,操作失败

