[CU]uvm lab2-router
注1:uvm lab1 - __见贤思齐 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
注2:lab1相应的makefile见IC仿真makefile示例3 - __见贤思齐 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com);
注3:结合synopsys uvm lab guide阅读;
注4:uvm1.1 lab链接第三方资源 – 路科验证 (rockeric.com).
注5:synopsys uvm1.2 lab guide - IC验证资料 - EETOP 创芯网论坛 (原名:电子顶级开发网) -
注6:uvm1.2 lab链接UVM1.2 Lab验证资料(入门必备) - IC验证资料 - EETOP 创芯网论坛 (原名:电子顶级开发网) -
学习目标
(1) 创建uvm transaction类;
(2) sequence内创建uvm transaction;
(3) 将sequence配置给sequencer的某一phase进行sequence的执行;
(4) 利用factory机制进行transaction的override;
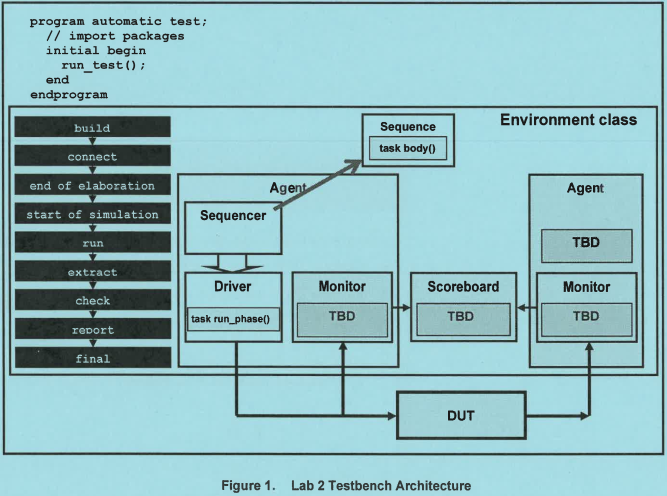
1.test.sv
1 program automatic test; 2 import uvm_pkg::*; 3 4 `include "test_collection.sv" 5 6 initial begin 7 $timeformat(-9, 1, "ns", 10); 8 run_test(); 9 end 10 11 endprogram
2.test_collection.sv(派生于uvm_test)
1 `ifndef TEST_COLLECTION__SV 2 `define TEST_COLLECTION__SV 3 4 `include "router_env.sv" 5 6 class test_base extends uvm_test; 7 `uvm_component_utils(test_base) 8 router_env env; 9 10 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 11 super.new(name, parent); 12 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 13 endfunction 14 15 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 16 super.build_phase(phase); 17 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 18 env = router_env::type_id::create("env", this); 19 endfunction 20 21 // 22 // The start_of_simulation_phase method from lab1 is moved to final_phase 23 // for the convinience of seeing the topology and factory registry at the 24 // end of simulation. In practice, you should implement both phases to 25 // display the topology and the factory registry. 26 // 27 virtual function void final_phase(uvm_phase phase); 28 super.final_phase(phase); 29 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 30 uvm_top.print_topology(); 31 uvm_factory::get().print(); 32 endfunction 33 endclass 34 35 // Lab 2 - Include the packet_da_3.sv file 36 // 37 // ToDo 38 `include "packet_da_3.sv" 39 40 41 class test_da_3_inst extends test_base; 42 `uvm_component_utils(test_da_3_inst) 43 44 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 45 super.new(name, parent); 46 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 47 endfunction 48 49 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 50 super.build_phase(phase); 51 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 52 53 // Lab 2 - Use instance override to configure the packet sequencer 54 // to use packet_da_3 instead of packet 55 // 56 // ToDo 57 set_inst_override_by_type("env.i_agent*.seqr.*", packet::get_type(), packet_da_3::get_type()); 58 //set_inst_override_by_type("env.i_agent.seqr.packet_sequence.req", packet::get_type(), packet_da_3::get_type()); 59 60 endfunction 61 62 endclass 63 64 // Optional Lab 2 - Create a test to globally set all packet instances to packet_da_3 65 66 class test_da_3_type extends test_base; 67 `uvm_component_utils(test_da_3_type) 68 69 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 70 super.new(name, parent); 71 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 72 endfunction 73 74 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 75 super.build_phase(phase); 76 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 77 set_type_override_by_type(packet::get_type(), packet_da_3::get_type()); 78 endfunction 79 endclass 80 81 82 `endif
3.router_env.sv(派生于uvm_env)
1 `ifndef ROUTER_ENV__SV 2 `define ROUTER_ENV__SV 3 4 // The files content needed by the environment must be included 5 6 `include "input_agent.sv" 7 8 9 // Lab 1 - Declare the router_env class, extended from uvm_env 10 // 11 // ToDo 12 class router_env extends uvm_env; 13 14 // Lab 1 - Create an input_agent handle called i_agent 15 // 16 // ToDo 17 input_agent i_agent; 18 19 `uvm_component_utils(router_env) 20 21 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 22 super.new(name, parent); 23 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 24 endfunction: new 25 26 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 27 super.build_phase(phase); 28 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 29 30 // Lab 1 - Construct the i_agent object using the proxy create() method 31 // 32 // ToDo 33 i_agent = input_agent::type_id::create("i_agent", this); 34 35 // Lab 1 - Set the input sequencer to execute packet_sequence as the default_sequence in main_phase 36 // Use uvm_config_db #(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, "i_agent.seqr.main_phase", "default_sequence", packet_sequence::get_type()); 37 // 38 // ToDo 39 uvm_config_db #(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, "i_agent.seqr.main_phase", "default_sequence", packet_sequence::get_type()); 40 41 endfunction: build_phase 42 43 endclass: router_env 44 45 `endif
4.input_agent.sv(派生于uvm_agent)
1 `ifndef INPUT_AGENT__SV 2 `define INPUT_AGENT__SV 3 4 // The files content needed by the agent must be included 5 6 `include "packet_sequence.sv" 7 `include "driver.sv" 8 9 // Lab 1 - Use typedef to create a class called packet_sequencer from the uvm_sequencer class parameterized with packet type 10 // 11 // ToDo 12 typedef uvm_sequencer #(packet) packet_sequencer; 13 14 // Lab 1 - Declare the input_agent class, extended from uvm_agent 15 // 16 // ToDo 17 class input_agent extends uvm_agent; 18 19 // Lab 1 - Create a packet_sequencer handle, call it seqr 20 // 21 // ToDo 22 packet_sequencer seqr; 23 24 // Lab 1 - Create a driver handle, call it drv 25 // 26 // ToDo 27 driver drv; 28 29 `uvm_component_utils(input_agent) 30 31 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 32 super.new(name, parent); 33 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 34 endfunction: new 35 36 virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); 37 super.build_phase(phase); 38 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 39 40 // Lab 1 - Construct the packet_sequencer and driver objects using the proxy create() method 41 // 42 // ToDo 43 seqr = packet_sequencer::type_id::create("seqr", this); 44 drv = driver::type_id::create("drv", this); 45 46 endfunction: build_phase 47 48 virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); 49 super.connect_phase(phase); 50 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 51 52 // Lab 1 - Connect the seq_item_port in drv to the seqr's seq_item_export 53 // 54 // ToDo 55 drv.seq_item_port.connect(seqr.seq_item_export); 56 57 endfunction: connect_phase 58 59 endclass: input_agent 60 61 `endif
4.1 driver.sv (派生于uvm_driver)
1 `ifndef DRIVER__SV 2 `define DRIVER__SV 3 4 // Lab 1 - Declare a class driver that extends uvm_driver processing packet type 5 // 6 // ToDo 7 class driver extends uvm_driver #(packet); 8 9 // Since the factory registration and the constructor are the same as what 10 // you have already done. There is no learning benefit in re-typing them. 11 // These are entered for you in all subsequence tasks and labs. 12 `uvm_component_utils(driver) 13 14 function new(string name, uvm_component parent); 15 super.new(name, parent); 16 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 17 endfunction: new 18 19 virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); 20 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 21 forever begin 22 // seq_item_port is built into the uvm_driver base class 23 // It is typically used to pull a sequence_item from the sequencer connected to the driver 24 // You will be doing the driver to sequencer connection in the environment 25 seq_item_port.get_next_item(req); 26 27 // Lab 1 - Call the req object's print() method to display content 28 // 29 // ToDo 30 req.print(); 31 32 // Once the driver finishes processing the requested sequence item, the driver must call item_done() 33 // to indicate to the sequencer that the sequence item has completed processing 34 seq_item_port.item_done(); 35 end 36 endtask: run_phase 37 38 endclass: driver 39 40 `endif
5.packet_sequence.sv (派生于uvm_sequence)
(1) 注意set_automatic_phase_objection(1)的使用;
1 // Function: set_automatic_phase_objection 2 // Sets the 'automatically object to starting phase' bit. 3 // 4 // The most common interaction with the starting phase 5 // within a sequence is to simply ~raise~ the phase's objection 6 // prior to executing the sequence, and ~drop~ the objection 7 // after ending the sequence (either naturally, or 8 // via a call to <kill>). In order to 9 // simplify this interaction for the user, the UVM 10 // provides the ability to perform this functionality 11 // automatically. 12 // 13 // For example: 14 //| function my_sequence::new(string name="unnamed"); 15 //| super.new(name); 16 //| set_automatic_phase_objection(1); 17 //| endfunction : new 18 // 19 // From a timeline point of view, the automatic phase objection 20 // looks like: 21 //| start() is executed 22 //| --! Objection is raised !-- 23 //| pre_start() is executed 24 //| pre_body() is optionally executed 25 //| body() is executed 26 //| post_body() is optionally executed 27 //| post_start() is executed 28 //| --! Objection is dropped !-- 29 //| start() unblocks 30 // 31 // This functionality can also be enabled in sequences 32 // which were not written with UVM Run-Time Phasing in mind: 33 //| my_legacy_seq_type seq = new("seq"); 34 //| seq.set_automatic_phase_objection(1); 35 //| seq.start(my_sequencer); 36 // 37 // Internally, the <uvm_sequence_base> uses a <uvm_get_to_lock_dap> to 38 // protect the ~automatic_phase_objection~ value from being modified 39 // after the reference has been read. Once the sequence has ended 40 // its execution (either via natural termination, or being killed), 41 // then the ~automatic_phase_objection~ value can be modified again. 42 // 43 // NEVER set the automatic phase objection bit to 1 if your sequence 44 // runs with a forever loop inside of the body, as the objection will 45 // never get dropped! 46 function void set_automatic_phase_objection(bit value); 47 m_automatic_phase_objection_dap.set(value); 48 endfunction : set_automatic_phase_objection
1 `ifndef PACKET_SEQUENCE__SV 2 `define PACKET_SEQUENCE__SV 3 4 `include "packet.sv" 5 6 // Lab 1 - Declare the class packet_sequence that extends uvm_sequence typed to packet 7 // 8 // ToDo 9 class packet_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(packet); 10 11 12 // Since the factory registration and the constructor are the same as what 13 // you have already done. There is no learning benefit in re-typing them. 14 // These are entered for you in all subsequence tasks and labs. 15 16 `uvm_object_utils(packet_sequence) 17 18 function new(string name = "packet_sequence"); 19 super.new(name); 20 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); //`ifdef UVM_POST_VERSION_1_1 set_automatic_phase_objection(1); `endif 21 endfunction: new 22 23 // Lab 1 - Create the body task with no argument 24 // Lab 1 - Add trace statement: `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 25 // Lab 1 - Check to see if there is a starting phase 26 // Lab 1 - If yes, raise the phase objection 27 // Lab 1 - Then, generate 10 random packets 28 // Lab 1 - When done, drop the phase objection 29 // Lab 1 - Reference the lecture slides for exact syntax 30 // 31 // ToDo 32 task body(); 33 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 34 if (starting_phase != null) 35 starting_phase.raise_objection(this); 36 repeat(10) begin 37 `uvm_do(req); 38 end 39 if (starting_phase != null) 40 starting_phase.drop_objection(this); 41 endtask: body 42 43 endclass: packet_sequence 44 45 `endif
5.1 packet.sv(派生于uvm_sequence_item)
1 `ifndef PACKET__SV 2 `define PACKET__SV 3 4 // Lab 1 - Declare the class packet that extends uvm_sequence_item 5 // 6 // ToDo 7 class packet extends uvm_sequence_item; 8 9 // Lab 1 - Declare the random 4-bit sa and da fields 10 // 11 // ToDo 12 rand bit [3:0] sa, da; 13 14 // Lab 1 - Declare the random 8-bit payload queue 15 // 16 // ToDo 17 rand bit[7:0] payload[$]; 18 19 `uvm_object_utils_begin(packet) 20 `uvm_field_int(sa, UVM_ALL_ON | UVM_NOCOMPARE) 21 `uvm_field_int(da, UVM_ALL_ON) 22 `uvm_field_queue_int(payload, UVM_ALL_ON) 23 `uvm_object_utils_end 24 25 constraint valid { 26 payload.size inside {[1:10]}; 27 } 28 29 // Lab 1 - Create the constructor with one argument: string name="packet" 30 // Lab 1 - Call super.new() with this argument 31 // Lab 1 - Lastly, print a message with: 32 // Lab 1 - `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 33 // 34 // ToDo 35 function new(string name = "packet"); 36 super.new(name); 37 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 38 endfunction: new 39 40 41 endclass: packet 42 `endif
5.2 packet_da_3.sv(派生于uvm_sequence_item)
1 `ifndef PACKET_DA_3__SV 2 `define PACKET_DA_3__SV 3 4 class packet_da_3 extends packet; 5 `uvm_object_utils(packet_da_3) 6 7 // Lab 2 - set the constraint for destination address (da) to 3 8 // 9 // ToDo 10 constraint da_3 { 11 da == 3; 12 } 13 14 function new(string name = "packet_da_3"); 15 super.new(name); 16 `uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH); 17 endfunction 18 endclass 19 20 `endif
6.makefile在uvm_lab2中的使用
(1) make test=test_da_3_inst
(2) make test=test_base plus=uvm_set_inst_override=packet,packet_da_3,\*.req
(3) make test=test_base plus=uvm_set_type_override=packet,packet_da_3

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号