[CU]uvm lab4-router
注1:uvm lab1 - __见贤思齐 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
注2:uvm lab2 - __见贤思齐 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
注3:uvm lab3 - __见贤思齐 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
注4:IC仿真makefile示例4 - __见贤思齐 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
注5:结合synopsys uvm lab guide阅读;
注6:uvm1.1 lab链接第三方资源 – 路科验证 (rockeric.com).
注7:synopsys uvm1.2 lab guide - IC验证资料 - EETOP 创芯网论坛 (原名:电子顶级开发网) -
注8:uvm1.2 lab链接UVM1.2 Lab验证资料(入门必备) - IC验证资料 - EETOP 创芯网论坛 (原名:电子顶级开发网) -
学习目标
(1) 添加virtual interface的使用;
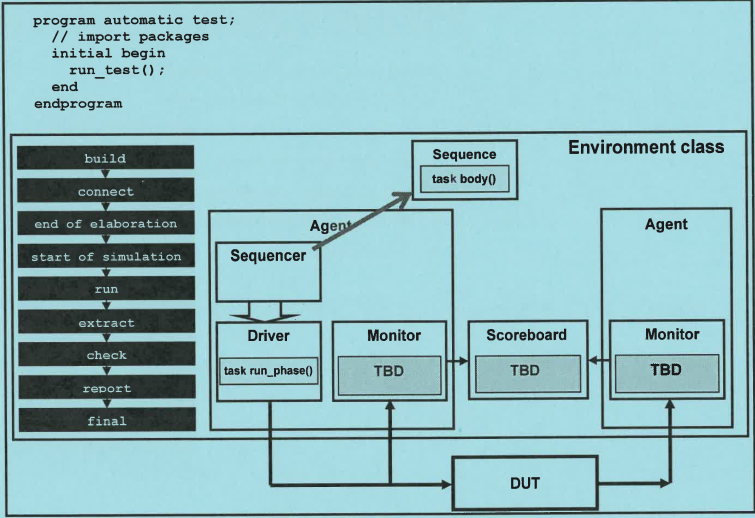
1.test.sv
1 program automatic test; 2 import uvm_pkg::*; 3 4 `include "test_collection.sv" 5 6 initial begin 7 $timeformat(-9, 1, "ns", 10); 8 run_test(); 9 end 10 11 endprogram
2.router_test_top.sv
1 module router_test_top; 2 parameter simulation_cycle = 100 ; 3 bit SystemClock; 4 5 router_io sigs(SystemClock); 6 host_io host(SystemClock); 7 router dut(sigs, host); 8 9 initial begin 10 forever #(simulation_cycle/2) SystemClock = ~SystemClock ; 11 end 12 endmodule
2.1 router_io.sv (interface的使用)
1 `ifndef ROUTER_IO__SV 2 `define ROUTER_IO__SV 3 4 interface router_io(input bit clk); 5 6 logic reset_n ; 7 logic [15:0] frame_n ; 8 logic [15:0] valid_n ; 9 logic [15:0] din ; 10 logic [15:0] dout ; 11 logic [15:0] busy_n ; 12 logic [15:0] valido_n ; 13 logic [15:0] frameo_n ; 14 15 clocking drvClk @(posedge clk); 16 output reset_n; 17 output frame_n; 18 output valid_n; 19 output din; 20 input busy_n; 21 endclocking: drvClk 22 23 clocking iMonClk @(posedge clk); 24 input frame_n; 25 input valid_n; 26 input din; 27 input busy_n; 28 endclocking: iMonClk 29 30 clocking oMonClk @(posedge clk); 31 input dout; 32 input valido_n; 33 input frameo_n; 34 endclocking: oMonClk 35 36 modport driver(clocking drvClk, output reset_n); 37 modport imon(clocking iMonClk); 38 modport omon(clocking oMonClk); 39 modport dut(input clk, reset_n, frame_n, valid_n, din, output dout, busy_n, valido_n, frameo_n); 40 41 endinterface: router_io 42 43 `endif
2.2 host_io.sv (interface的使用)
1 `ifndef HOST_IO__SV 2 `define HOST_IO__SV 3 interface host_io(input logic clk); 4 logic wr_n; 5 logic [15:0] address; 6 wire [15:0] data; 7 8 clocking cb @(posedge clk); 9 inout data; 10 output address; 11 output wr_n; 12 endclocking 13 14 clocking mon @(posedge clk); 15 input data; 16 input address; 17 input wr_n; 18 endclocking 19 20 modport dut(input clk, input wr_n, address, inout data); 21 endinterface: host_io 22 `endif
3.test_collection.sv(派生于uvm_test)
1 `ifndef TEST_COLLECTION__SV 2 `define TEST_COLLECTION__SV 3 4 `include "router_env.sv" 5 6 class test_base extends uvm_test; 7 `uvm_component_utils(test_base) 8 9 router_env env; 10 //virtual router_io router_vif,reset_vif; 11 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 12 super.new(name, parent); 13 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 14 endfunction 15 16 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 17 super.build_phase(phase); 18 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 19 env = router_env::type_id::create("env", this); 20 21 // Lab 4 - Task 5, Step 3 22 // 23 // Configure the router environment agents' virtual interface by using SystemVerilog's 24 // cross module reference (XMR) to access the interface 25 // 26 // At the test level, configuration of components dedicated to a DUT interface should be done via 27 // the agent connected to that interface. The test developer should treat the agent as the 28 // Bus Functional Model (BFM) for the interface without needing to know anything about the 29 // sub-components of the agent. 30 // 31 // uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "env.i_agent", "router_io", router_test_top.sigs); 32 // uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "env.r_agent", "router_io", router_test_top.sigs); 33 // 34 // ToDo 35 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "env.i_agent", "router_io", router_test_top.sigs); 36 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "env.r_agent", "router_io", router_test_top.sigs); 37 //注1:可以在test_base中声明virtual router_io router_vif与virtual router_io reset_vif;在test.sv中进行config_db::set(),在test_base中进行config_db::get(),然后config_db::set()给test_base的子组件; 38 //uvm_resource_db#(virtual router_io)::read_by_type("router_vif",router_vif,this); 39 //uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this,"env.i_agt","vif",router_vif); 40 //reset_vif与router_vif仿照line38-39做同样处理; 41 endfunction 42 43 virtual function void final_phase(uvm_phase phase); 44 super.final_phase(phase); 45 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 46 uvm_top.print_topology(); 47 48 uvm_factory::get().print(); 49 endfunction 50 endclass 51 52 `include "packet_da_3.sv" 53 54 class test_da_3_inst extends test_base; 55 `uvm_component_utils(test_da_3_inst) 56 57 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 58 super.new(name, parent); 59 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 60 endfunction 61 62 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 63 super.build_phase(phase); 64 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 65 set_inst_override_by_type("env.i_agent*.seqr.*", packet::get_type(), packet_da_3::get_type()); 66 endfunction 67 endclass 68 69 class test_da_3_type extends test_base; 70 `uvm_component_utils(test_da_3_type) 71 72 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 73 super.new(name, parent); 74 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 75 endfunction 76 77 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 78 super.build_phase(phase); 79 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 80 set_type_override_by_type(packet::get_type(), packet_da_3::get_type()); 81 endfunction 82 endclass 83 84 class test_da_3_seq extends test_base; 85 `uvm_component_utils(test_da_3_seq) 86 87 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 88 super.new(name, parent); 89 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 90 endfunction 91 92 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 93 super.build_phase(phase); 94 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 95 uvm_config_db#(bit[15:0])::set(this, "env.i_agent*.seqr", "da_enable", 16'h0008); 96 uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this, "env.i_agent*.seqr", "item_count", 20); 97 endfunction 98 endclass 99 100 `endif
4.router_env.sv (派生于uvm_env)
1 `ifndef ROUTER_ENV__SV 2 `define ROUTER_ENV__SV 3 4 `include "input_agent.sv" 5 6 // Lab 3 - Task 7, Step 2 7 // 8 // To save lab time, the reset agent with its sequencer, driver and monitor has been done 9 // for you. You will need to add an instance of it in the environment. 10 // 11 // Include the reset_agent.sv file 12 // 13 // ToDo 14 `include "reset_agent.sv" 15 16 17 class router_env extends uvm_env; 18 input_agent i_agent; 19 20 // Lab 3 - Task 7, Step 3 21 // 22 // Create an instance of reset_agent, call it r_agent 23 // 24 // ToDo 25 reset_agent r_agent; 26 27 28 `uvm_component_utils(router_env) 29 30 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 31 super.new(name, parent); 32 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 33 endfunction 34 35 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 36 super.build_phase(phase); 37 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 38 39 i_agent = input_agent::type_id::create("i_agent", this); 40 uvm_config_db #(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, "i_agent.seqr.main_phase", "default_sequence", packet_sequence::get_type()); 41 //uvm_config_db #(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, "i_agent.seqr.reset_phase", "default_sequence", router_input_port_reset_sequence::get_type()); 42 // Lab 3 - Task 7, Step 4 43 // 44 // Construct the r_agent object with the proxy create() method. 45 // 46 // ToDo 47 r_agent = reset_agent::type_id::create("r_agent", this); 48 49 50 // Lab 3 - Task 7, Step 5 51 // 52 // Configure r_agent's seqr to execute reset_sequence at reset_phase: 53 // uvm_config_db #(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, "r_agent.seqr.reset_phase", "default_sequence", reset_sequence::get_type()); 54 // 55 // ToDo 56 uvm_config_db #(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, "r_agent.seqr.reset_phase", "default_sequence", reset_sequence::get_type()); 57 58 59 endfunction 60 61 endclass 62 63 `endif
5.input_agent.sv(派生于uvm_agent)
注1:agent包含sequencer, driver,monitor; 更高层次的组件(如env, test)应该将agent当作黑盒子,也就是说,sequencer. driver, monitor的配置应该由agent完成,更高层次的组件仅仅负责配置agent,而不需要负责agent内的子组件;
1 `ifndef INPUT_AGENT__SV 2 `define INPUT_AGENT__SV 3 4 // The files content needed by the agent must be included 5 6 `include "packet_sequence.sv" 7 `include "driver.sv" 8 9 typedef uvm_sequencer #(packet) packet_sequencer; 10 11 class input_agent extends uvm_agent; 12 13 // For this lab, the input agent has been modified to have port_id and virtual interface also. 14 virtual router_io sigs; // DUT virtual interface 15 int port_id = -1; // Agent's designated port 16 packet_sequencer seqr; 17 driver drv; 18 19 // For this lab, the input agent has been modified to have port_id. 20 `uvm_component_utils_begin(input_agent) 21 `uvm_field_int(port_id, UVM_DEFAULT | UVM_DEC) 22 `uvm_component_utils_end 23 24 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 25 super.new(name, parent); 26 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 27 endfunction: new 28 29 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 30 super.build_phase(phase); 31 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 32 33 // For this lab, the input agent has been modified to retrieve port_id and virtual interface. 34 // The agent then configures its child components to use the same port_id and virtual interface. 35 uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this, "", "port_id", port_id); 36 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(this, "", "router_io", sigs); 37 38 seqr = packet_sequencer::type_id::create("seqr", this); 39 drv = driver::type_id::create("drv", this); 40 41 uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this, "drv", "port_id", port_id); 42 uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this, "seqr", "port_id", port_id); 43 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "drv", "router_io", sigs); 44 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "seqr", "router_io", sigs); 45 endfunction: build_phase 46 47 virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); 48 super.connect_phase(phase); 49 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 50 drv.seq_item_port.connect(seqr.seq_item_export); 51 endfunction: connect_phase 52 53 virtual function void start_of_simulation_phase(uvm_phase phase); 54 super.start_of_simulation_phase(phase); 55 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 56 `uvm_info("AGNTCFG", $sformatf("Using port_id of %0d", port_id), UVM_MEDIUM); 57 endfunction: start_of_simulation_phase 58 endclass 59 60 `endif
5.1 driver.sv
1 `ifndef DRIVER__SV 2 `define DRIVER__SV 3 4 class driver extends uvm_driver #(packet); 5 // Lab 4 - Task 2, Step 2 and 3 6 // Create the new fields as shown below. 7 // 8 // virtual router_io sigs; // DUT virtual interface 9 // int port_id = -1; // Driver's designated port 10 // 11 // The intent of the port_id field is to designate the driver for driving a specific port. 12 // 13 // If port_id is set in the range of 0 through 15, the driver will only drive 14 // the packet it gets from the sequencer through the DUT if the port_id matches the 15 // packet's source address (sa) field. If not, the packet is dropped. 16 // 17 // If port_id is -1 (the default), the driver will drive all packets it gets from 18 // the sequencer through the DUT without checking the packet's source address. 19 // 20 // Example: If port_id is 3 and req.sa is also 3, 21 // (req is the packet handle that sequencer passed to the driver) 22 // The driver will drive the packet through port 3 of DUT: sigs.drvClk.din[req.sa]; 23 // 24 // Example: If port_id is 3 and req.sa is 7, 25 // The driver will drop the packet. 26 // 27 // Example: If port_id is -1 and req.sa is 7, 28 // The driver will drive the packet through port 7 of DUT: sigs.drvClk.din[req.sa]; 29 // 30 // ToDo 31 virtual router_io sigs; // DUT virtual interface 32 int port_id = -1; // Driver's designated port 33 34 35 // Lab 4 - Task 2, Step 4 36 // 37 // Embed the port_id field in the `uvm_component_utils macro. 38 // Note: You will need to change the macro to `uvm_component_utils_begin 39 // with a corresponding `uvm_component_utils_end 40 // 41 // ToDo 42 `uvm_component_utils_begin(driver) 43 `uvm_field_int(port_id, UVM_DEFAULT | UVM_DEC) 44 `uvm_component_utils_end 45 46 47 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 48 super.new(name, parent); 49 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 50 endfunction: new 51 52 53 function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 54 super.build_phase(phase); 55 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 56 57 // Lab 4 - Task 2, Step 5 58 // 59 // Retrieve the port_id configuration and the virtual interface. 60 // 61 // uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this, "", "port_id", port_id); 62 // if (!(port_id inside {-1, [0:15]})) begin 63 // `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", $sformatf("port_id must be {-1, [0:15]}, not %0d!", port_id)); 64 // end 65 // uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(this, "", "router_io", sigs); 66 // if (sigs == null) begin 67 // `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for Driver not set"); 68 // end 69 // 70 // ToDo 71 uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this, "", "port_id", port_id); 72 if (!(port_id inside {-1, [0:15]})) begin 73 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", $sformatf("port_id must be {-1, [0:15]}, not %0d!", port_id)); 74 end 75 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(this, "", "router_io", sigs); 76 if (sigs == null) begin //检测virtual interface handle; 77 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for Driver not set"); 78 end 79 80 81 endfunction: build_phase 82 83 84 // 85 // The UVM start_of_simulation phase is designed for displaying the testbench configuration 86 // before any active verification operation starts. 87 // 88 // For the sake of lab time, the start_of_simulation method is done for you. 89 // 90 virtual function void start_of_simulation_phase(uvm_phase phase); 91 super.start_of_simulation_phase(phase); 92 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 93 `uvm_info("DRV_CFG", $sformatf("port_id is: %0d", port_id), UVM_MEDIUM); 94 endfunction: start_of_simulation_phase 95 96 97 virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); 98 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 99 100 forever begin 101 seq_item_port.get_next_item(req); 102 103 // Lab 4 - Task 2, Step 6 104 // 105 // Check port_id to see if the driver should accept or drop the packet. 106 // If port_id is -1, or if port_id matches req object's sa field, 107 // call send() method to drive the content of the req object through the DUT. 108 // Otherwise, drop the req object without processing. Like the following: 109 // 110 // if (port_id inside { -1, req.sa }) begin 111 // send(req); 112 // `uvm_info("DRV_RUN", {"\n", req.sprint()}, UVM_MEDIUM); 113 // end 114 // 115 // ToDo 116 if (port_id inside { -1, req.sa }) begin 117 send(req); 118 `uvm_info("DRV_RUN", {"\n", req.sprint()}, UVM_MEDIUM); 119 end 120 121 122 seq_item_port.item_done(); 123 end 124 endtask: run_phase 125 126 127 // Lab 4 - Task 8, Step 3 128 // 129 // The driver is fully responsible for asserting and de-asserting the signal set 130 // that it is assigned to handle. This includes setting the signal state at reset. 131 // 132 // At the pre_reset phase, the signals should be set to default values (x for logic, 133 // z for wire) to emulate power-up condition. 134 // 135 // At the reset phase, the signals should be set to the de-asserted states. 136 // 137 // These two methods are done for you. 138 // 139 // Caution: for this lab, we are not using the port_id because this lab is still 140 // just a part of initial bringup process. There is only one agent in the 141 // environment. So, if port_id is -1 (not using port_id), then the reset phases 142 // will initialized the signals for all router (DUT) ports. In the next lab, 143 // when you implement a dedicated agent for each port, the port_id will be set 144 // and the reset phases will only initialize its designated port. 145 // 146 // For this lab, just un-comment both the pre_reset and reset phase code. 147 // 148 // ToDo 149 //reset信号的assertion与deassertion由reset_sequence和reset_agent处理;其他控制信号,由driver的reset_phase来处理(方法1,不推荐该方法); 150 virtual task pre_reset_phase(uvm_phase phase); 151 super.pre_reset_phase(phase); 152 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 153 phase.raise_objection(this); 154 if (port_id == -1) begin 155 sigs.drvClk.frame_n <= 'x; 156 sigs.drvClk.valid_n <= 'x; 157 sigs.drvClk.din <= 'x; 158 end else begin 159 sigs.drvClk.frame_n[port_id] <= 'x; 160 sigs.drvClk.valid_n[port_id] <= 'x; 161 sigs.drvClk.din[port_id] <= 'x; 162 end 163 phase.drop_objection(this); 164 endtask: pre_reset_phase 165 166 virtual task reset_phase(uvm_phase phase); 167 super.reset_phase(phase); 168 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 169 phase.raise_objection(this); 170 if (port_id == -1) begin 171 sigs.drvClk.frame_n <= '1; 172 sigs.drvClk.valid_n <= '1; 173 sigs.drvClk.din <= '0; 174 end else begin 175 sigs.drvClk.frame_n[port_id] <= '1; 176 sigs.drvClk.valid_n[port_id] <= '1; 177 sigs.drvClk.din[port_id] <= '0; 178 end 179 phase.drop_objection(this); 180 endtask: reset_phase 181 182 // 183 // In the interest of lab time, all device drivers have been done for you: 184 // 185 186 virtual task send(packet tr); 187 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 188 send_address(tr); 189 send_pad(tr); 190 send_payload(tr); 191 endtask: send 192 193 virtual task send_address(packet tr); 194 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 195 sigs.drvClk.frame_n[tr.sa] <= 1'b0; 196 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) begin 197 sigs.drvClk.din[tr.sa] <= tr.da[i]; 198 @(sigs.drvClk); 199 end 200 endtask: send_address 201 202 virtual task send_pad(packet tr); 203 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 204 sigs.drvClk.din[tr.sa] <= 1'b1; 205 sigs.drvClk.valid_n[tr.sa] <= 1'b1; 206 repeat(5) @(sigs.drvClk); 207 endtask: send_pad 208 209 virtual task send_payload(packet tr); 210 logic [7:0] datum; 211 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 212 while(!sigs.drvClk.busy_n[tr.sa]) @(sigs.drvClk); 213 foreach(tr.payload[index]) begin 214 datum = tr.payload[index]; 215 for(int i=0; i<$size(tr.payload, 2); i++) begin 216 sigs.drvClk.din[tr.sa] <= datum[i]; 217 sigs.drvClk.valid_n[tr.sa] <= 1'b0; 218 sigs.drvClk.frame_n[tr.sa] <= ((tr.payload.size()-1) == index) && (i==7); 219 @(sigs.drvClk); 220 end 221 end 222 sigs.drvClk.valid_n[tr.sa] <= 1'b1; 223 endtask: send_payload 224 225 endclass: driver 226 227 `endif
6.reset_agent.sv(含reset_sequencer, reset_driver, reset_monitor)
1 `ifndef RESET_AGENT__SV 2 `define RESET_AGENT__SV 3 4 `include "reset_sequence.sv" 5 6 typedef class reset_driver; 7 typedef class reset_monitor; 8 typedef uvm_sequencer#(reset_tr) reset_sequencer; 9 10 class reset_agent extends uvm_agent; 11 virtual router_io sigs; // DUT virtual interface 12 reset_sequencer seqr; 13 reset_driver drv; 14 reset_monitor mon; 15 16 `uvm_component_utils(reset_agent) 17 18 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 19 super.new(name, parent); 20 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 21 endfunction: new 22 23 function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 24 super.build_phase(phase); 25 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 26 27 uvm_config_db#(uvm_active_passive_enum)::get(this, "", "is_active", is_active); 28 `uvm_info("RSTCFG", $sformatf("Reset agent %s setting for is_active is: %p", this.get_name(), is_active), UVM_MEDIUM); 29 30 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(this, "", "router_io", sigs); 31 32 if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin 33 seqr = reset_sequencer::type_id::create("seqr", this); 34 drv = reset_driver::type_id::create("drv", this); 35 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "drv", "router_io", sigs); 36 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "seqr", "router_io", sigs); 37 end 38 mon = reset_monitor::type_id::create("mon", this); 39 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::set(this, "mon", "router_io", sigs); 40 endfunction: build_phase 41 42 virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); 43 super.connect_phase(phase); 44 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 45 if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin 46 drv.seq_item_port.connect(seqr.seq_item_export); 47 end 48 endfunction: connect_phase 49 endclass 50 51 /* 52 class reset_tr extends uvm_sequence_item; 53 typedef enum {ASSERT, DEASSERT} kind_e; 54 rand kind_e kind; 55 rand int unsigned cycles = 1; 56 endclass 57 */ 58 59 class reset_driver extends uvm_driver #(reset_tr); 60 virtual router_io sigs; // DUT virtual interface 61 `uvm_component_utils(reset_driver) 62 63 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 64 super.new(name, parent); 65 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 66 endfunction: new 67 68 function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 69 super.build_phase(phase); 70 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 71 72 if (!uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(this, "", "router_io", sigs)) begin 73 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for reset driver not set"); 74 end 75 endfunction: build_phase 76 77 virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); 78 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 79 80 forever begin 81 seq_item_port.get_next_item(req); 82 drive(req); 83 seq_item_port.item_done(); 84 end 85 endtask: run_phase 86 //注1:reset_agent和reset_sequence只处理了reset信号的assertion与de-assertion;其他控制信号的处理要么通过一个单独的sequence来deassert,要么在driver的reset_phase控制; 87 virtual task drive(reset_tr tr); 88 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 89 if (tr.kind == reset_tr::ASSERT) begin 90 sigs.reset_n = 1'b0; 91 repeat(tr.cycles) @(sigs.drvClk); 92 end else begin 93 sigs.reset_n <= '1; 94 repeat(tr.cycles) @(sigs.drvClk); 95 end 96 endtask: drive 97 endclass 98 99 class reset_monitor extends uvm_monitor; 100 virtual router_io sigs; // DUT virtual interface 101 uvm_analysis_port #(reset_tr) analysis_port; 102 `uvm_component_utils(reset_monitor) 103 104 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 105 super.new(name, parent); 106 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 107 endfunction: new 108 109 function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 110 super.build_phase(phase); 111 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 112 113 if (!uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(this, "", "router_io", sigs)) begin 114 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for reset monitor not set"); 115 end 116 117 analysis_port = new("analysis_port", this); 118 endfunction: build_phase 119 120 virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); 121 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 122 123 forever begin 124 reset_tr tr = reset_tr::type_id::create("tr", this); 125 detect(tr); 126 analysis_port.write(tr); 127 end 128 endtask: run_phase 129 130 virtual task detect(reset_tr tr); 131 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 132 @(sigs.reset_n); 133 assert(!$isunknown(sigs.reset_n)); 134 if (sigs.reset_n == 1'b0) begin 135 tr.kind = reset_tr::ASSERT; 136 end else begin 137 tr.kind = reset_tr::DEASSERT; 138 end 139 endtask: detect 140 endclass 141 142 `endif
7.packet_sequence.sv
1 `ifndef PACKET_SEQUENCE__SV 2 `define PACKET_SEQUENCE__SV 3 4 `include "packet.sv" 5 6 class packet_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(packet); 7 8 // Lab 3 - Task 2, Step 2 9 // Create the new fields as shown below. 10 // 11 // int item_count = 10; 12 // int port_id = -1; 13 // bit[15:0] da_enable = '1; 14 // int valid_da[$]; 15 // 16 // The intent of the item_count field is to control how many packet objects 17 // to create and pass on to the driver per execution of the body() task. 18 // 19 // The intent of the port_id field is to constrain the packet's source address. 20 // 21 // The lab DUT has 16 input ports needing to be tested. Each input agent created 22 // to drive a particular port will be assigned a port_id specifying which port it 23 // should exercise. Because of this, the sequence within an input agent when 24 // when generating packets need to constrain the packet's source address. 25 // 26 // The rule for constrainint the source address shall be as follows: 27 // If port_id is inside the range of {[0:15]}, then the source address shall be port_id. 28 // If port_id is -1 (unconfigured), the source address shall be in the range of {[0:15]} 29 // port_id outside the range of {-1, {[0:15]} is not allowed. 30 // 31 // The intent of the da_enable fields is to enable corresponding destination 32 // addresses to be generated. A value of 1 in a particular bit position will 33 // enable the corresponding address as a valid address to generate. A value of 0 34 // prohibit the corresponding address from being generated. 35 // 36 // Example: if the sequence were to be configured to generate only packets 37 // for destination address 3, then the da_enable need to be configured as: 38 // 16'b0000_0000_0000_1000 39 // 40 // Note that the default value is '1, meaning that all addresses are enabled. 41 // 42 // To simplify the constraint coding, a corresponding set of queue, valid_da 43 // is needed. This queue is populated based on the value of da_enable. 44 // 45 // Example: if da_enable is 16'b0000_0011_0000_1000, then the valid_da queue 46 // will populated with 3, 8 and 9. 47 // 48 // ToDo 49 int item_count = 10; 50 int port_id = -1; 51 bit[15:0] da_enable = '1; 52 int valid_da[$]; 53 54 55 // 56 // To save lab time, the `uvm_object_utils macro is filled in for you. 57 // 58 `uvm_object_utils_begin(packet_sequence) 59 `uvm_field_int(item_count, UVM_ALL_ON) 60 `uvm_field_int(port_id, UVM_ALL_ON) 61 `uvm_field_int(da_enable, UVM_ALL_ON) 62 `uvm_field_queue_int(valid_da, UVM_ALL_ON) 63 `uvm_object_utils_end 64 65 // 66 // The valid_da queue must be populated with legal set of addresses as specified 67 // by the da_enable field. Since the first thing that the sequencer performs is 68 // the randomization of its default_sequence, a good place to retreive the configuration 69 // fields and populate the valid_da queue is in the pre_randomize() method. 70 // 71 // To simplify your code development, the code is done for you as follows: 72 // 73 function void pre_randomize(); 74 uvm_config_db#(int)::get(m_sequencer, "", "item_count", item_count); 75 uvm_config_db#(int)::get(m_sequencer, "", "port_id", port_id); 76 uvm_config_db#(bit[15:0])::get(m_sequencer, "", "da_enable", da_enable); 77 if (!(port_id inside {-1, [0:15]})) begin 78 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR", $sformatf("Illegal port_id value of %0d", port_id)); 79 end 80 81 valid_da.delete(); 82 for (int i=0; i<16; i++) 83 if (da_enable[i]) 84 valid_da.push_back(i); 85 endfunction 86 87 function new(string name = "packet_sequence"); 88 super.new(name); 89 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 90 endfunction 91 92 task body(); 93 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 94 95 if (starting_phase != null) 96 starting_phase.raise_objection(this); 97 98 // Lab 3 - Task 2, Step 3 99 // Instead of hard coding the number of item to be generated, replace the 100 // hard-coded value 10 in the repeat() statement to use item_count. 101 // 102 // ToDo 103 repeat(item_count) begin 104 105 106 // Lab 3 - Task 2, Step 3 107 // 108 // As stated in the comment at the beginning of the file. If the port_id is unconfigured (-1) 109 // then the legal values for the source address shall be in the range of {[0:15]}. If the 110 // port_id is configured, then the source address shall be port_id. This will give the test 111 // the ability to test whether or not the driver drops the packet it is not configured to drive. 112 // 113 // For destination address, the legal values should be picked out of the valid_da array. 114 // 115 // Change the following `uvm_do(req) macro to: 116 // `uvm_do_with(req, {if (port_id == -1) sa inside {[0:15]}; else sa == port_id; da inside valid_da;}); 117 // 118 // ToDo 119 `uvm_do_with(req, {if (port_id == -1) sa inside {[0:15]}; else sa == port_id; da inside valid_da;}); 120 121 122 end 123 124 if (starting_phase != null) 125 starting_phase.drop_objection(this); 126 endtask 127 128 endclass 129 130 `endif
7.1packet.sv
1 `ifndef PACKET__SV 2 `define PACKET__SV 3 4 // Lab 1 - Declare the class packet that extends uvm_sequence_item 5 // 6 // ToDo 7 class packet extends uvm_sequence_item; 8 9 // Lab 1 - Declare the random 4-bit sa and da fields 10 // 11 // ToDo 12 rand bit [3:0] sa, da; 13 14 // Lab 1 - Declare the random 8-bit payload queue 15 // 16 // ToDo 17 rand bit[7:0] payload[$]; 18 19 `uvm_object_utils_begin(packet) 20 `uvm_field_int(sa, UVM_ALL_ON | UVM_NOCOMPARE) 21 `uvm_field_int(da, UVM_ALL_ON) 22 `uvm_field_queue_int(payload, UVM_ALL_ON) 23 `uvm_object_utils_end 24 25 constraint valid { 26 payload.size inside {[1:10]}; 27 } 28 29 // Lab 1 - Create the constructor with one argument: string name="packet" 30 // Lab 1 - Call super.new() with this argument 31 // Lab 1 - Lastly, print a message with: 32 // Lab 1 - `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 33 // 34 // ToDo 35 function new(string name = "packet"); 36 super.new(name); 37 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 38 endfunction: new 39 40 41 endclass: packet 42 `endif
7.2 packet_da_3.sv
1 `ifndef PACKET_DA_3__SV 2 `define PACKET_DA_3__SV 3 4 class packet_da_3 extends packet; 5 `uvm_object_utils(packet_da_3) 6 7 // Lab 2 - set the constraint for destination address (da) to 3 8 // 9 // ToDo 10 constraint da_3 { 11 da == 3; 12 } 13 14 function new(string name = "packet_da_3"); 15 super.new(name); 16 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 17 endfunction 18 endclass 19 20 `endif
8.reset_sequence.sv
1 `ifndef RESET_SEQUENCE__SV 2 `define RESET_SEQUENCE__SV 3 4 // Reset structure is done in the same way as all other UVM component structure. 5 // A reset agent contains a reset sequencer, driver and monitor. 6 // 7 // The reset sequencer executes a reset sequence (this file), and passes the reset 8 // transaction (reset_tr) to the reset driver. The reset driver then assert/de-assert 9 // the reset signal as specified in the reset transaction. 10 // 11 // Within the reset transaction class, there is a control command field called kind. 12 // If the kind field is ASSERT, then the driver will assert the reset signal for 13 // the number of clock cycles are specified in the cycles field. Similar action 14 // takes place for the DEASSERT command. 15 // 16 // For example, if the reset signal need to be asserted for 2 cycles then de-asserted 17 // for 15 clock cycles, the potential code might look like: 18 // 19 // reset_tr tr = reset_tr::type_id::create("tr"); 20 // tr.randomize() with {kind == ASSERT; cycles == 2;}; 21 // tr.randomize() with {kind == DEASSERT; cycles == 15;; 22 23 class reset_tr extends uvm_sequence_item; 24 typedef enum {ASSERT, DEASSERT} kind_e; 25 rand kind_e kind; 26 rand int unsigned cycles = 1; 27 28 `uvm_object_utils_begin(reset_tr) 29 `uvm_field_enum(kind_e, kind, UVM_ALL_ON) 30 `uvm_field_int(cycles, UVM_ALL_ON) 31 `uvm_object_utils_end 32 33 function new(string name = "reset_tr"); 34 super.new(name); 35 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 36 endfunction: new 37 endclass 38 39 class reset_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(reset_tr); 40 `uvm_object_utils(reset_sequence) 41 42 function new(string name = "reset_sequence"); 43 super.new(name); 44 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 45 endfunction 46 47 task body(); 48 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 49 50 if (starting_phase != null) 51 starting_phase.raise_objection(this); 52 53 // Lab 4 - Task 6, Step 2 54 // 55 // Enter the code to assert reset for 2 cycles, followed by de-assert of reset for 15 cycles. 56 // 57 // ToDo 58 `uvm_do_with(req, {kind == ASSERT; cycles == 2;}); 59 `uvm_do_with(req, {kind == DEASSERT; cycles == 15;}); 60 61 62 if (starting_phase != null) 63 starting_phase.drop_objection(this); 64 endtask 65 66 endclass 67 68 `endif
9.router_input_port_reset_sequence.sv
注1:reset_sequence和reset_agent仅仅处理了reset信号的assertion与de-assertion,其他控制信号的de-assertion可以由router_input_port_reset_sequence控制(方法2,推荐),该sequence可以在sequencer的reset_phase执行;
注2:注意get_sequencer()的使用;
注3:该sequence可以用input_agent的sequencer执行;
1 class router_input_port_reset_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(packet); 2 virtual router_io vif; 3 input port_id=-1; 4 5 `uvm_object_utils_begin(router_input_port_reset_sequence) 6 `uvm_field_int(port_id, UVM_DEFAULT | UVM_DEC) 7 `uvm_object_utils_end 8 9 function new(string name="router_input_port_reset_sequence"); 10 super.new(name); 11 `uvm_info("TRACE",$sformatf("%m"),UVM_HIGH) 12 `ifdef UVM_POST_VERSION_1_1 13 set_automatic_phase_objection(1); 14 `endif 15 endfunction 16 17 virtual task pre_start(); 18 `ifdef UVM_VERSION_1_1 19 if((get_parent_sequence()==null) && (starting_phase!=null)) begin 20 starting_phase.raise_objection(this); 21 end 22 `endif 23 24 uvm_config_db#(int)::get(get_sequencer(),"","port_id",port_id); 25 if(!(port_id inside {-1,[0:15]})) begin 26 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR",$sformatf("port_id must be {-1,[0:15]}, not %0d!",port_id)) 27 end 28 uvm_config_db#(virtual router_io)::get(get_sequencer(),"","vif",vif); 29 if(vif==null) begin 30 `uvm_fatal("CFGERR","Interface for the Driver Reset Sequence not set") 31 end 32 endtask: pre_start 33 34 `ifdef UVM_VERSION_1_1 35 virtual task post_start(); 36 if((get_parent_sequence()==null) && (starting_phase!=null)) begin 37 starting_phase.drop_objection(this); 38 end 39 endtask: post_start 40 `endif 41 42 virtual task body(); 43 if(port_id==-1) begin 44 vif.frame_n='1; 45 vif.valid_n='1; 46 vif.din='0; 47 end 48 else begin 49 vif.frame_n='1; 50 vif.valid_n='1; 51 vif.din='0; 52 end 53 endtask 54 endclass


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号