JAVA Socket通信 打造属于自己的网盘
近一个月没敲JAVA代码了,最近老师布置了一个写JAVA网盘的作业,总共花了十几个小时,总算写完了,debug真的累,感觉自己还是菜了,没有那种有一个想法就能马上用代码实现的能力。。。。不扯了,下面开始正题。
功能介绍
- 支持1个客户端,1个服务器端。服务器提供网盘空间。
- 首先运行服务器。服务器运行之后,客户端运行网盘客户端。
- 运行客户端。用户能够输入昵称。确定,则连接到服务器。连接成功,即可出现客户端面。
- 可以在网盘中新建文件夹,删除空文件夹,重命名文件夹;可以将自己电脑上某个文件上传到网盘中的某个文件夹下(支持单文件),可以删除单个文件、重命名文件、下载单个文件。
- 可实现大文件传输
整体思路
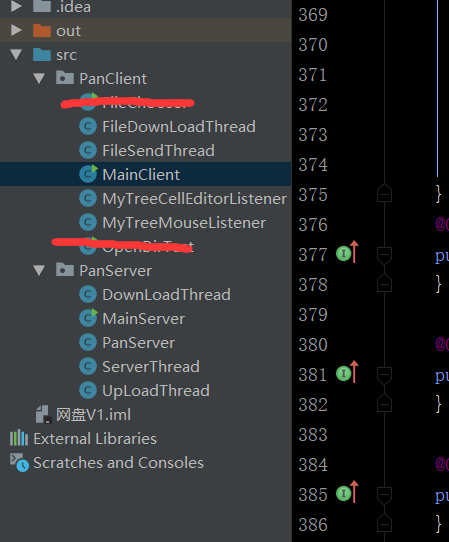
大概分了这么几个类
服务器端
MainServer:
原来是想做个服务器界面的,但还是有点懒,就算了,所以这个类现在就用来创建Panserver对象
public class MainServer { private PanServer panServer;//服务器对象 public static void main(String[] args){ MainServer ms =new MainServer(); ms.actionServer(); } // 开启服务器 public void actionServer() { // 1.要得到服务器状态 if (null == panServer) { panServer = new PanServer(8888); panServer.start(); } else if (panServer.isRunning()) {// 己经在运行 panServer.stopPanServer(); panServer = null; } } }
Panserver:
用于建立服务器SocketServer的类
package PanServer; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * 〈服务器socketserver创建〉 * * @author ITryagain * @create 2018/12/5 * @since 1.0.0 */ public class PanServer extends Thread { private ServerSocket ss;//服务器对象 private int port;//端口 private boolean running=false;//服务器是否在运行中 PanServer(int port){ this.port=port; } public void run(){ setupServer(); } //在指定端口上启动服务器 private void setupServer(){ try{ ss=new ServerSocket(this.port); running=true; System.out.println("服务器创建成功:"+this.port); while(running){ Socket client = ss.accept(); System.out.println("进入了一个客户机对象:"+client.getRemoteSocketAddress()); ServerThread ct = new ServerThread(client); ct.start(); } }catch(IOException e){ // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /* * 查询服务器是否在运行 * * @return: true为运行中 */ public boolean isRunning() { return this.running; } // 关闭服务器 public void stopPanServer() { this.running = false; try { ss.close(); } catch (Exception e) {} } }
else
剩下的三个类就是服务器实现的关键了
其中最重要的是ServerThread类,该类用于实现与客户端的通信,通过接收客户端的指令进行不同的操作,其中函数如下图所示
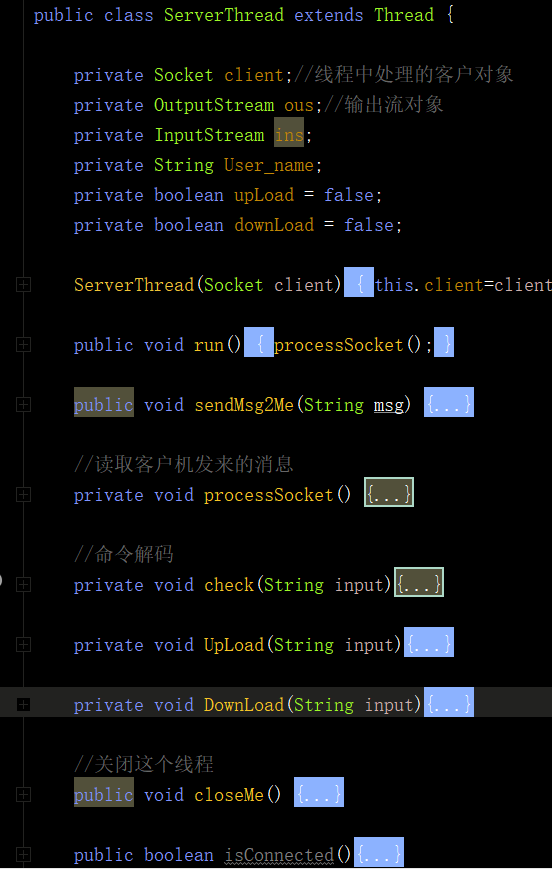
首先,我们在建立连接时,需要输入用户名,并创建一个文件夹,文件名为用户名,因此,我们需要一个接收一开始发送的用户名信息,写在processSocket内
Socket sc=this.client; ins=sc.getInputStream(); ous=sc.getOutputStream(); //将输入流ins封装为可以读取一行字符串也就是以\r\n结尾的字符串 BufferedReader brd=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ins)); sendMsg2Me("欢迎您使用!请输入你的用户名:"); User_name=brd.readLine(); System.out.println(User_name);
这样我们就读取了用户名,读取用户名后,马上就能创建文件夹
File directory = new File("D:\\"+User_name); if(!directory.exists()){ directory.mkdir(); }
然后就进入while循环,不断从客户端读取用户操作信息
String input=brd.readLine();//一行一行的读取客户机发来的消息 while(true) { System.out.println("服务器收到的是"+input); if((!this.upLoad)&&(!this.downLoad)){ check(input); } if(this.upLoad){//上传中 UpLoad(input); } if(this.downLoad){//下载中 DownLoad(input); } input=brd.readLine();//读取下一条 System.out.println(input);
}
这里我用了三个函数来分别处理三种状态,其中check函数用来解码,这里我给出其中新建文件夹的写法示例,删除和重命名与之类似
private void check(String input){ if(input.charAt(0)=='~'){ String tmp=input.substring(input.indexOf("~")+1,input.indexOf("#")); System.out.println(tmp); if(tmp.equals("downLoad")){ this.downLoad=true; }else if(tmp.equals("upLoad")){ this.upLoad=true; }else if(tmp.equals("new")){ //新建文件夹 System.out.println(input.substring(input.indexOf("#")+1)); File directory = new File(input.substring(input.indexOf("#")+1)); if(!directory.exists()){ directory.mkdir(); } }else if(tmp.equals("delete")){ //删除文件夹 }else if(tmp.equals("change")){ //重命名文件夹 } } }
然后剩下的就是UpLoad和DownLoad函数了,这两个函数分别对应了上传和下载功能,我一开始把这两个功能都放在一开始建立的SockerServer里面了,结果发现文件上传了之后关闭流时把我线程也关了orz。。。还是太菜了,这种错都能写出来,百度了一番,看到好多人都是再开几个端口解决的。。。一开始就想到这方法了,但不想这么干,总觉的应该还有更好的办法,可最终还是决定用这种方法了(真香)。这里就给出其中一个函数的写法吧
private void UpLoad(String input){ System.out.println("上传文件"); UpLoadThread upLoadThread = new UpLoadThread(8889,input); upLoadThread.start(); this.upLoad=false; }
既然给了UoLoad的写法,就顺便讲讲upLoadThread吧
/** * 〈服务器接受文件线程〉 * * @author ITryagain * @create 2018/12/8 * @since 1.0.0 */ public class UpLoadThread extends Thread{ private ServerSocket UpLoadServer; private int port; private String input; private FileOutputStream fos; UpLoadThread(int port,String input){ this.port=port; this.input=input; } public void run(){ } private static DecimalFormat df = null; static { // 设置数字格式,保留一位有效小数 df = new DecimalFormat("#0.0"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); df.setMinimumFractionDigits(1); df.setMaximumFractionDigits(1); } /** * 格式化文件大小 * @param length * @return */ private String getFormatFileSize(long length) { } }
大致函数就是这样的,其中run方法里面就是文件接收了,(如果发现缺了什么自己补一补,就一个变量的申明没加上去)
try{ UpLoadServer = new ServerSocket(port); socket = UpLoadServer.accept(); dis = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); //文件名和长度 String fileName = input.substring(input.indexOf("#")+1); long fileLength = dis.readLong(); File file = new File(fileName); fos = new FileOutputStream(file); //开始接收文件 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int length=0; while((length = dis.read(bytes, 0, bytes.length)) != -1) { fos.write(bytes, 0, length); fos.flush(); } System.out.println("======== 文件接收成功 [File Name:" + fileName + "] [Size:" + getFormatFileSize(fileLength) + "] ========"); try { if(fos!=null) fos.close(); if(dis != null) dis.close(); if(socket !=null) socket.close(); if(UpLoadServer!=null) UpLoadServer.close(); } catch (Exception e) {} }catch(IOException e){ }
然后就是 getFormatFileSize() 函数了,这个函数是用来干嘛的呢?就是用来转化一下文件大小单位的,不然到时候一个几 GB 的文件显示的就是 *****
******B了,那么长一串,看着也不舒服。
private String getFormatFileSize(long length) { double size = ((double) length) / (1 << 30); if(size >= 1) { return df.format(size) + "GB"; } size = ((double) length) / (1 << 20); if(size >= 1) { return df.format(size) + "MB"; } size = ((double) length) / (1 << 10); if(size >= 1) { return df.format(size) + "KB"; } return length + "B"; }
服务器端剩下没讲的代码其实都差不多,就自己去实现吧
客户端
客户端就比较麻烦了,尤其是这个界面,花了我老半天时间
MainClient:
这个类就是客户端用于创建界面以及管理线程的类了,界面我是用JTree来实现的,看下函数先吧
public class MainClient extends JFrame implements ActionListener, TreeModelListener { private JTree tree; private int ServerIP = 8888; private JLabel statusLabel; private DefaultTreeModel treeModel; private String oldNodeName; private OutputStream ous; private Socket client; private String name; private String stress = "D:\\"; private String downLoadStress="D:\\下载\\"; public static void main(String[] args){ MainClient mc=new MainClient(); mc.showLoginUI(); } public void showLoginUI(){ } // 登陆事件处理 private void loginAction() { } //显示操作窗口 private void showMainUI() { } @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { if (e.getActionCommand().equals("新建文件夹")) { } if (e.getActionCommand().equals("删除文件夹")) { } if (e.getActionCommand().equals("上传文件")) { } if(e.getActionCommand().equals("下载文件")){ } } @Override /* * 修改文件名字 */ public void treeNodesChanged(TreeModelEvent e) { } //选择上传文件 public void chooseSendFile(){ } public void sendFile(File file,String path) throws IOException{ } private String getSendPath(TreePath parentPath){ } //选择下载文件 public void chooseDownLoadFile() { } //下载文件 public void downloadFile(String path) throws IOException{ } private String getDownLoadPath(TreePath parentPath){ } private void newFile(String path){ } private void deleteFile(String path){ } private void ChangeFileName(String NewName,String path){ } @Override public void treeNodesInserted(TreeModelEvent e) { } @Override public void treeNodesRemoved(TreeModelEvent e) { } @Override public void treeStructureChanged(TreeModelEvent e) { } }
先来看看界面吧,打开后你可能只能看到三个按钮,拉动一下框框就能看到第四个了,大小设置有点问题。
private void showMainUI() { JFrame frame=new JFrame("网盘"); Container contentPane = frame.getContentPane(); DefaultMutableTreeNode root = new DefaultMutableTreeNode(name); tree = new JTree(root); tree.addMouseListener(new MyTreeMouseListener(oldNodeName)); treeModel = (DefaultTreeModel)tree.getModel(); treeModel.addTreeModelListener(this); tree.setEditable(true); tree.getCellEditor().addCellEditorListener(new MyTreeCellEditorListener(tree)); JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(); scrollPane.setViewportView(tree); JPanel toolBarPanel = new JPanel(); JButton b = new JButton("新建文件夹"); b.addActionListener(this); toolBarPanel.add(b); b = new JButton("删除文件夹"); b.addActionListener(this); toolBarPanel.add(b); b = new JButton("上传文件"); b.addActionListener(this); toolBarPanel.add(b); b = new JButton("下载文件"); b.addActionListener(this); toolBarPanel.add(b); statusLabel = new JLabel("Action"); contentPane.add(toolBarPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH); contentPane.add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER); contentPane.add(statusLabel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); frame.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); frame.requestFocus(); frame.setSize(400, 400); frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); tree.setRootVisible(false); }
里面两监听类的实现(提醒一下,可能到后面你做重命名文件夹会遇到坑,跟其中一个监听类有关,提醒一下oldNodeName是用来记录修改前的文件夹名称的,想办法获取这个变量的值就能很快实现文件夹重命名的功能),还有文件路径的实现也自己好好想想
至于界面的其它一些功能实现可以去看这篇博客(包括两个监听类的实现以及 actionPerformed() 和 treeNodesChanged() 等函数的实现)https://www.cnblogs.com/freshier/p/4614811.html
然后这里给出NewFile()函数写法
private void newFile(String path){ String fileName = "~new#"+path+"\r\n"; System.out.println(fileName); try { this.ous.write(fileName.getBytes()); this.ous.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
至于 delete 和 change 的写法与此类似
前面我给出了服务器上传文件的类,这里就给出客户端上传文件的类的写法
先看下 sendFile() 函数
public void sendFile(File file,String path) throws IOException{ String fileName = "~upLoad#"+path+"\\"+file.getName()+"\r\n"; System.out.println(fileName); this.ous.write(fileName.getBytes()); this.ous.flush(); FileSendThread send_socket = new FileSendThread(8889,file,path); send_socket.start(); }
FileSendThread:
客户端上传文件的类
public class FileSendThread extends Thread { private Socket fileSendSocket; private int port; private String path; private File file; private OutputStream ous; private FileInputStream fis; private DataOutputStream dos; FileSendThread(int port, File file,String path){ this.port=port; this.file=file; this.path=path; } public void run(){ try{ fileSendSocket = new Socket("localhost",this.port); // 发送: 文件名称 文件长度 this.ous = fileSendSocket.getOutputStream(); dos = new DataOutputStream(this.ous); dos.writeLong(file.length()); //开始传输文件 System.out.println("======开始传输文件======="); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int length; long progress = 0; fis = new FileInputStream(file); while((length=fis.read(bytes,0,bytes.length))!=-1){ dos.write(bytes,0,length); dos.flush(); progress = progress + length; System.out.print("| " + (100*progress/file.length()) + "% |"); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("======== 文件传输成功 ========"); }catch(IOException e1){ }finally { try { if (fis != null) fis.close(); if (dos != null) dos.close(); }catch(IOException e){ // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
至于下载功能,与上传类似,把服务器和客户端上传类中的部分代码换一换就好了。
到了这里你们是否还记得我们在通信连接建立时需要传输用户名?实现方式如下
登陆框的实现,我这里算是偷懒了,直接利用了 JOptionPane
public void showLoginUI(){ name = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入用户名"); System.out.println(name); loginAction(); }
// 登陆事件处理 private void loginAction() { try { this.client = new Socket("localhost",ServerIP); if(loginServer()){ showMainUI(); }else{ JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"登陆失败","确定",JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE); } } catch (IOException e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"连接失败","确定",JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE); } }
private boolean loginServer(){ try{ this.ous = this.client.getOutputStream(); String _name=name+"\r\n"; this.ous.write(_name.getBytes()); this.ous.flush(); return true; }catch(IOException e){ return false; } }
顺便介绍几个方法
文件夹重命名
File directory = new File("D:\a.txt"); directory.renameTo(new File("D:\b.txt"));
这里实现的是将a.txt重命名为b.txt,对文件夹也有效
文件夹删除
boolean success = (new File("D:\a.txt").delete(); if(success){ System.out.println("删除成功"); }else{ ystem.out.println("删除失败"); }
还有String的几个操作
1、我的编码
- 上传文件 ~upLoad#文件路径+文件
- 下载文件 ~downLoad#文件路径+文件
- 文件重命名 ~change#文件路径+原文件名@文件路径+新文件名
- 新建文件夹 ~new#文件路径+文件名
- 删除文件夹 ~delete#文件路径+文件名
2.String中的 subString() 和 indexOf() 函数
总结
到这里,我的网盘介绍算是完了,因为这是作业并且还没检查的缘故,就没有把所有代码放出来了,就介绍了下思路,顺便给将要写网盘或者正在写网盘的你们一点思路,相信有了这些思路,你们能很快地写完网盘,或者有了写的思路。太久没写代码果然不行,搞了一个多月的强化学习、机器学习和数据挖掘,差点就不会写代码了(面向搜索引擎编程感觉还行。。。百度有时很强大,可能只是你没学会正确的搜索的姿势)
检查完了,开源第一版代码https://github.com/leo6033/JAVA-Pan


