廖雪峰Java11多线程编程-1线程的概念-5中断线程
1.中断线程:
- 如果线程需要执行一个长时间任务,就可能需要中断线程。场景:从网络上下载一个100M的文件,用户在下载过程中中断下载任务的执行。
- 中断线程就是其他线程给该线程发一个信号,该线程收到信号后结束执行run()方法
1.1中断线程
需要检测isInterrupted()标志,其他线程通过调用interrupt()方法中断该线程
class HelloThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
while(!isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Thread t = new HelloThread();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
t.interrupt();
}
}
1.2中断等待状态的线程
如果线程处于等待状态,该线程会捕获InterruptedException。捕获到InterruptedException说明有其他线程对其调用了interrupt()方法,通常情况下该线程应该立即结束运行。
class HelloThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
while(!isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("Hello");
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
}
}
1.3设置running标志位中断线程
如果其他线程把HelloThread的标志位置设为false,while循环检测到running的值为false后,就会退出循环,结束run方法。
注意:线程间共享变量需要使用volatile关键字标记,确保线程能读取到更新后的变量值
class HelloThread extends Thread{
public volatile boolean running = true;
public void run(){
while(running){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
HelloThread t = new HelloThread();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
t.running = false;
}
}
 问题:为什么要对线程间共享变量使用关键字volatile声明呢?
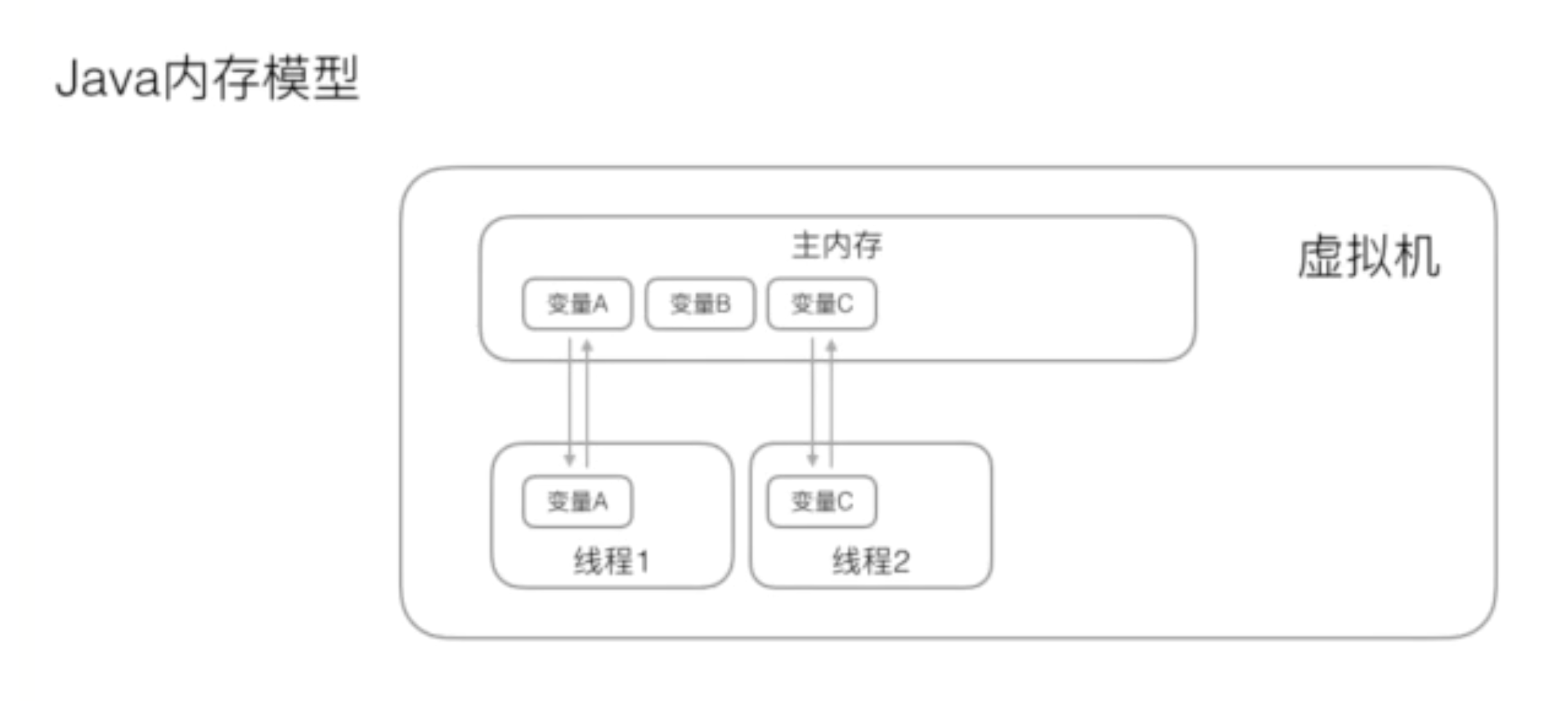
这涉及到Java的内存模型。在Java虚拟机中,变量的值保存在主内存中,但是当线程访问一个变量的时候,会先获取一个副本,并且保存自己的工作内存中。如果线程修改变量的值,虚拟机会在某个时刻把修改后的值回写到主内存,但是这个时间是不确定的。这会导致如果一个线程更新了某个变量,另一个线程读取的变量还是更新之前的。
问题:为什么要对线程间共享变量使用关键字volatile声明呢?
这涉及到Java的内存模型。在Java虚拟机中,变量的值保存在主内存中,但是当线程访问一个变量的时候,会先获取一个副本,并且保存自己的工作内存中。如果线程修改变量的值,虚拟机会在某个时刻把修改后的值回写到主内存,但是这个时间是不确定的。这会导致如果一个线程更新了某个变量,另一个线程读取的变量还是更新之前的。
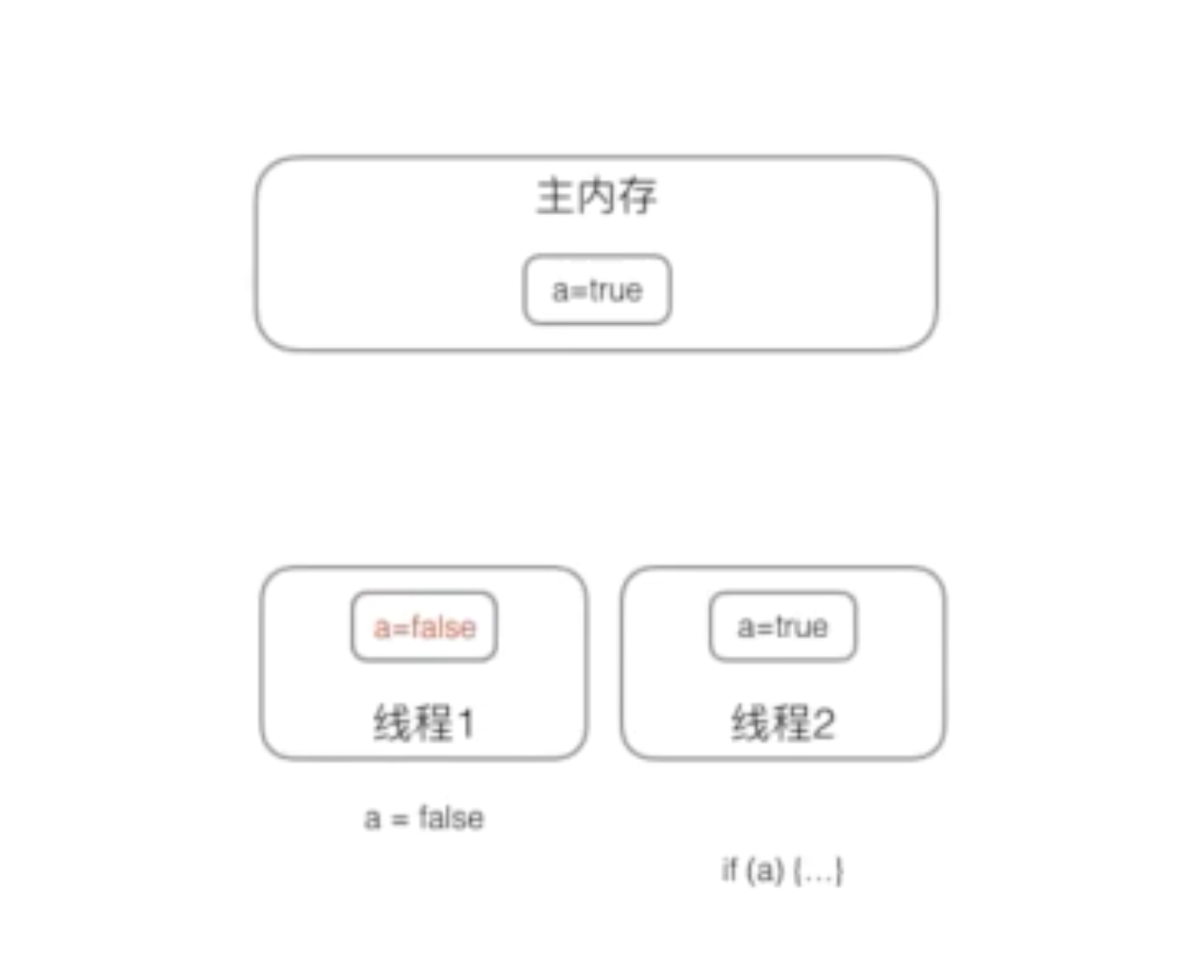 如主内存中a的值是true。线程1执行时,先读取主内存中a的值(true),将a的值改写为false。但此时仅仅是线程1变量a的副本变为false,主内存中变量a还是true。
什么时候虚拟机将线程1修改后的值回写主内存,将a的值更新为false。这个时间是不确定的。
这时执行线程2,线程2读取的值可能仍然是true,而不是线程1更新后的false。
如主内存中a的值是true。线程1执行时,先读取主内存中a的值(true),将a的值改写为false。但此时仅仅是线程1变量a的副本变为false,主内存中变量a还是true。
什么时候虚拟机将线程1修改后的值回写主内存,将a的值更新为false。这个时间是不确定的。
这时执行线程2,线程2读取的值可能仍然是true,而不是线程1更新后的false。
volatile关键字的目的是告诉虚拟机:
- 每次访问变量时,总是获取主内存的最新值
- 每次修改变量后,立刻回写到到主内存
volatile关键字解决的是可见性问题:
- 当一个线程修改了某个共享变量的值,其他线程能够立刻看到修改后的值
2示例
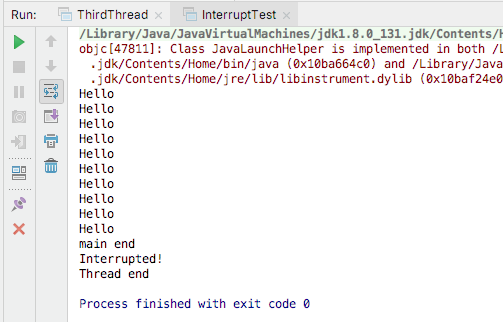
2.1使用interrupt()中断线程
class InterrptThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
while(!isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("Hello");
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
System.out.println("Interrupted!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Thread end");
}
}
public class InterruptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Thread t = new InterrptThread();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
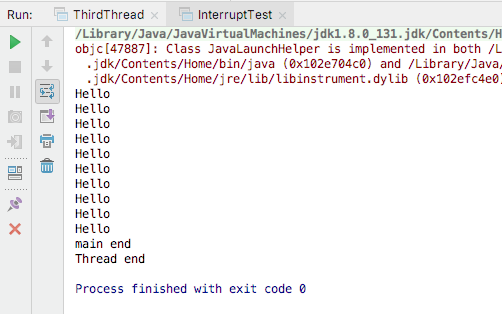
 ### 2.2使用标志位中断线程
```#java
class InterrptThread extends Thread{
volatile boolean running = true;
public void run(){
while(running){
System.out.println("Hello");
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
System.out.println("Interrupted!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Thread end");
}
}
public class InterruptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
InterrptThread t = new InterrptThread();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
t.running = false;
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
```
### 2.2使用标志位中断线程
```#java
class InterrptThread extends Thread{
volatile boolean running = true;
public void run(){
while(running){
System.out.println("Hello");
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
System.out.println("Interrupted!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Thread end");
}
}
public class InterruptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
InterrptThread t = new InterrptThread();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
t.running = false;
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
```
3总结:
- 调用interrupt()方法可以中断一个线程
- 通过检测isInterrupted()标志获取当前线程是否已中断
- 如果线程处于等待状态,该线程会捕获InterruptedException
- isInterrupted()为true或者捕获了InterruptedException都应该立刻结束
- 通过标志位判断需要正确使用volatile关键字
- volatile关键字解决了共享变量在线程间的可见性问题


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号