树状数组及应用
1.树状数组的原理
在程序设计时,我们需要维护一个一维数组A的前缀和S,设S[i]=A[1]+A[2]+…+A[i]。
如果我们修改了任意一个元素A[i]的值,则相关的前缀和S[i]、S[i+1]、…、S[n]都会发生变化。若采用传统的线性顺序扫描方法求连续数组元素的和,则每次修改A[i]后,调整前缀和S的时间复杂度为O(n)。若修改数组A中元素的频度为m,则调整前缀和S的时间复杂度为O(m*n)。
为提高维护前缀和的效率,可引入“树状数组”。树状数组通过将线性结构转换成伪树状结构(线性结构只能逐个扫描元素,而树状结构可以实现跳跃式扫描),使得修改数组元素值后,维护前缀和的时间复杂度为O(log2n),从而大大提高整体效率。
设有数组A[n],相应的树状数组为C[n],当n=9时,其树形结构如图1所示。
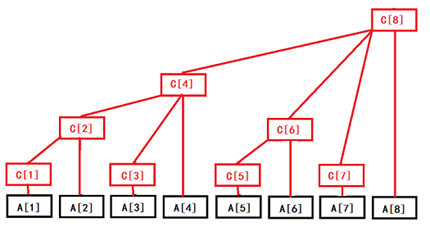
图1 树状数组结构示意图
在图1中,设黑色数组元素A[1]~A[8]代表原来的数组A,红色数组元素C[1]~C[8]就代表了树状数组C。若图中每个结点元素存放其子结点元素值的和,则有
C[1] = A[1];
C[2] = A[1] + A[2];
C[3] = A[3];
C[4] = A[1] + A[2] + A[3] + A[4];
C[5] = A[5];
C[6] = A[5] + A[6];
C[7] = A[7];
C[8] = A[1] + A[2] + A[3] + A[4] + A[5] + A[6] + A[7] + A[8];
可以发现,树状数组各元素的值是有规律的
C[i] = A[i - 2k+1] + A[i - 2k+2] + ... + A[i]; // k为i的二进制中最右端1的位号
例如i =6时,其二进制数为110,最右端1的位置为1,故k =1,C[6]=A[6-2+1]+A[6];
i = 8时,其二进制数为1000,最右端1的位置为3,故k = 3,C[8]=A[8-8+1]+…+A[8]。
(1)求前缀和。
我们先来看如何利用树状数组C,求A数组中前i项的和。
例如,i=5时,
S[5]=A[1]+A[2]+A[3]+A[4]+A[5] ;
由图1知,C[4]=A[1]+A[2]+A[3]+A[4]; C[5]=A[5];
故: S[5]=C[4]+C[5];
序号写为二进制可得:S[(101)]=C[(100)]+C[(101)]。
再如,i=7时,
S[7]=A[1]+A[2]+A[3]+A[4]+A[5]+A[6]+A[7] ;
由图1知,C[4]=A[1]+A[2]+A[3]+A[4]; C[6]=A[5]+A[6]; C[7]=A[7];
故: S[7]=C[4]+C[6]+C[7];
序号写为二进制可得:S[(111)]=C[(100)]+C[(110)]+C[(111)];
观察上面的两个示例,树状数组其根本实质就是二进制的应用。
由此,可将求前缀和的操作写成如下函数:
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while(i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
其中,函数lowbit(i)的返回值为2k,k为i的二进制中最右端1的位号。
下面以i=7为例模拟函数getsum(7)的执行过程。
i=7(二进制数为111),res+=C[7]=C[7], lowbit(7)=001(二进制表示,对应1),i=7-1=6;
i=6(二进制数为110),res+=C[6], lowbit(6)=010(二进制表示,对应2),i=6-2=4;
i=4(二进制数为100),res+=C[4], lowbit(4)=100(二进制表示,对应4),i=4-4=0;
i=0,结束循环,返回res(=C[7]+C[6]+C[4])。
这样,利用树状数组能快速求任意区间[a,b]的和:A[a] + A[a+1] +…+ A[b],直接调用getsum(b)-getsum(a-1)即可。
(2)单点更新。
下面我们再讨论树状数组如何生成并维护。
当修改数组A中的某一个元素A[i]的值时 应当如何更新数组树状C呢?
当修改A[i]的值时,可以从C[i]往根结点一路上溯,调整这条路线上的所有C[k]即可。
例如,修改A[1]时,需要向上更新C[1] 、C[2]、C[4]、C[8],表示成二进制对应为:
C[(001)]、C[(010)]、C[(100)]、C[(1000)]
再如,修改A[5]时,需要向上更新C[5] 、C[6]、C[8],表示成二进制对应为:
C[(101)]、C[(110)]、C[(1000)]
观察上面的两个示例,单点更新其实与求前缀和互为逆运算。
由此,可将单点更新的操作写成如下函数:
void update(int i,int value) // 修改A[i]值使其增加value后,更新树状数组
{
while (i<=n)
{
c[i]+=value;
i+=lowbit(i);
}
}
下面以修改A[5]为例,模拟函数update(5,val)的执行过程。
i=5(二进制数为101),C[5]+=val,lowbit(5)=001(二进制表示,对应1),i=5+1=6;
i=6(二进制数为110),C[6]+=val,lowbit(6)=010(二进制表示,对应2),i=6+2=8;
i=8(二进制数为1000),C[8]+=val,lowbit(8)=10000(二进制表示,对应16),i=8+16=24;
i=24>n,结束循环。循环期间,C[5]、C[6]、C[8]进行了更新。
有了单点更新函数,就很容易根据给定数组A构造对应的树状数组C了。初始时,令数组C的全部元素值为0,依次用数组A的元素值A[1]~A[n],调用函数update(I,A[i]),即可构造出对应的树状数组C。
(3)lowbit函数的实现。
函数lowbit(i)的返回值为2k,k为i的二进制中最右端1的位号。这可以用一个表达式i&(-i)简单地实现,即2^k = i&(-i) 。
这里利用了负数的存储特性,在计算机中负整数是以补码存储的,对于整数运算 x&(-x)有:
1)当i为0时,即 0 & 0,结果为0;
2)当i为奇数时,最后一个比特位为1,取反加1没有进位,故x和-x除最后一位外前面的位正好相反(按位与结果为0),最后1位都为1,按位与后结果为1。
3)当i为偶数,且为2的m次方时,x的二进制表示中只有一位是1(设为从右往左的第m+1位),其右边有m位0,故x取反加1后,从右到左第有m个0,第m+1位及其左边全是1。这样,x& (-x) 得到的就是x。
4)当i为偶数,却不为2的m次方的形式时,可以写作i= y * (2^k)。其中,y的最低位为1。实际上就是把i用一个奇数左移k位来表示。这时,i的二进制表示最右边有k个0,从右往左第k+1位为1。当对i取反时,最右边的k位0变成1,第k+1位变为0;再加1,最右边的k位就又变成了0,第k+1位因为进位的关系变成了1。左边的位因为没有进位,正好和i原来对应的位上的值相反。二者按位与,得到:第k+1位上为1,左边右边都为0。结果为2^k。
2.树状数组的应用
下面我们通过实例介绍树状数组的应用。
2.1 单点更新、区间查询
对给定数组的某个元素进行更新,然后对区间的和值进行查询。
例1 【模板】树状数组 1
本题选自洛谷题库(https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3374)
题目描述
已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作:
将某一个数加上x
求出某区间每一个数的和
输入格式
第一行包含两个正整数 n,m,分别表示该数列数字的个数和操作的总个数。
第二行包含 n 个用空格分隔的整数,其中第 i 个数字表示数列第 i 项的初始值。
接下来 m 行每行包含3 个整数,表示一个操作,具体如下:
1 x k 含义:将第 x 个数加上 k
2 x y 含义:输出区间 [x,y]内每个数的和
输出格式
输出包含若干行整数,即为所有操作 22 的结果。
输入样例
5 5
1 5 4 2 3
1 1 3
2 2 5
1 3 -1
1 4 2
2 1 4
输出样例
14
16
(1)编程思路。
典型的树状数组应用模板题。直接编写并调用前面介绍的三个函数即可。
(2)源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int n;
int c[500001];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int value)
{
while (i<=n)
{
c[i]+=value;
i+=lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while(i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
int i,p,x,y;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
update(i,x);
}
for (i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&p,&x,&y);
if (p==1) update(x,y);
else printf("%d\n",getsum(y)-getsum(x-1));
}
return 0;
}
2.2 区间更新、单点查询
设有数组A[n],若要将区间[x,y]内的所有元素的值全部加上k或者减去k,然后查询某个元素A[i]的值,这种时候该怎么做呢?
如果直接采用数组A的初始各元素值建立树状数组C,然后将[x,y]区间内每个值都更新,最后利用getsum(i)-getsum(i-1)得到待查询元素A[i]的值。这种办法的复杂度肯定是不行的。最好的办法是引入差分,利用差分建树。
设有数组A[n+1],且令A[0]=0,利用公式 B[i]=A[i]-A[i-1] (1≤i≤n) 建立差分数组B。
显然有 A[i]=B[1]+B[2]+B[3]+ …+B[i]
=A[1]-A[0]+A[2]-A[1]+…+A[i]-A[i-1] =A[i]
这样,待查询数组元素A[i]的值就是差分数组B的前i项的和。
当数组A的区间[x,y]内的所有元素(A[x]~A[y])的值全部加上k或者减去k时,区间内的元素的差值是不变的,因此对应B数组只有B[x] 加上k或者减去k、B[y+1] 减去k或加上k,其余元素值不变。
这样,我们用差分数组B构造树状数组C,每次区间修改就只进行两次单点修改。
例2 【模板】树状数组 2
本题选自洛谷题库(https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3368)
题目描述
已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作:
将某区间每一个数加上x;
求出某一个数的值。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N、M,分别表示该数列数字的个数和操作的总个数。
第二行包含 N 个用空格分隔的整数,其中第 i 个数字表示数列第 i 项的初始值。
接下来 M 行每行包含 2 或 4个整数,表示一个操作,具体如下:
操作 1: 格式:1 x y k 含义:将区间 [x,y]内每个数加上k;
操作 2: 格式:2 x 含义:输出第 x 个数的值。
输出格式
输出包含若干行整数,即为所有操作 22 的结果。
输入样例
5 5
1 5 4 2 3
1 2 4 2
2 3
1 1 5 -1
1 3 5 7
2 4
输出样例
6
10
(1)编程思路。
典型的区间更新、单点查询模板题。利用数组相邻元素的差值构造树状数组。
(2)源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int n;
int a[500001],c[500001];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int value)
{
while (i<=n)
{
c[i]+=value;
i+=lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while(i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int m,i;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
for (i = 1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
update(i,a[i] - a[i-1]);
}
for (i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int f,x,y,k;
scanf("%d",&f);
if (f==1)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&k);
update(x,k);
update(y+1,-k);
}
if (f==2)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("%d\n",getsum(x));
}
}
return 0;
}
例3 Color the ball
本题选自杭州电子科技大学OJ题库(http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1556)。
Problem Description
N个气球排成一排,从左到右依次编号为1,2,3....N。每次给定2个整数a b(a <= b),lele便为骑上他的“小飞鸽”牌电动车从气球a开始到气球b依次给每个气球涂一次颜色。但是N次以后lele已经忘记了第I个气球已经涂过几次颜色了,你能帮他算出每个气球被涂过几次颜色吗?
Input
每个测试实例第一行为一个整数N,(N <= 100000).接下来的N行,每行包括2个整数a b(1 <= a <= b <= N)。
当N = 0,输入结束。
Output
每个测试实例输出一行,包括N个整数,第I个数代表第I个气球总共被涂色的次数。
Sample Input
3
1 1
2 2
3 3
3
1 1
1 2
1 3
0
Sample Output
1 1 1
3 2 1
(1)编程思路。
设有数组A[N+1],A[i]的值表示编号为i的气球被涂色的次数,初始时元素值全为0。从气球a开始到气球b依次给每个气球涂一次颜色相当于对数组A的区间[a,b]中的每个元素加1。若定义数组A的差值数组B(差值数组的初始值显然也全为0),则对数组A的区间[a,b]中的各元素进行加1修改操作,只需对应对数组B的两个元素B[a]和B[b+1]进行单点修改即可,其中B[a]加1,B[b+1]减1。
根据树状数组的原理,A[i]的值就是差值数组B的前i项的和,调用函数getsum(i)即可。
(2)源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int n;
int c[100001];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int value)
{
while (i<=n)
{
c[i]+=value;
i+=lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while(i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%d",&n) && n!=0)
{
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
update(a, 1);
update(b + 1, -1);
}
for (int i = 1; i<n; i++)
{
printf("%d ",getsum(i));
}
printf("%d\n",getsum(n));
}
return 0;
}
例4 Matrix
本题选自北京大学OJ题库(http://poj.org/problem?id=2155)。
Description
Given an N*N matrix A, whose elements are either 0 or 1. A[i, j] means the number in the i-th row and j-th column. Initially we have A[i, j] = 0 (1 <= i, j <= N).
We can change the matrix in the following way. Given a rectangle whose upper-left corner is (x1, y1) and lower-right corner is (x2, y2), we change all the elements in the rectangle by using "not" operation (if it is a '0' then change it into '1' otherwise change it into '0'). To maintain the information of the matrix, you are asked to write a program to receive and execute two kinds of instructions.
1. C x1 y1 x2 y2 (1 <= x1 <= x2 <= n, 1 <= y1 <= y2 <= n) changes the matrix by using the rectangle whose upper-left corner is (x1, y1) and lower-right corner is (x2, y2).
2. Q x y (1 <= x, y <= n) querys A[x, y].
Input
The first line of the input is an integer X (X <= 10) representing the number of test cases. The following X blocks each represents a test case.
The first line of each block contains two numbers N and T (2 <= N <= 1000, 1 <= T <= 50000) representing the size of the matrix and the number of the instructions. The following T lines each represents an instruction having the format "Q x y" or "C x1 y1 x2 y2", which has been described above.
Output
For each querying output one line, which has an integer representing A[x, y].
There is a blank line between every two continuous test cases.
Sample Input
1
2 10
C 2 1 2 2
Q 2 2
C 2 1 2 1
Q 1 1
C 1 1 2 1
C 1 2 1 2
C 1 1 2 2
Q 1 1
C 1 1 2 1
Q 2 1
Sample Output
1
0
0
1
(1)编程思路。
本题的题意是给定N*N矩阵A,矩阵中的元素值非0即1,初始时元素值全为0。对矩阵中的子矩阵[x1, y1, x2, y2](x1、y1表示子矩阵左上角元素下标,x2、y2表示子矩阵右下角元素坐标)中的各元素进行变反操作(0变1,1变0),查询矩阵中元素A[x][y]的值。
根据题目中矩阵A的元素值不是 1 就是 0这一特点,我们只需记录每个元素值改变过几次,即可得到每个元素的值。
由例3可知,当数组是一维时,若要修改[x,y]区间的值,只需修改x和y+1这两个点的值(将点x值加1,点y+1值减1)。查询k点的值时,调用函数getsum(k)即可。
当数组为二维时,解决方法类同一维。要修改范围[x1, y1, x2, y2],只需修改这四个点:(x1,y1), (x1,y2+1), (x2+1,y1), (x2+1,y2+1)。查询点(x,y)的值时,调用函数getsum(x, y)。
按树状数组的原理,需要将单点修改和求前缀和函数修改为二维的处理情况。
(2)源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int n;
int c[1001][1001];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int x, int y, int value)
{
for (int i = x; i<= n; i+=lowbit(i))
for (int j=y; j<= n; j+=lowbit(j))
c[i][j]+=value;
}
int getsum(int x, int y)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = x; i>0; i-=lowbit(i))
for (int j = y; j > 0; j -= lowbit(j))
res += c[i][j];
return res;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int m,x1,y1,x2,y2;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
char op[5];
while (m--)
{
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &x1, &y1);
if (op[0] == 'C')
{
scanf("%d%d", &x2, &y2);
update(x1, y1, 1);
update(x1, y2+1, 1);
update(x2+1, y1, 1);
update(x2+1, y2+1, 1);
}
else
{
printf("%d\n", getsum(x1,y1) %2);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
例5 Flowers
本题选自杭州电子科技大学OJ题库(http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4325)。
Problem Description
As is known to all, the blooming time and duration varies between different kinds of flowers. Now there is a garden planted full of flowers. The gardener wants to know how many flowers will bloom in the garden in a specific time. But there are too many flowers in the garden, so he wants you to help him.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1 <= t <= 10), the number of test cases.
For each case, the first line contains two integer N and M, where N (1 <= N <= 10^5) is the number of flowers, and M (1 <= M <= 10^5) is the query times.
In the next N lines, each line contains two integer Si and Ti (1 <= Si <= Ti <= 10^9), means i-th flower will be blooming at time [Si, Ti].
In the next M lines, each line contains an integer Ti, means the time of i-th query.
Output
For each case, output the case number as shown and then print M lines. Each line contains an integer, meaning the number of blooming flowers.
Sample outputs are available for more details.
Sample Input
2
1 1
5 10
4
2 3
1 4
4 8
1
4
6
Sample Output
Case #1:
0
Case #2:
1
2
1
(1)编程思路1。
本题的题意是:有n朵花和m个时间点,第i朵花正在开放的时间是si和ti,问在第mi个时间点有多少朵花正在开放?
类同例3的编程思路。初始时所有时间点都没有花儿开放。第i朵花正在开放的时间是si和ti,相当于对区间[si,ti]中每个元素加1(有一朵花开放)。问在第mi个时间点有多少朵花正在开放,调用函数getsum(mi)得到结果。
先定义树状数组的大小为int c[100005];,仿例3编写如下的源程序。
(2)可以Accepted但存在缺陷的源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int n;
int c[100005];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int value)
{
while (i<=100005)
{
c[i]+=value;
i+=lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while(i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
for (int k=1;k<=t;k++)
{
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
int m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int i,s,t;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&s,&t);
update(s, 1);
update(t + 1, -1);
}
printf("Case #%d:\n",k);
for (i = 1; i<=m; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t);
printf("%d\n",getsum(t));
}
}
return 0;
}
这个源程序提交给OJ系统后,可以Accepted。但实际上这个程序是存在问题的,因为按题意花开的开始时间和结束时间Si 和Ti数据范围为1 <= Si <= Ti <= 10^9,而程序中定义的数组C,最大为100005。之所以Accepted,是因为测试数据集太弱,与题目中数据说明存在偏差。如果测试数据中输入的Si或Ti大于10^5,程序运行会出错。但将数组C定义为int C[10e9+1]是不现实地,因为数组C会过大,无法通过编译。
(3)编程思路2。
由题意,输入的Si 和Ti数据范围为1 <= Si <= Ti <= 10^9,而花儿朵数N的范围为1 <= N <= 10^5,每朵花开放有两个时间点,查询时间点个数M的范围为1 <= N <= 10^5,因此可以想办法将1~ 10^9范围的数据缩小到1~3*10^5的范围。为了将较大的数据范围缩小到一个较小的数据范围,可以进行离散化处理。
离散化的处理方法是:将原始数据按从小到大顺序排列,然后对数据编名次(相同的数据名次相同),然后各原始数据用其名次表示。
以测试样例为例说明。
例如,两朵花的开放时间点分别为1、4和4、8,3个查询时间点为1、4、6,这7个时间点按从小到大排序为1、1、4、4、6、8,相应名次为1、1、2、2、3、4,这样离散化后,1用1表示,4用2表示,6用3表示,8用4表示。
又如,3朵花的开放时间点分别为100、420,420、8900和123456789、987654321,4个查询时间点为10、400、6000和87654,这10个时间点按从小到大排序为:
10、100、400、420、420、6000、8900、87654、123456789、987654321,相应名次为1、2、3、4、4、5、6、7、8、9,这样离散化后,10用1表示,100用2表示,400用3表示,420用4表示,…,987654321用5表示。
离散化之后就可以采用树状数组解决问题了。
(4)正确进行离散化处理的源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int id,x;
};
struct node a[300005];
int c[300005],rankk[300005];
bool cmp(struct node a,struct node b)
{
return a.x<b.x;
}
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int n,int value)
{
while (i<=n)
{
c[i]+=value;
i+=lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while(i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
for (int k=1;k<=t;k++)
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
memset(rankk,0,sizeof(rankk));
int temp=2*n+m,i;
for (i=1;i<=temp;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i].x);
a[i].id=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+temp,cmp);
int cnt=1;
rankk[a[1].id]=cnt;
for (i=2;i<=temp;i++)
{
if(a[i].x==a[i-1].x) // 判重
rankk[a[i].id]=cnt;
else
rankk[a[i].id]=++cnt;
}
for (i=1;i<2*n;i+=2)
{
update(rankk[i],cnt,1);
update(rankk[i+1]+1,cnt,-1);
}
printf("Case #%d:\n",k);
for (i=2*n+1;i<=temp;i++)
{
printf("%d\n",getsum(rankk[i]));
}
}
return 0;
}
2.3 区间更新、区间查询
由前面介绍的树状数组原理可知,树状数组的本质就是实现时间复杂度为O(log2n) 的“单点更新,区间查询”,将其进行变形,利用差值建树状数组,可以实现“区间更新,单点查询”。那么,如何实现“区间更新,区间查询”呢?
设有数组a[n+1],且令a[0]=0,利用公式 c[i]=a[i]-a[i-1] (1≤i≤n) 建立差分数组c。
观察式子:
a[1]+a[2]+...+a[n]
=(a[1]-0)+(a[1]-0+a[2]-a[1])+…+ (a[1]-0 +a[2]-a[1]+…+a[n]-a[n-1])
= (c[1]) + (c[1]+c[2]) + … + (c[1]+c[2]+ … +c[n])
= n*c[1] + (n-1)*c[2] +... +c[n]
= n * (c[1]+c[2]+...+c[n]) - (0*c[1]+1*c[2]+...+(n-1)*c[n])
再建立一个树状数组c2,其中c2[i] = (i-1)*c[i],由此,
a[1]+a[2]+...+a[n] = n* getsum (c,n) - getsum (c2,n)
// 其中,getsum (c,n)表示树状数组c的前n项的和
而x到y的区间和即为:
(y* getsum (c,y) - getsum (c2,y))- ((x-1)* getsum (c,x-1) - getsum (c2,x-1))
例6 【模板】线段树 1
本题选自洛谷题库(https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/ P3372)
题目描述
已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作:
将某区间每一个数加上 k。
求出某区间每一个数的和。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n, m,分别表示该数列数字的个数和操作的总个数。
第二行包含 n 个用空格分隔的整数,其中第 i 个数字表示数列第 i 项的初始值。
接下来m行每行包含3或4个整数,表示一个操作,具体如下:
1 x y k:将区间 [x, y]内每个数加上 k。
2 x y:输出区间 [x,y] 内每个数的和。
输出格式
输出包含若干行整数,即为所有操作 2 的结果。
输入样例
5 5
1 5 4 2 3
2 2 4
1 2 3 2
2 3 4
1 1 5 1
2 1 4
输出样例
11
8
20
(1)编程思路。
典型的区间更新、区间查询模板题。利用数组相邻元素的差值构造树状数组c1,再利用树状数组c1构造树状数组c2。
(2)源程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef long long LL;
#define MAXN 100001
LL n;
LL c1[MAXN],c2[MAXN];
LL lowbit(LL x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(LL x,LL value,LL *c)
{
while(x<=n)
{
c[x]+=value;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
LL getsum(LL x,LL *c)
{
LL sum=0;
while(x>0)
{
sum+=c[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int q,op;
LL x,y,d;
scanf("%lld%d",&n,&q);
memset(c1,0,sizeof(c1));
memset(c2,0,sizeof(c2));
y=0;
for (int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
scanf("%lld",&x);
d=x-y;
update(i,d,c1);
update(i,(i-1)*d,c2);
y=x;
}
for(int i=0;i<q;++i)
{
scanf("%d",&op);
if (op==1)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&x,&y,&d);
update(x,d,c1);
update(y+1,-d,c1);
update(x,(x-1)*d,c2);
update(y+1,-y*d,c2);
}
else
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&y);
printf("%lld\n",getsum(y,c1)*y-getsum(x-1,c1)*(x-1) -getsum(y,c2)+getsum(x-1,c2));
}
}
return 0;
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
2019-12-18 JavaScript图形实例:纺织物图案
2019-12-18 JavaScript图形实例:布纹图案