[CU]config_db机制1-config_db作用,优点及原理
注1:该篇文章涉及的几个关键类: uvm_resource_pool, uvm_resource & uvm_resource_base, uvm_resource_db & uvm_config_db;
注2:该篇文章主要描述config_db机制原理性的内容;
1. 作用,优点
(1) UVM中用于在不同component之间共享资源的一种机制,即实现了资源共享(也可描述为在UVM验证平台间传递参数),又避免了全局变量的弊端.
(2) umv_config_db是从uvm_resource_db派生而来,对uvm_resource_db的一些功能进行了扩展,主要体现在对资源的写入和读取上.
注1:具体应用如将virtual interface传递到环境中(实现DUT与TB的交互)或传递配置对象(config object)到环境或变量的设置(如命令行中设置参数).
2. 原理
问题1: 资源存放在什么地方, 队列/关联数组/动态数组?
(1) 资源存放在uvm_resource_pool类的关联数组中;
(2) uvm_resources是uvm_resource_pool类的全局唯一实例,用于存储和释放配置资源信息;
1 class uvm_resource_types; 2 3 // types uses for setting overrides 4 typedef bit[1:0] override_t; 5 typedef enum override_t { TYPE_OVERRIDE = 2'b01, 6 NAME_OVERRIDE = 2'b10 } override_e; 7 8 // general purpose queue of resourcex 9 typedef uvm_queue#(uvm_resource_base) rsrc_q_t; 10 11 // enum for setting resource search priority 12 typedef enum { PRI_HIGH, PRI_LOW } priority_e; 13 14 // access record for resources. A set of these is stored for each 15 // resource by accessing object. It's updated for each read/write. 16 typedef struct 17 { 18 time read_time; 19 time write_time; 20 int unsigned read_count; 21 int unsigned write_count; 22 } access_t; 23 24 endclass
//src/base/uvm_resource.svh
1 class uvm_resource_pool; 2 static local uvm_resource_pool rp = get(); 3 4 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rtab [string]; //name table; 5 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t ttab [uvm_resource_base]; //type table; 6 get_t get_record [$]; // history of gets 7 8 local function new(); 9 endfunction 10 11 12 // Function: get 13 // 14 // Returns the singleton handle to the resource pool 15 16 static function uvm_resource_pool get(); 17 if(rp == null) 18 rp = new(); 19 return rp; 20 endfunction 21 22 ... 23 endclass
1 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // static global resource pool handle 3 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 4 const uvm_resource_pool uvm_resources = uvm_resource_pool::get();
(3) uvm_resources中有两个resource数组用于存放配置信息,这两个数组一个是由层次名字索引,一个是由类型索引;
注1: rtab是一个联合数组,索引为string,内容是一个队列;
注2: ttab是关联数组,索引是uvm_resource_base类型,内容也是队列;
1 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rtab [string]; 2 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t ttab [uvm_resource_base];
(4) uvm_config_db::set()通过层次和变量名,将这些信息放置到uvm_pkg唯一的全局变量uvm_pkg::uvm_resources中;
(5) uvm_config_db::get()通过层次,在uvm_resources已有的配置信息池中,索引到该配置;
问题2: 资源以什么形式存放?
(1) uvm_resource#(type T)类(派生于uvm_resource_base),可以用来存放任意数据的容器数据结构;
(2) uvm_resource中会包含资源名称(name),类型(type),可见范围(scope)和值(value)等信息;
1 virtual class uvm_resource_base extends uvm_object; 2 3 protected string scope; 4 protected bit modified; 5 protected bit read_only; 6 7 uvm_resource_types::access_t access[string]; 8 9 // variable: precedence 10 // 11 // This variable is used to associate a precedence that a resource 12 // has with respect to other resources which match the same scope 13 // and name. Resources are set to the <default_precedence> initially, 14 // and may be set to a higher or lower precedence as desired. 15 16 int unsigned precedence; 17 18 // variable: default_precedence 19 // 20 // The default precedence for an resource that has been created. 21 // When two resources have the same precedence, the first resource 22 // found has precedence. 23 // 24 25 static int unsigned default_precedence = 1000; 26 27 // Function: new 28 // 29 // constructor for uvm_resource_base. The constructor takes two 30 // arguments, the name of the resource and a regular expression which 31 // represents the set of scopes over which this resource is visible. 32 33 function new(string name = "", string s = "*"); 34 super.new(name); 35 set_scope(s); 36 modified = 0; 37 read_only = 0; 38 precedence = default_precedence; 39 endfunction 40 41 ... 42 endclass
1 class uvm_resource #(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_base; 2 3 typedef uvm_resource#(T) this_type; 4 5 // singleton handle that represents the type of this resource 6 static this_type my_type = get_type(); 7 8 // Can't be rand since things like rand strings are not legal. 9 protected T val; 10 11 ... 12 //---------------------- 13 // Group: Type Interface 14 //---------------------- 15 // 16 // Resources can be identified by type using a static type handle. 17 // The parent class provides the virtual function interface 18 // <get_type_handle>. Here we implement it by returning the static type 19 // handle. 20 21 // Function: get_type 22 // 23 // Static function that returns the static type handle. The return 24 // type is this_type, which is the type of the parameterized class. 25 26 static function this_type get_type(); 27 if(my_type == null) 28 my_type = new(); 29 return my_type; 30 endfunction 31 ... 32 endclass
1 class uvm_resource #(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_base; 2 3 typedef uvm_resource#(T) this_type; 4 5 ... 6 // Function: get_by_name 7 // 8 // looks up a resource by ~name~ in the name map. The first resource 9 // with the specified name, whose type is the current type, and is 10 // visible in the specified ~scope~ is returned, if one exists. The 11 // ~rpterr~ flag indicates whether or not an error should be reported 12 // if the search fails. If ~rpterr~ is set to one then a failure 13 // message is issued, including suggested spelling alternatives, based 14 // on resource names that exist in the database, gathered by the spell 15 // checker. 16 17 static function this_type get_by_name(string scope, 18 string name, 19 bit rpterr = 1); 20 21 uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get(); 22 uvm_resource_base rsrc_base; 23 this_type rsrc; 24 string msg; 25 26 rsrc_base = rp.get_by_name(scope, name, my_type, rpterr); 27 if(rsrc_base == null) 28 return null; 29 30 if(!$cast(rsrc, rsrc_base)) begin 31 if(rpterr) begin 32 $sformat(msg, "Resource with name %s in scope %s has incorrect type", name, scope); 33 `uvm_warning("RSRCTYPE", msg); 34 end 35 return null; 36 end 37 38 return rsrc; 39 40 endfunction 41 42 // Function: get_by_type 43 // 44 // looks up a resource by ~type_handle~ in the type map. The first resource 45 // with the specified ~type_handle~ that is visible in the specified ~scope~ is 46 // returned, if one exists. If there is no resource matching the specifications, 47 // ~null~ is returned. 48 49 static function this_type get_by_type(string scope = "", 50 uvm_resource_base type_handle); 51 52 uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get(); 53 uvm_resource_base rsrc_base; 54 this_type rsrc; 55 string msg; 56 57 if(type_handle == null) 58 return null; 59 60 rsrc_base = rp.get_by_type(scope, type_handle); 61 if(rsrc_base == null) 62 return null; 63 64 if(!$cast(rsrc, rsrc_base)) begin 65 $sformat(msg, "Resource with specified type handle in scope %s was not located", scope); 66 `uvm_warning("RSRCNF", msg); 67 return null; 68 end 69 70 return rsrc; 71 72 endfunction 73 74 ... 75 endclass
问题3: 资源如何存取? 怎么通过set函数把要共享的资源放入要存放的地方,怎么使用get函数把资源从存放的地方取出?
(1) uvm_resource_db#(type T)类;
1 class uvm_resource_db #(type T=uvm_object); 2 3 typedef uvm_resource #(T) rsrc_t; 4 5 protected function new(); 6 endfunction 7 8 // function: get_by_type 9 // 10 // Get a resource by type. The type is specified in the db 11 // class parameter so the only argument to this function is the 12 // ~scope~. 13 14 static function rsrc_t get_by_type(string scope); 15 return rsrc_t::get_by_type(scope, rsrc_t::get_type()); 16 endfunction 17 18 // function: get_by_name 19 // 20 // Imports a resource by ~name~. The first argument is the current 21 // ~scope~ of the resource to be retrieved and the second argument is 22 // the ~name~. The ~rpterr~ flag indicates whether or not to generate 23 // a warning if no matching resource is found. 24 25 static function rsrc_t get_by_name(string scope, 26 string name, 27 bit rpterr=1); 28 29 return rsrc_t::get_by_name(scope, name, rpterr); 30 endfunction // function: read_by_name 31 // 32 // locate a resource by ~name~ and ~scope~ and read its value. The value 33 // is returned through the output argument ~val~. The return value is a bit 34 // that indicates whether or not the read was successful. The ~accessor~ 35 // is used for auditing. 36 static function bit read_by_name(input string scope, 37 input string name, 38 inout T val, input uvm_object accessor = null); 39 40 rsrc_t rsrc = get_by_name(scope, name); //retrieve uvm_resource; 41 42 if(uvm_resource_db_options::is_tracing()) 43 m_show_msg("RSRCDB/RDBYNAM","Resource", "read", scope, name, accessor, rsrc); 44 45 if(rsrc == null) 46 return 0; 47 48 val = rsrc.read(accessor); //retrieve value stored in uvm_resource; 49 50 return 1; 51 52 endfunction 53 54 // function: read_by_type 55 // 56 // Read a value by type. The value is returned through the output 57 // argument ~val~. The ~scope~ is used for the lookup. The return 58 // value is a bit that indicates whether or not the read is successful. 59 // The ~accessor~ is used for auditing. 60 static function bit read_by_type(input string scope, 61 inout T val, 62 input uvm_object accessor = null); 63 64 rsrc_t rsrc = get_by_type(scope); //retrieve uvm_resource; 65 66 if(uvm_resource_db_options::is_tracing()) 67 m_show_msg("RSRCDB/RDBYTYP", "Resource","read", scope, "", accessor, rsrc); 68 69 if(rsrc == null) 70 return 0; 71 72 val = rsrc.read(accessor); //retrieve value stored in uvm_resource; 73 74 return 1; 75 76 endfunction 77 78 ... 79 endclass
2.1. 资源共享所记录的信息
(1) 以uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this, “tb.env.agent.driver”, “ifg_num”, 8)为例:
问题1: 资源的类型? int;
问题2: 谁进行了资源的存放(由最顶层的case,还是tb,还是env)? this,即顶层的case;
问题3: 这个资源要共享给谁? tb.env.agent.driver(对应uvm_resource new函数中的scope), ifg_num(对应uvm_resource new函数中的name);
问题4: 共享资源的值? 8.
class uvm_config_db#(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_db#(T); ... static function void set(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, T value); uvm_root top; uvm_phase curr_phase; uvm_resource#(T) r; bit exists; string lookup; uvm_pool#(string,uvm_resource#(T)) pool; string rstate; uvm_coreservice_t cs = uvm_coreservice_t::get(); //take care of random stability during allocation process p = process::self(); if(p != null) rstate = p.get_randstate(); top = cs.get_root(); curr_phase = top.m_current_phase; if(cntxt == null) cntxt = top; if(inst_name == "") inst_name = cntxt.get_full_name(); else if(cntxt.get_full_name() != "") inst_name = {cntxt.get_full_name(), ".", inst_name}; if(!m_rsc.exists(cntxt)) begin m_rsc[cntxt] = new; end pool = m_rsc[cntxt]; // Insert the token in the middle to prevent cache // oddities like i=foobar,f=xyz and i=foo,f=barxyz. // Can't just use '.', because '.' isn't illegal // in field names lookup = {inst_name, "__M_UVM__", field_name}; if(!pool.exists(lookup)) begin r = new(field_name, inst_name); pool.add(lookup, r); end else begin r = pool.get(lookup); exists = 1; end if(curr_phase != null && curr_phase.get_name() == "build") r.precedence = uvm_resource_base::default_precedence - (cntxt.get_depth()); else r.precedence = uvm_resource_base::default_precedence; r.write(value, cntxt); if(exists) begin uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get(); rp.set_priority_name(r, uvm_resource_types::PRI_HIGH); end else begin //Doesn't exist yet, so put it in resource db at the head. r.set_override(); end //trigger any waiters if(m_waiters.exists(field_name)) begin m_uvm_waiter w; for(int i=0; i<m_waiters[field_name].size(); ++i) begin w = m_waiters[field_name].get(i); if(uvm_re_match(uvm_glob_to_re(inst_name),w.inst_name) == 0) ->w.trigger; end end if(p != null) p.set_randstate(rstate); if(uvm_config_db_options::is_tracing()) m_show_msg("CFGDB/SET", "Configuration","set", inst_name, field_name, cntxt, r); endfunction ... endclass
(2) 与以上记录内容相对应的变量如下:
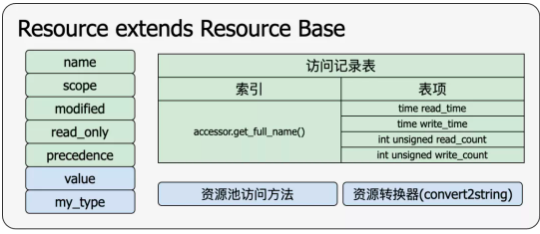
(2.1) uvm_resource_base中有一个整型变量int unsigned precedence来存放优先级信息.
(2.2) uvm_resource_base中有一个字符串变量scope用来存放目标路径信息,即protected string scope;
(2.3) uvm_resource#(type T)中有一个变量val用来存放变量值,即protected T val.
2.2. uvm_resource #(type T) (资源的存放形式)
(1)uvm_resource是uvm_resource_base的参数化子类;
1 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // Class: uvm_resource #(T) 3 // 4 // Parameterized resource. Provides essential access methods to read 5 // from and write to the resource database. 6 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 8 class uvm_resource #(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_base; 9 10 typedef uvm_resource#(T) this_type; 11 12 // singleton handle that represents the type of this resource 13 static this_type my_type = get_type(); 14 15 // Can't be rand since things like rand strings are not legal. 16 protected T val; 17 ... 18 endclass
(2) uvm_resource在uvm_resource_base的基础上又添加了一个value成员变量,之所以放到uvm_resource中,是因为uvm_resource创建时已经知道了资源的类型;
1 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // Class: uvm_resource_base 3 // 4 // Non-parameterized base class for resources. Supports interfaces for 5 // scope matching, and virtual functions for printing the resource and 6 // for printing the accessor list 7 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 8 9 virtual class uvm_resource_base extends uvm_object; 10 11 protected string scope; 12 protected bit modified; 13 protected bit read_only; 14 15 uvm_resource_types::access_t access[string]; 16 17 // variable: precedence 18 // 19 // This variable is used to associate a precedence that a resource 20 // has with respect to other resources which match the same scope 21 // and name. Resources are set to the <default_precedence> initially, 22 // and may be set to a higher or lower precedence as desired. 23 24 int unsigned precedence; 25 26 // variable: default_precedence 27 // 28 // The default precedence for an resource that has been created. 29 // When two resources have the same precedence, the first resource 30 // found has precedence. 31 // 32 33 static int unsigned default_precedence = 1000; 34 ... 35 36 endclass
2.2.1. uvm_resource_base
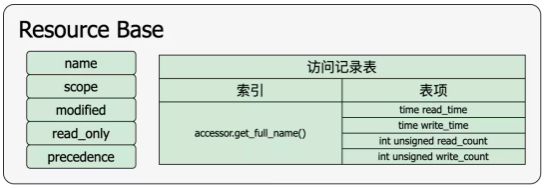
(1) uvm_resource_base是资源的非参数化基类,它描述一个资源该有的属性,包括资源的名字(name),可见范围(scope,定义哪些层次范围内能看到该资源),只读属性(read-only)、修改标记(modified)、访问记录表(access[string],string记录访问者的名字,value包含访问者对该资源的读写次数和最近一次的读写时间)以及优先级(precedence).
2.2.2. functions/tasks of resource
1 class uvm_resource #(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_base; 2 ... 3 // Function: get_by_name 4 // 5 // looks up a resource by ~name~ in the name map. The first resource 6 // with the specified name, whose type is the current type, and is 7 // visible in the specified ~scope~ is returned, if one exists. The 8 // ~rpterr~ flag indicates whether or not an error should be reported 9 // if the search fails. If ~rpterr~ is set to one then a failure 10 // message is issued, including suggested spelling alternatives, based 11 // on resource names that exist in the database, gathered by the spell 12 // checker. 13 14 static function this_type get_by_name(string scope, 15 string name, 16 bit rpterr = 1); 17 18 uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get(); 19 uvm_resource_base rsrc_base; 20 this_type rsrc; 21 string msg; 22 23 rsrc_base = rp.get_by_name(scope, name, my_type, rpterr); 24 if(rsrc_base == null) 25 return null; 26 27 if(!$cast(rsrc, rsrc_base)) begin 28 if(rpterr) begin 29 $sformat(msg, "Resource with name %s in scope %s has incorrect type", name, scope); 30 `uvm_warning("RSRCTYPE", msg); 31 end 32 return null; 33 end 34 35 return rsrc; 36 37 endfunction 38 // Function: get_by_type 39 // 40 // looks up a resource by ~type_handle~ in the type map. The first resource 41 // with the specified ~type_handle~ that is visible in the specified ~scope~ is 42 // returned, if one exists. If there is no resource matching the specifications, 43 // ~null~ is returned. 44 45 static function this_type get_by_type(string scope = "", 46 uvm_resource_base type_handle); 47 48 uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get(); 49 uvm_resource_base rsrc_base; 50 this_type rsrc; 51 string msg; 52 53 if(type_handle == null) 54 return null; 55 56 rsrc_base = rp.get_by_type(scope, type_handle); 57 if(rsrc_base == null) 58 return null; 59 60 if(!$cast(rsrc, rsrc_base)) begin 61 $sformat(msg, "Resource with specified type handle in scope %s was not located", scope); 62 `uvm_warning("RSRCNF", msg); 63 return null; 64 end 65 66 return rsrc; 67 68 endfunction 69 70 //---------------------------- 71 // Group: Read/Write Interface 72 //---------------------------- 73 // 74 // <read> and <write> provide a type-safe interface for getting and 75 // setting the object in the resource container. The interface is 76 // type safe because the value argument for <write> and the return 77 // value of <read> are T, the type supplied in the class parameter. 78 // If either of these functions is used in an incorrect type context 79 // the compiler will complain. 80 81 // Function: read 82 // 83 // Return the object stored in the resource container. If an ~accessor~ 84 // object is supplied then also update the accessor record for this 85 // resource. 86 87 function T read(uvm_object accessor = null); 88 record_read_access(accessor); 89 return val; 90 endfunction 91 92 // Function: write 93 // Modify the object stored in this resource container. If the 94 // resource is read-only then issue an error message and return 95 // without modifying the object in the container. If the resource is 96 // not read-only and an ~accessor~ object has been supplied then also 97 // update the accessor record. Lastly, replace the object value in 98 // the container with the value supplied as the argument, ~t~, and 99 // release any processes blocked on 100 // <uvm_resource_base::wait_modified>. If the value to be written is 101 // the same as the value already present in the resource then the 102 // write is not done. That also means that the accessor record is not 103 // updated and the modified bit is not set. 104 105 function void write(T t, uvm_object accessor = null); 106 107 if(is_read_only()) begin 108 uvm_report_error("resource", $sformatf("resource %s is read only -- cannot modify", get_name())); 109 return; 110 end 111 112 // Set the modified bit and record the transaction only if the value 113 // has actually changed. 114 if(val == t) 115 return; 116 117 record_write_access(accessor); 118 119 // set the value and set the dirty bit 120 val = t; 121 modified = 1; 122 endfunction 123 124 ... 125 endclass
2.3. uvm_resource_pool (资源放在什么地方)
1 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // Class: uvm_resource_pool 3 // 4 // The global (singleton) resource database. 5 // 6 // Each resource is stored both by primary name and by type handle. The 7 // resource pool contains two associative arrays, one with name as the 8 // key and one with the type handle as the key. Each associative array 9 // contains a queue of resources. Each resource has a regular 10 // expression that represents the set of scopes over which it is visible.
1 // The scope is stored in the resource itself (not in the pool) so 2 // whether you get by name or by type the resource's visibility is 3 // the same.
(1) resource pool包含两个关联数组,一个用名字作为索引,一个用类型作为索引; 每个索引对应的值都是一个resources队列;
(2)每一个resource都通过名字和type进行存储;
(3)每一个resource都有一个正则表达式,用于代表哪些范围可见该资源; scope信息存储在resource内,所以无论是通过get_by_name还是get_by_type, resource的scope是相同的;
1 // 2 //| +------+------------+ +------------+------+ 3 //| | name | rsrc queue | | rsrc queue | type | 4 //| +------+------------+ +------------+------+ 5 //| | | | | | | 6 //| +------+------------+ +-+-+ +------------+------+ 7 //| | | | | | |<--+---* | T | 8 //| +------+------------+ +-+-+ +-+-+ +------------+------+ 9 //| | A | *---+-->| | | | | | | 10 //| +------+------------+ +-+-+ | +------------+------+ 11 //| | | | | | | | | 12 //| +------+------------+ +-------+ +-+ +------------+------+ 13 //| | | | | | | | | 14 //| +------+------------+ | | +------------+------+ 15 //| | | | V V | | | 16 //| +------+------------+ +------+ +------------+------+ 17 //| | | | | rsrc | | | | 18 //| +------+------------+ +------+ +------------+------+ 19 //
(4)上面方框图展示了一个名字为A,类型为T的资源在resource_pool内是怎么存储的;
(4.1) 对于type T, resource_pool在type map内包含一个与之对应的entry; 对于name A, resource_pool在name type内包含一个与之对应的entry;
(4.2) resource_pool的两个关联数组的queue里面都会包含一个 resource entry,该resource的name为A, type为T;
(4.3) name_map中,对于索引为A的resource queue,其内部可能包含名字为A,但类型可能是T也可能不是T的资源; 类似地, type map中,对于索引为T的resource queue,其内部可能包含类型为T,但名字可能是A也可能不是A的资源;
(5) 可以通过调用resource_pool.set将资源添加到pool中,通过调用get_by_type或者get_by_name可以从resource_pool中获取该resource;
2.3.1. functions/tasks of resource_pool




1 class uvm_resource_pool; 2 3 static local uvm_resource_pool rp = get(); 4 5 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rtab [string]; 6 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t ttab [uvm_resource_base]; 7 8 get_t get_record [$]; // history of gets 9 10 local function new(); 11 endfunction 12 ... 13 // Function: get 14 // 15 // Returns the singleton handle to the resource pool 16 17 static function uvm_resource_pool get(); 18 if(rp == null) 19 rp = new(); 20 return rp; 21 endfunction 22 23 // Function: set 24 // 25 // Add a new resource to the resource pool. The resource is inserted 26 // into both the name map and type map so it can be located by 27 // either. 28 // 29 // An object creates a resources and ~sets~ it into the resource pool. 30 // Later, other objects that want to access the resource must ~get~ it 31 // from the pool 32 // 33 // Overrides can be specified using this interface. Either a name 34 // override, a type override or both can be specified. If an 35 // override is specified then the resource is entered at the front of 36 // the queue instead of at the back. It is not recommended that users 37 // specify the override parameter directly, rather they use the 38 // <set_override>, <set_name_override>, or <set_type_override> 39 // functions. 40 // 41 function void set (uvm_resource_base rsrc, 42 uvm_resource_types::override_t override = 0); 43 44 uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rq; 45 string name; 46 uvm_resource_base type_handle; 47 48 // If resource handle is ~null~ then there is nothing to do. 49 if(rsrc == null) 50 return; 51 52 // insert into the name map. Resources with empty names are 53 // anonymous resources and are not entered into the name map 54 name = rsrc.get_name(); 55 if(name != "") begin 56 if(rtab.exists(name)) 57 rq = rtab[name]; 58 else 59 rq = new(); 60 61 // Insert the resource into the queue associated with its name. 62 // If we are doing a name override then insert it in the front of 63 // the queue, otherwise insert it in the back. 64 if(override & uvm_resource_types::NAME_OVERRIDE) 65 rq.push_front(rsrc); 66 else 67 rq.push_back(rsrc); 68 69 rtab[name] = rq; 70 end 71 72 // insert into the type map 73 type_handle = rsrc.get_type_handle(); 74 if(ttab.exists(type_handle)) 75 rq = ttab[type_handle]; 76 else 77 rq = new(); 78 79 // insert the resource into the queue associated with its type. If 80 // we are doing a type override then insert it in the front of the 81 // queue, otherwise insert it in the back of the queue. 82 if(override & uvm_resource_types::TYPE_OVERRIDE) 83 rq.push_front(rsrc); 84 else 85 rq.push_back(rsrc); 86 ttab[type_handle] = rq; 87 88 endfunction 89 90 ... 91 endclass
2.3.2 uvm_resource_types

2.4. uvm_resource_db(访问存在uvm_resource_pool中的uvm_resource/资源的接口)
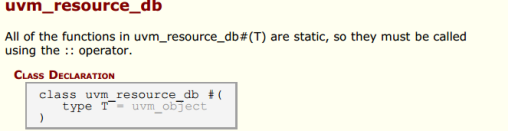
1 // The <uvm_resource_db> class provides a convenience interface for 2 // the resources facility. In many cases basic operations such as 3 // creating and setting a resource or getting a resource could take 4 // multiple lines of code using the interfaces in <uvm_resource_base> or 5 // <uvm_resource#(T)>. The convenience layer in <uvm_resource_db> 6 // reduces many of those operations to a single line of code. 7 // 8 // If the run-time ~+UVM_RESOURCE_DB_TRACE~ command line option is 9 // specified, all resource DB accesses (read and write) are displayed.
(1) 资源的存取可以通过uvm_resource_db类实现;相较于直接使用uvm_resource_base或者uvm_resource的方法,通过使用uvm_resource_db提供的静态方法可以容易实现资源的存取;
以uvm_resource_db::set为例描述,uvm_resource_db::set实现往uvm_resource_pool中写入资源,set函数的四个参数:scope表示路径信息; name表示名字; val表示共享的资源;
1 class uvm_resource_db #(type T=uvm_object); 2 3 ... 4 // function: set 5 // 6 // Create a new resource, write a ~val~ to it, and set it into the 7 // database using ~name~ and ~scope~ as the lookup parameters. The 8 // ~accessor~ is used for auditing. 9 static function void set(input string scope, input string name, 10 T val, input uvm_object accessor = null); 11 12 rsrc_t rsrc = new(name, scope); //typedef uvm_resource #(T) rsrc_t; 13 rsrc.write(val, accessor); //uvm_resource.write(); 14 rsrc.set(); //put uvm_resource into uvm_resource_pool; 15 16 if(uvm_resource_db_options::is_tracing()) 17 m_show_msg("RSRCDB/SET", "Resource","set", scope, name, accessor, rsrc); 18 endfunction 19 ... 20 endclass
(2) 该类的所有成员变量都是静态的,所以,是否实例化并不重要.

2.4.1. functions/tasks of uvm_resource_db
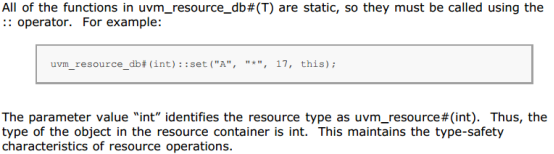


2.5. uvm_config_db(访问存在uvm_resource_pool中的uvm_resource/资源的接口)









【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?