Bloom’S Taxonomy
引用:https://www.learning-theories.com/blooms-taxonomy-bloom.html
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a model that is a hierarchy — a way to classify thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity.
CONTRIBUTORS
- Benjamin S. Bloom (1913-1999)
KEY CONCEPTS
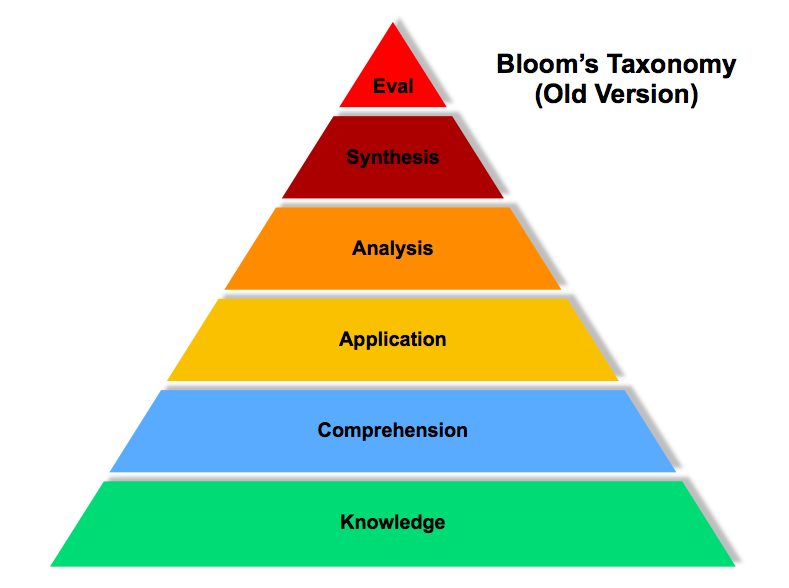
Bloom’s model consists of six levels, with the three lower levels (knowledge, comprehension, and application) being more basic than the higher levels (analysis, synthesis, and evaluation)[1]. Some think of the levels as a stairway, in which learners are encouraged to achieve a higher level of thinking. If a student has mastered a higher level, then he or she is considered to have mastered the levels below.
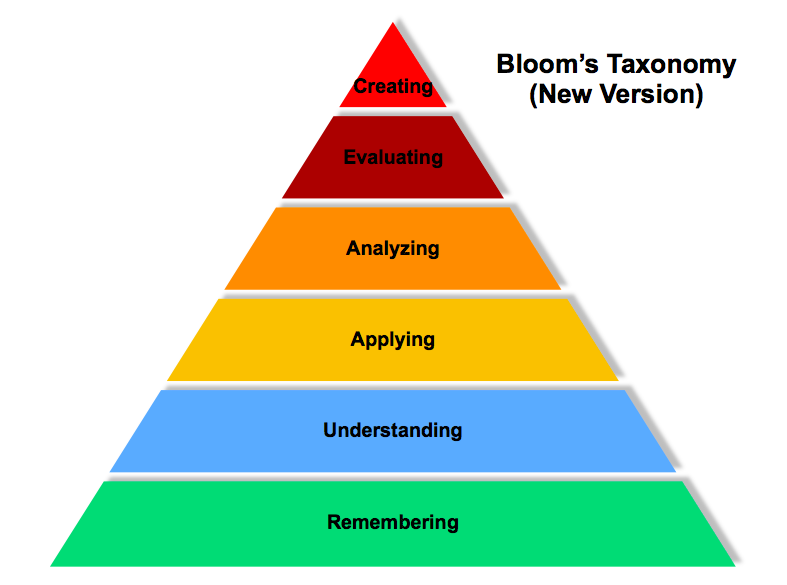
Bloom’s model has been updated to account for 21st century needs[2].
NEW MODEL:
我的看法
Bloom的这篇关于认知领域的6个分类:识记,理解,应用, 分析, 评价, 创造。对学习者(也就是我)有很好的帮助。
在学习的过程中,应当始终明确我学习的东西的它属于那个层次,并且我应该去要达到那个层次。刻意保持这样的意识有助于主次分明,突出学习的重点和难点,提交学习的效率。
REFERENCES
[1]: Bloom, B. S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals.
[2]: Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., & Bloom, B. S. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. Allyn & Bacon.



【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步