代码随想录算法训练营第十六天 | 104.二叉树的最大深度 111.二叉树的最小深度 222.二叉树的节点个数
104.二叉树的最大深度
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数(前序遍历)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数(后序遍历)
递归法
// 二叉树的最大高度和最大深度相同,可以求最大高度来表示最大深度
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
if(node == nullptr) return 0;
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left); // 左
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right); // 右
int height = 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight); //中
return height;
}
};
层序遍历法
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
// 每一层出队时记录深度
depth++;
while(size--) {
TreeNode* temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(temp->left) que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) que.push(temp->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
111.二叉树的最小深度
注:最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量,空节点不算叶节点
class Solution {
public:
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
if(node == nullptr) return 0;
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left); // 左
int rightHeignt = getHeight(node->right); // 右
if(node->left == nullptr && node->right) return 1 + rightHeignt; // 中
if(node->right == nullptr && node->left) return 1 + leftHeight;
else return 1 + min(leftHeight, rightHeignt);
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
};
222.二叉树的节点个数
深度优先遍历
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
- 空间复杂度:o(logn)
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int leftCount = countNodes(root->left);
int rightCount = countNodes(root->right);
int result = 1 + leftCount + rightCount;
return result;
}
};
完全二叉树
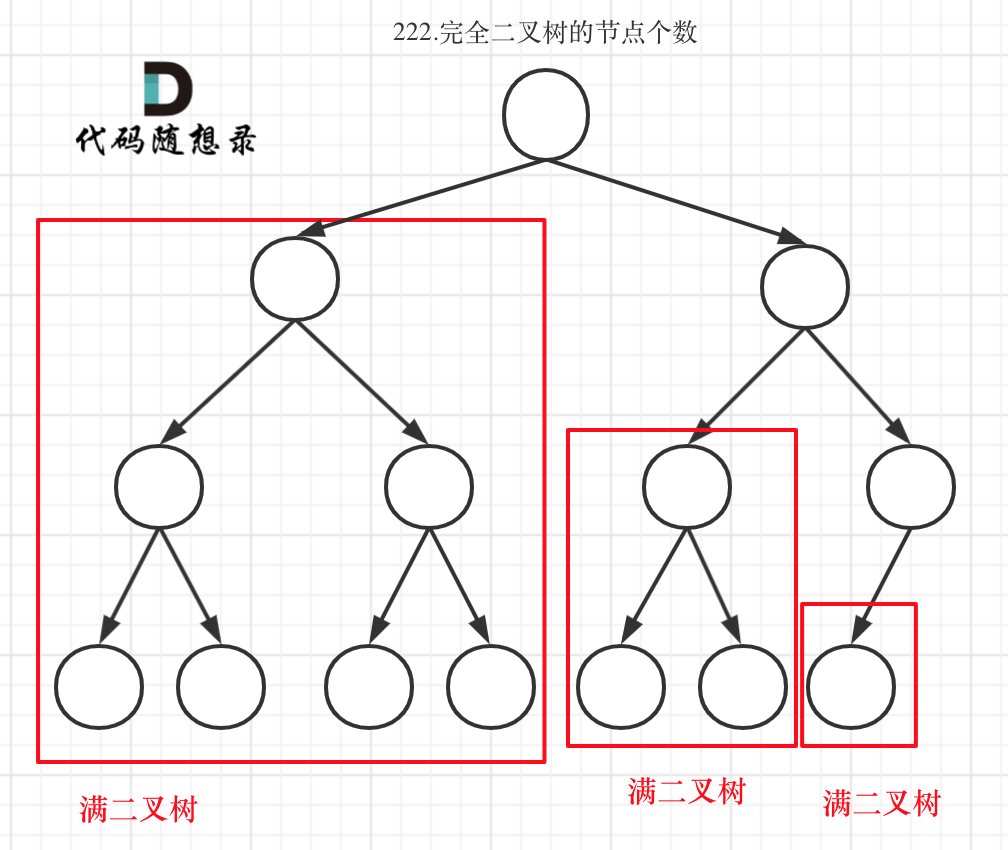
- 在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树。
- 满二叉树的节点个数为2n - 1
- 时间复杂度:o(logn × logn)
- 空间复杂度:o(logn)
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int leftDepth = 0;
int rightDepth = 0;
TreeNode * left = root->left;
TreeNode * right = root->right;
while(left) {
leftDepth++;
left = left->left;
}
while(right) {
rightDepth++;
right = right->right;
}
// 当前子树为满二叉树,则通过计算获得子树的节点个数
if(leftDepth == rightDepth) return (2 << leftDepth) - 1;
else return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号