02 | Django REST framework+Vue 生鲜超市 ——商品列表页
APIview使用实现商品列表页
(1)安装
- pip install coreapi drf的文档支持
- pip install django-guardian drf对象级别的权限支持
(2)配置def文档的url
MxShop/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url,include
import xadmin
from MxShop.settings import MEDIA_ROOT
from django.views.static import serve
from rest_framework.documentation import include_docs_urls
urlpatterns = [
url(r'docs/', include_docs_urls(title="慕学生鲜")),
url(r'^api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework')),
]
(3)配置rest_framework
settings.py中添加
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'rest_framework',
]
(4)goods文件夹下面新建serializers.py
用drf的序列化实现商品列表页展示,代码如下:

from rest_framework import serializers class GoodsSerializer(serializers.Serializer): name = serializers.CharField(required=True,max_length=100) click_num = serializers.IntegerField(default=0) goods_front_image = serializers.ImageField()
(5)在goods/views.py

from rest_framework.views import APIView from goods.serializers import GoodsSerializer from .models import Goods from rest_framework.response import Response class GoodsListView(APIView): ''' 商品列表 ''' def get(self,request,format=None): goods = Goods.objects.all() goods_serialzer = GoodsSerializer(goods,many=True) return Response(goods_serialzer.data)
(6)MxShop/urls.py
url('goods/',GoodsListView.as_view(),name='goods-list')
访问
http://127.0.0.1:8000/goods/
返回结果如下

Modelserializer实现商品列表页
上面是用Serializer实现的,需要自己手动添加字段,如果用Modelserializer,会更加的方便,直接用__all__和Serializer搭配使用可以更为方便的帮助我们序列化

from rest_framework import serializers from .models import Goods #Serializer实现商品列表页 # class GoodsSerializer(serializers.Serializer): # name = serializers.CharField(required=True,max_length=100) # click_num = serializers.IntegerField(default=0) # goods_front_image = serializers.ImageField() #ModelSerializer实现商品列表页 class GoodsSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): class Meta: model = Goods fields = '__all__'
返回结果

category只显示分类的id,Serialzer还可以嵌套使用,覆盖外键字段追踪到外键中所有的字段

from rest_framework import serializers from .models import Goods,GoodsCategory #Serializer实现商品列表页 # class GoodsSerializer(serializers.Serializer): # name = serializers.CharField(required=True,max_length=100) # click_num = serializers.IntegerField(default=0) # goods_front_image = serializers.ImageField() class CategorySerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): class Meta: model = GoodsCategory fields = "__all__" #ModelSerializer实现商品列表页 class GoodsSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): #覆盖外键字段 category = CategorySerializer() class Meta: model = Goods fields = '__all__'
返回结果

GenericView实现商品列表页
mixins和generic一起用用
GenericAPIView继承APIView,封装了很多方法

class GenericAPIView(views.APIView): """ Base class for all other generic views. """ # You'll need to either set these attributes, # or override `get_queryset()`/`get_serializer_class()`. # If you are overriding a view method, it is important that you call # `get_queryset()` instead of accessing the `queryset` property directly, # as `queryset` will get evaluated only once, and those results are cached # for all subsequent requests. queryset = None serializer_class = None # If you want to use object lookups other than pk, set 'lookup_field'. # For more complex lookup requirements override `get_object()`. lookup_field = 'pk' lookup_url_kwarg = None # The filter backend classes to use for queryset filtering filter_backends = api_settings.DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS # The style to use for queryset pagination. pagination_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS def get_queryset(self): """ Get the list of items for this view. This must be an iterable, and may be a queryset. Defaults to using `self.queryset`. This method should always be used rather than accessing `self.queryset` directly, as `self.queryset` gets evaluated only once, and those results are cached for all subsequent requests. You may want to override this if you need to provide different querysets depending on the incoming request. (Eg. return a list of items that is specific to the user) """ assert self.queryset is not None, ( "'%s' should either include a `queryset` attribute, " "or override the `get_queryset()` method." % self.__class__.__name__ ) queryset = self.queryset if isinstance(queryset, QuerySet): # Ensure queryset is re-evaluated on each request. queryset = queryset.all() return queryset def get_object(self): """ Returns the object the view is displaying. You may want to override this if you need to provide non-standard queryset lookups. Eg if objects are referenced using multiple keyword arguments in the url conf. """ queryset = self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset()) # Perform the lookup filtering. lookup_url_kwarg = self.lookup_url_kwarg or self.lookup_field assert lookup_url_kwarg in self.kwargs, ( 'Expected view %s to be called with a URL keyword argument ' 'named "%s". Fix your URL conf, or set the `.lookup_field` ' 'attribute on the view correctly.' % (self.__class__.__name__, lookup_url_kwarg) ) filter_kwargs = {self.lookup_field: self.kwargs[lookup_url_kwarg]} obj = get_object_or_404(queryset, **filter_kwargs) # May raise a permission denied self.check_object_permissions(self.request, obj) return obj def get_serializer(self, *args, **kwargs): """ Return the serializer instance that should be used for validating and deserializing input, and for serializing output. """ serializer_class = self.get_serializer_class() kwargs['context'] = self.get_serializer_context() return serializer_class(*args, **kwargs) def get_serializer_class(self): """ Return the class to use for the serializer. Defaults to using `self.serializer_class`. You may want to override this if you need to provide different serializations depending on the incoming request. (Eg. admins get full serialization, others get basic serialization) """ assert self.serializer_class is not None, ( "'%s' should either include a `serializer_class` attribute, " "or override the `get_serializer_class()` method." % self.__class__.__name__ ) return self.serializer_class def get_serializer_context(self): """ Extra context provided to the serializer class. """ return { 'request': self.request, 'format': self.format_kwarg, 'view': self } def filter_queryset(self, queryset): """ Given a queryset, filter it with whichever filter backend is in use. You are unlikely to want to override this method, although you may need to call it either from a list view, or from a custom `get_object` method if you want to apply the configured filtering backend to the default queryset. """ for backend in list(self.filter_backends): queryset = backend().filter_queryset(self.request, queryset, self) return queryset @property def paginator(self): """ The paginator instance associated with the view, or `None`. """ if not hasattr(self, '_paginator'): if self.pagination_class is None: self._paginator = None else: self._paginator = self.pagination_class() return self._paginator def paginate_queryset(self, queryset): """ Return a single page of results, or `None` if pagination is disabled. """ if self.paginator is None: return None return self.paginator.paginate_queryset(queryset, self.request, view=self) def get_paginated_response(self, data): """ Return a paginated style `Response` object for the given output data. """ assert self.paginator is not None return self.paginator.get_paginated_response(data) GenericAPIView源码
用的时候需要定义queryset和serializer_class
GenericAPIView里面默认为空
- queryset = None # 指的是我们查询的数据库
- serializer_class = None # 自定义的序列化类
ListModelMixin里面list方法帮我们做好了分页和序列化的工作,所以我们可以直接使用list方法

class ListModelMixin(object): """ List a queryset. """ def list(self, request, *args, **kwargs): queryset = self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset()) page = self.paginate_queryset(queryset) if page is not None: serializer = self.get_serializer(page, many=True) return self.get_paginated_response(serializer.data) serializer = self.get_serializer(queryset, many=True) return Response(serializer.data) ListModelMixin源码
使用ListModelMixin 实现如下:

from goods.serializers import GoodsSerializer from .models import Goods from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework import mixins from rest_framework import generics class GoodsListView(mixins.ListModelMixin,generics.GenericAPIView): '商品列表页' queryset = Goods.objects.all() serializer_class = GoodsSerializer def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs): return self.list(request,*args,**kwargs)
那么我们是否可以对上面的代码继续优化,把只要前端访问的是get方法就可以直接的去调用list方法,这是我们可以直接继承 generics.ListAPIView
class ListAPIView(mixins.ListModelMixin, GenericAPIView): """ Concrete view for listing a queryset. """ def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs)
根据源码 我们可以看到,它实现了get和list的绑定
为此只要写三行代码就可以实现查询所有商品的信息了

from goods.serializers import GoodsSerializer from .models import Goods from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework import mixins from rest_framework import generics class GoodsListView(generics.ListAPIView): '商品列表页' queryset = Goods.objects.all() serializer_class = GoodsSerializer
添加分页功能
先看rest_framework/settings.py源码,里面可以找到如何配置:比如认证、权限和分页等等

""" Settings for REST framework are all namespaced in the REST_FRAMEWORK setting. For example your project's `settings.py` file might look like this: REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer', 'rest_framework.renderers.TemplateHTMLRenderer', ) 'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser' ) } This module provides the `api_setting` object, that is used to access REST framework settings, checking for user settings first, then falling back to the defaults. """ from __future__ import unicode_literals from importlib import import_module from django.conf import settings from django.test.signals import setting_changed from django.utils import six from rest_framework import ISO_8601 DEFAULTS = { # Base API policies 'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer', 'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer', ), 'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser' ), 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication', 'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication' ), 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny', ), 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (), 'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation', 'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.metadata.SimpleMetadata', 'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': None, # Generic view behavior 'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': None, 'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': (), # Schema 'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.AutoSchema', # Throttling 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': { 'user': None, 'anon': None, }, 'NUM_PROXIES': None, # Pagination 'PAGE_SIZE': None, # Filtering 'SEARCH_PARAM': 'search', 'ORDERING_PARAM': 'ordering', # Versioning 'DEFAULT_VERSION': None, 'ALLOWED_VERSIONS': None, 'VERSION_PARAM': 'version', # Authentication 'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': 'django.contrib.auth.models.AnonymousUser', 'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None, # View configuration 'VIEW_NAME_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_name', 'VIEW_DESCRIPTION_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_description', # Exception handling 'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler', 'NON_FIELD_ERRORS_KEY': 'non_field_errors', # Testing 'TEST_REQUEST_RENDERER_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.renderers.MultiPartRenderer', 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer' ), 'TEST_REQUEST_DEFAULT_FORMAT': 'multipart', # Hyperlink settings 'URL_FORMAT_OVERRIDE': 'format', 'FORMAT_SUFFIX_KWARG': 'format', 'URL_FIELD_NAME': 'url', # Input and output formats 'DATE_FORMAT': ISO_8601, 'DATE_INPUT_FORMATS': (ISO_8601,), 'DATETIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601, 'DATETIME_INPUT_FORMATS': (ISO_8601,), 'TIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601, 'TIME_INPUT_FORMATS': (ISO_8601,), # Encoding 'UNICODE_JSON': True, 'COMPACT_JSON': True, 'STRICT_JSON': True, 'COERCE_DECIMAL_TO_STRING': True, 'UPLOADED_FILES_USE_URL': True, # Browseable API 'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF': 1000, 'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF_TEXT': "More than {count} items...", # Schemas 'SCHEMA_COERCE_PATH_PK': True, 'SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES': { 'retrieve': 'read', 'destroy': 'delete' }, } # List of settings that may be in string import notation. IMPORT_STRINGS = ( 'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES', 'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES', 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES', 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES', 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES', 'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS', 'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS', 'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS', 'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS', 'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS', 'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS', 'EXCEPTION_HANDLER', 'TEST_REQUEST_RENDERER_CLASSES', 'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER', 'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN', 'VIEW_NAME_FUNCTION', 'VIEW_DESCRIPTION_FUNCTION' ) # List of settings that have been removed REMOVED_SETTINGS = ( "PAGINATE_BY", "PAGINATE_BY_PARAM", "MAX_PAGINATE_BY", ) def perform_import(val, setting_name): """ If the given setting is a string import notation, then perform the necessary import or imports. """ if val is None: return None elif isinstance(val, six.string_types): return import_from_string(val, setting_name) elif isinstance(val, (list, tuple)): return [import_from_string(item, setting_name) for item in val] return val def import_from_string(val, setting_name): """ Attempt to import a class from a string representation. """ try: # Nod to tastypie's use of importlib. module_path, class_name = val.rsplit('.', 1) module = import_module(module_path) return getattr(module, class_name) except (ImportError, AttributeError) as e: msg = "Could not import '%s' for API setting '%s'. %s: %s." % (val, setting_name, e.__class__.__name__, e) raise ImportError(msg) class APISettings(object): """ A settings object, that allows API settings to be accessed as properties. For example: from rest_framework.settings import api_settings print(api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES) Any setting with string import paths will be automatically resolved and return the class, rather than the string literal. """ def __init__(self, user_settings=None, defaults=None, import_strings=None): if user_settings: self._user_settings = self.__check_user_settings(user_settings) self.defaults = defaults or DEFAULTS self.import_strings = import_strings or IMPORT_STRINGS self._cached_attrs = set() @property def user_settings(self): if not hasattr(self, '_user_settings'): self._user_settings = getattr(settings, 'REST_FRAMEWORK', {}) return self._user_settings def __getattr__(self, attr): if attr not in self.defaults: raise AttributeError("Invalid API setting: '%s'" % attr) try: # Check if present in user settings val = self.user_settings[attr] except KeyError: # Fall back to defaults val = self.defaults[attr] # Coerce import strings into classes if attr in self.import_strings: val = perform_import(val, attr) # Cache the result self._cached_attrs.add(attr) setattr(self, attr, val) return val def __check_user_settings(self, user_settings): SETTINGS_DOC = "http://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/settings/" for setting in REMOVED_SETTINGS: if setting in user_settings: raise RuntimeError("The '%s' setting has been removed. Please refer to '%s' for available settings." % (setting, SETTINGS_DOC)) return user_settings def reload(self): for attr in self._cached_attrs: delattr(self, attr) self._cached_attrs.clear() if hasattr(self, '_user_settings'): delattr(self, '_user_settings') api_settings = APISettings(None, DEFAULTS, IMPORT_STRINGS) def reload_api_settings(*args, **kwargs): setting = kwargs['setting'] if setting == 'REST_FRAMEWORK': api_settings.reload() setting_changed.connect(reload_api_settings) rest_framework/settings源码

所有我们需要在settings.py中添加分页功能,配置如下:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
#分页
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination',
#每页显示的个数
'PAGE_SIZE': 10,
}
返回结果如下
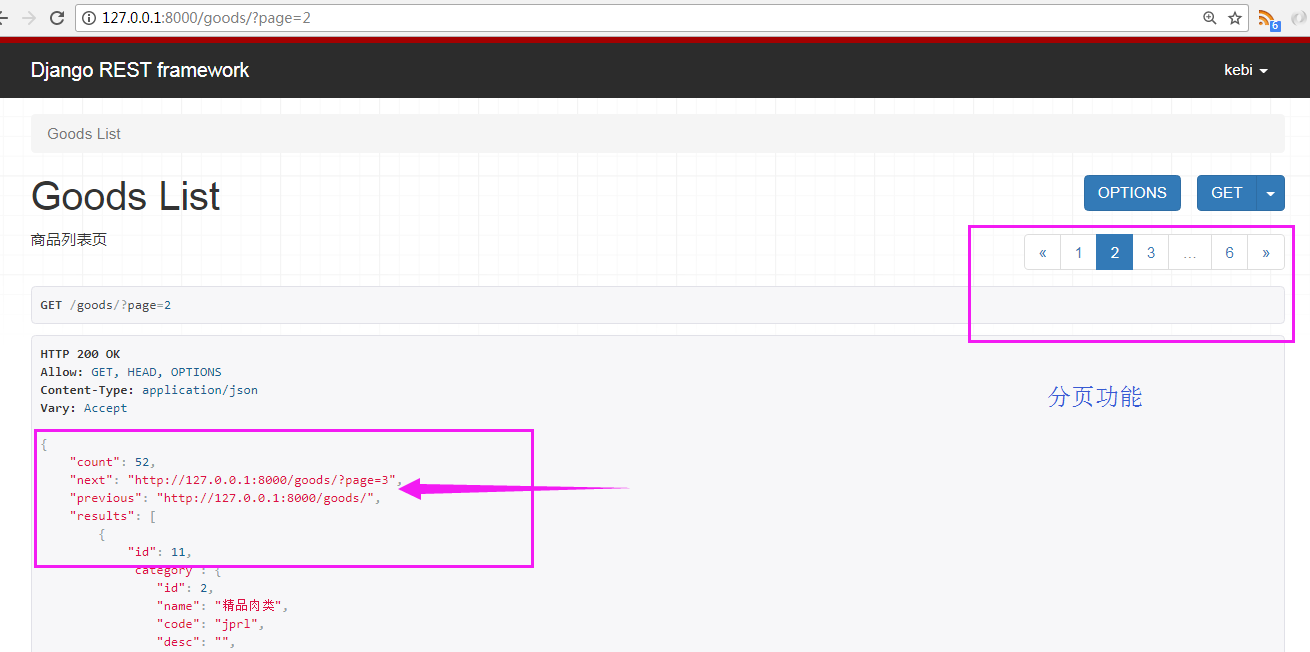
自定也分页功能

from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination class GoodsPagination(PageNumberPagination): ''' 商品列表自定义分页 ''' #默认每页显示的个数 page_size = 10 #可以动态改变每页显示的个数 page_size_query_param = 'page_size' #页码参数 page_query_param = 'page' #最多能显示多少页 max_page_size = 100 class GoodsListView(generics.ListAPIView): '商品列表页' pagination_class = GoodsPagination #分页 queryset = Goods.objects.all() serializer_class = GoodsSerializer
由于在我们的类属性中指明了分页的配置,所以在配置文件中的就会被覆盖掉了,我们可以把配置中的分页功能注销掉
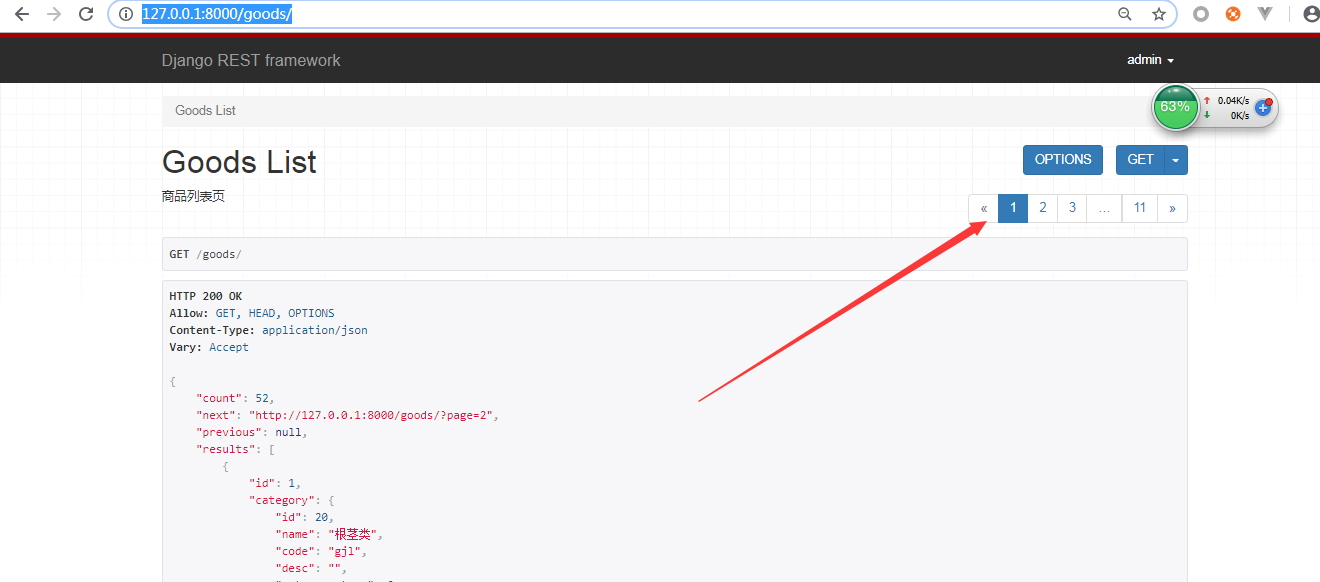
访问
http://127.0.0.1:8000/goods/
返回结果如下
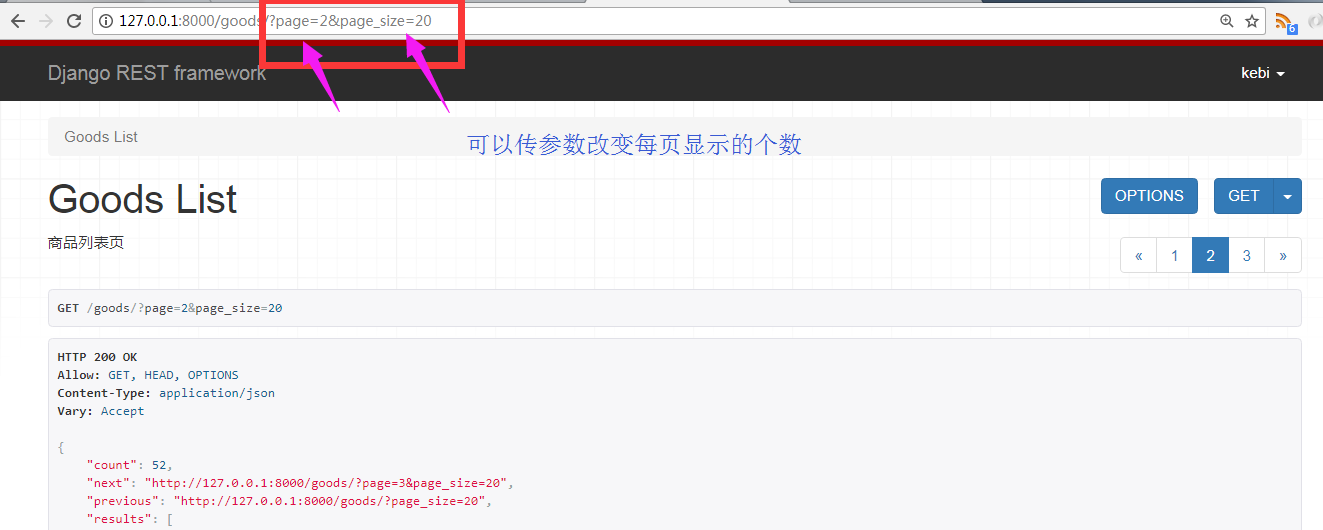
前端也可以自己在输入url时根据自己的需要自己指定
viewsets和router完成商品列表页
主要用到viewsets中的GenericViewSet
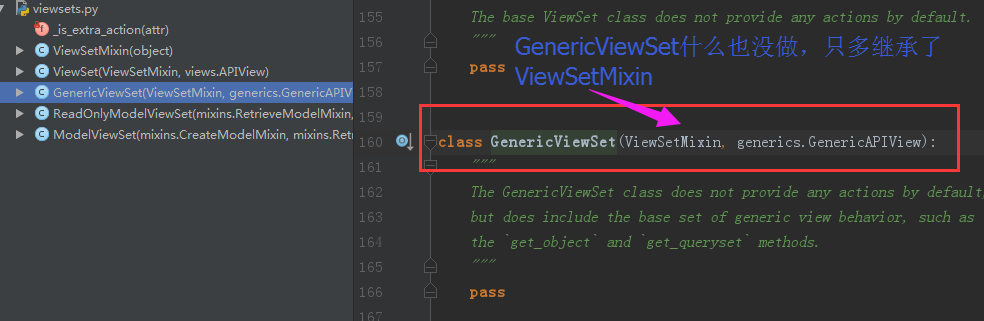
GenericViewSet继承

GenericViewSet在GenericAPIView的基础上封装了请求方法和视图函数的限制关系

再看下ViewSerMixin源码

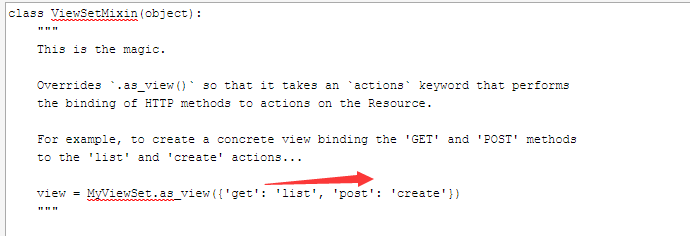
class ViewSetMixin(object): """ This is the magic. Overrides `.as_view()` so that it takes an `actions` keyword that performs the binding of HTTP methods to actions on the Resource. For example, to create a concrete view binding the 'GET' and 'POST' methods to the 'list' and 'create' actions... view = MyViewSet.as_view({'get': 'list', 'post': 'create'}) """ @classonlymethod def as_view(cls, actions=None, **initkwargs): """ Because of the way class based views create a closure around the instantiated view, we need to totally reimplement `.as_view`, and slightly modify the view function that is created and returned. """ # The suffix initkwarg is reserved for displaying the viewset type. # eg. 'List' or 'Instance'. cls.suffix = None # The detail initkwarg is reserved for introspecting the viewset type. cls.detail = None # Setting a basename allows a view to reverse its action urls. This # value is provided by the router through the initkwargs. cls.basename = None # actions must not be empty if not actions: raise TypeError("The `actions` argument must be provided when " "calling `.as_view()` on a ViewSet. For example " "`.as_view({'get': 'list'})`") # sanitize keyword arguments for key in initkwargs: if key in cls.http_method_names: raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a " "keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that." % (key, cls.__name__)) if not hasattr(cls, key): raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r" % ( cls.__name__, key)) def view(request, *args, **kwargs): self = cls(**initkwargs) # We also store the mapping of request methods to actions, # so that we can later set the action attribute. # eg. `self.action = 'list'` on an incoming GET request. self.action_map = actions # Bind methods to actions # This is the bit that's different to a standard view for method, action in actions.items(): handler = getattr(self, action) setattr(self, method, handler) if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'): self.head = self.get self.request = request self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs # And continue as usual return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) # take name and docstring from class update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=()) # and possible attributes set by decorators # like csrf_exempt from dispatch update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=()) # We need to set these on the view function, so that breadcrumb # generation can pick out these bits of information from a # resolved URL. view.cls = cls view.initkwargs = initkwargs view.suffix = initkwargs.get('suffix', None) view.actions = actions return csrf_exempt(view) def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ Set the `.action` attribute on the view, depending on the request method. """ request = super(ViewSetMixin, self).initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs) method = request.method.lower() if method == 'options': # This is a special case as we always provide handling for the # options method in the base `View` class. # Unlike the other explicitly defined actions, 'metadata' is implicit. self.action = 'metadata' else: self.action = self.action_map.get(method) return request def reverse_action(self, url_name, *args, **kwargs): """ Reverse the action for the given `url_name`. """ url_name = '%s-%s' % (self.basename, url_name) kwargs.setdefault('request', self.request) return reverse(url_name, *args, **kwargs) @classmethod def get_extra_actions(cls): """ Get the methods that are marked as an extra ViewSet `@action`. """ return [method for _, method in getmembers(cls, _is_extra_action)] ViewSetMixin源码
ViewSets和Routers结合使用
MxShop/urls.py 添加以下代码
from goods.views import GoodsListViewSet
from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter
router = DefaultRouter()
#配置goods的url
router.register(r'goods', GoodsListViewSet)
urlpatterns = [
#商品列表页
url('^', include(router.urls)), # 注意别忘了这个
]

from goods.serializers import GoodsSerializer from .models import Goods from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework import mixins,viewsets from rest_framework import generics from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination class GoodsPagination(PageNumberPagination): ''' 商品列表自定义分页 ''' #默认每页显示的个数 page_size = 5 #可以动态改变每页显示的个数 page_size_query_param = 'page_size' #页码参数 page_query_param = 'page' #最多能显示多少页 max_page_size = 100 class GoodsListViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin,viewsets.GenericViewSet): '商品列表页' # 分页 pagination_class = GoodsPagination #这里必须要定义一个默认的排序,否则会报错 queryset = Goods.objects.all().order_by('id') serializer_class = GoodsSerializer
drf的APIView、GenericView、viewsets和router的原理分析
视图 继承关系由下到上
GenericViewSet(viewsets) ----drf
GenericAPIView ---drf
APIView ---drf
View ----django
这些view功能的不同,主要的是有mixin的存在
mixins总共有五种:
CreateModelMixin
ListModelMixin
UpdateModelMixin
RetrieveModelMixin
DestoryModelMixin
总结:
视图函数的继承关系和功能的划分
GenericAPIView 继承ApiView通过它我们可以在类属性中配置qureset查询集和Serialize,为其子类提供灵活的自定制功能
GenericViewSet 继承ViewSetMixin, generics.GenericAPIView,在GenericAPIView的基础上封装了请求方法和视图函数的限制关系 如get对应list方法'post'对应 'create'方法等等
而 mixins总共有五种:
CreateModelMixin
ListModelMixin
UpdateModelMixin
RetrieveModelMixin
DestoryModelMixin
帮我们写好了增删改查与与请求方法之间的对应,我们可以把mixins和GenericViewSet 搭配使用简化我们的代码

""" Basic building blocks for generic class based views. We don't bind behaviour to http method handlers yet, which allows mixin classes to be composed in interesting ways. """ from __future__ import unicode_literals from rest_framework import status from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework.settings import api_settings class CreateModelMixin(object): """ Create a model instance. """ def create(self, request, *args, **kwargs): serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data) serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True) self.perform_create(serializer) headers = self.get_success_headers(serializer.data) return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED, headers=headers) def perform_create(self, serializer): serializer.save() def get_success_headers(self, data): try: return {'Location': str(data[api_settings.URL_FIELD_NAME])} except (TypeError, KeyError): return {} class ListModelMixin(object): """ List a queryset. """ def list(self, request, *args, **kwargs): queryset = self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset()) page = self.paginate_queryset(queryset) if page is not None: serializer = self.get_serializer(page, many=True) return self.get_paginated_response(serializer.data) serializer = self.get_serializer(queryset, many=True) return Response(serializer.data) class RetrieveModelMixin(object): """ Retrieve a model instance. """ def retrieve(self, request, *args, **kwargs): instance = self.get_object() serializer = self.get_serializer(instance) return Response(serializer.data) class UpdateModelMixin(object): """ Update a model instance. """ def update(self, request, *args, **kwargs): partial = kwargs.pop('partial', False) instance = self.get_object() serializer = self.get_serializer(instance, data=request.data, partial=partial) serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True) self.perform_update(serializer) if getattr(instance, '_prefetched_objects_cache', None): # If 'prefetch_related' has been applied to a queryset, we need to # forcibly invalidate the prefetch cache on the instance. instance._prefetched_objects_cache = {} return Response(serializer.data) def perform_update(self, serializer): serializer.save() def partial_update(self, request, *args, **kwargs): kwargs['partial'] = True return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs) class DestroyModelMixin(object): """ Destroy a model instance. """ def destroy(self, request, *args, **kwargs): instance = self.get_object() self.perform_destroy(instance) return Response(status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT) def perform_destroy(self, instance): instance.delete() mixins.py源码
以ListModelMixin为例:

如果不继承ListModelMixin的话,就无法将get和商品的列表关联起来,另外还有其中的分页等等,都无法实现。
还有其它几个mixin(增删改查局部),这些功能都是mixin做的
我们一般都是用viewsets
ViewSet类与View类其实几乎是相同的,但提供的是read或update这些操作,而不是get或put 等HTTP动作。同时,ViewSet为我们提供了默认的URL结构, 使得我们能更专注于API本身。
Router提供了一种简单,快速,集成的方式来定义一系列的urls
drf的request和response介绍
REST framework 的 Request 类扩展与标准的 HttpRequest,并做了相应的增强,比如更加灵活的请求解析(request parsing)和认证(request authentication)。
REST framwork 的 Request 对象提供了灵活的请求解析,允许你使用 JSON data 或 其他 media types 像通常处理表单数据一样处理请求。
request.data 返回请求主题的解析内容。这跟标准的 request.POST 和 request.FILES 类似,并且还具有以下特点:
- 包括所有解析的内容,文件(file) 和 非文件(non-file inputs)。
- 支持解析
POST以外的 HTTP method , 比如PUT,PATCH。 - 更加灵活,不仅仅支持表单数据,传入同样的 JSON 数据一样可以正确解析,并且不用做额外的处理(意思是前端不管提交的是表单数据,还是 JSON 数据,
.data都能够正确解析)。
.data 具体操作,以后再说~
request.query_params 等同于 request.GET,不过其名字更加容易理解。
为了代码更加清晰可读,推荐使用 request.query_params ,而不是 Django 中的 request.GET,这样那够让你的代码更加明显的体现出 ----- 任何 HTTP method 类型都可能包含查询参数(query parameters),而不仅仅只是 'GET' 请求。
.parser
APIView 类或者 @api_view 装饰器将根据视图上设置的 parser_classes 或 settings 文件中的 DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES 设置来确保此属性(.parsers)自动设置为 Parser 实例列表。
通常不需要关注该属性......
如果你非要看看它里面是什么,可以打印出来看看,大概长这样:
[<rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser object at 0x7fa850202d68>, <rest_framework.parsers.FormParser object at 0x7fa850202be0>, <rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser object at 0x7fa850202860>]
包含三个解析器 JSONParser,FormParser,MultiPartParser。
注意: 如果客户端发送格式错误的内容,则访问
request.data可能会引发ParseError。默认情况下, REST framework 的APIView类或者@api_view装饰器将捕获错误并返回400 Bad Request响应。 如果客户端发送的请求内容无法解析(不同于格式错误),则会引发UnsupportedMediaType异常,默认情况下会被捕获并返回415 Unsupported Media Type响应。
Responses
与基本的 HttpResponse 对象不同,TemplateResponse 对象保留了视图提供的用于计算响应的上下文的详细信息。直到需要时才会计算最终的响应输出,也就是在后面的响应过程中进行计算。 — Django 文档
REST framework 通过提供一个 Response 类来支持 HTTP 内容协商,该类允许你根据客户端请求返回不同的表现形式(如: JSON ,HTML 等)。
Response 类的子类是 Django 的 SimpleTemplateResponse。Response 对象使用数据进行初始化,数据应由 Python 对象(native Python primitives)组成。然后 REST framework 使用标准的 HTTP 内容协商来确定它应该如何渲染最终响应的内容。
当然,您也可以不使用 Response 类,直接返回常规 HttpResponse 或 StreamingHttpResponse 对象。 使用 Response 类只是提供了一个更好的交互方式,它可以返回多种格式。
除非由于某种原因需要大幅度定制 REST framework ,否则应该始终对返回 Response 对象的视图使用 APIView 类或 @api_view 装饰器。这样做可以确保视图执行内容协商,并在视图返回之前为响应选择适当的渲染器。
与普通 HttpResponse 对象不同,您不会使用渲染的内容实例化 Response 对象。相反,您传递的是未渲染的数据,可能包含任何 Python 对象。
由于 Response 类使用的渲染器不能处理复杂的数据类型(比如 Django 的模型实例),所以需要在创建 Response 对象之前将数据序列化为基本的数据类型。
你可以使用 REST framework 的 Serializer 类来执行序列化的操作,也可以用自己的方式来序列化。
构造方法: Response(data, status=None, template_name=None, headers=None, content_type=None)
参数:
data: 响应的序列化数据。status: 响应的状态代码。默认为200。template_name: 选择HTMLRenderer时使用的模板名称。headers: 设置 HTTP header,字典类型。content_type: 响应的内容类型,通常渲染器会根据内容协商的结果自动设置,但有些时候需要手动指定。
还没有渲染,但已经序列化的响应数据。
状态码
将会返回的响应内容,必须先调用 .render() 方法,才能访问 .content 。
只有在 response 的渲染器是 HTMLRenderer 或其他自定义模板渲染器时才需要提供。
用于将会返回的响应内容的渲染器实例。
从视图返回响应之前由 APIView 或 @api_view 自动设置。
内容协商阶段选择的媒体类型。
从视图返回响应之前由 APIView 或 @api_view 自动设置。
.renderer_context
将传递给渲染器的 .render() 方法的附加的上下文信息字典。
从视图返回响应之前由 APIView 或 @api_view 自动设置。
Response 类扩展于 SimpleTemplateResponse,并且响应中也提供了所有常用的属性和方法。例如,您可以用标准方式在响应中设置 header:
response = Response() response['Cache-Control'] = 'no-cache'
.render()
与其他任何 TemplateResponse 一样,调用此方法将响应的序列化数据呈现为最终响应内容。响应内容将设置为在 accepted_renderer 实例上调用 .render(data,accepted_media_type,renderer_context) 方法的结果。
通常不需要自己调用 .render() ,因为它是由 Django 处理的。
drf的过滤器
drf的filter用法 http://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/filtering/
(1)配置到app里面
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django_filters',
]
(2)在goods目录下创建filters.py
自定义一个过滤器

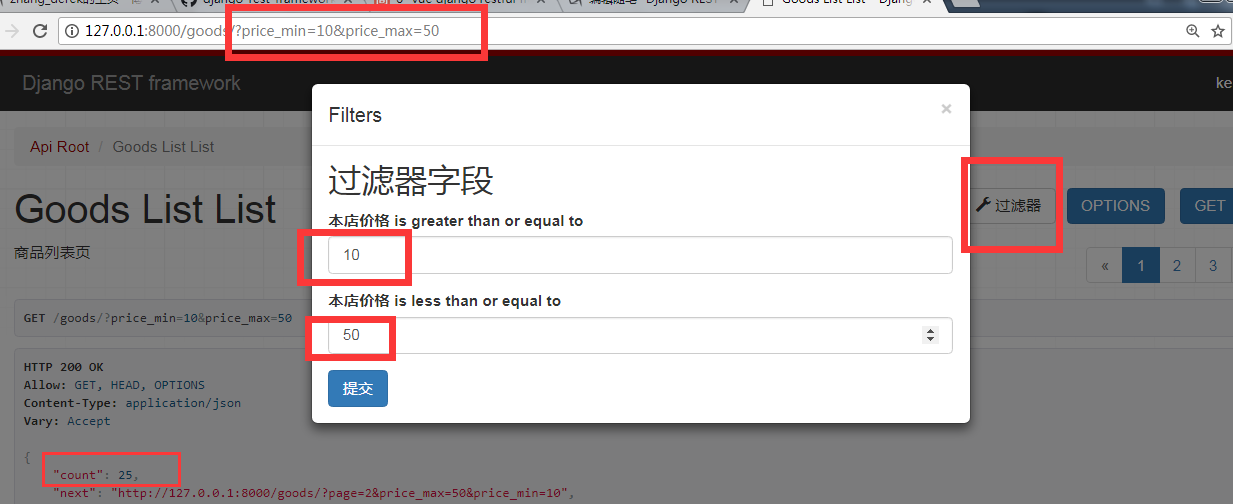
import django_filters from .models import Goods class GoodsFilter(django_filters.rest_framework.FilterSet): ''' 商品过滤的类 ''' #两个参数,name是要过滤的字段,lookup是执行的行为,‘小与等于本店价格’ price_min = django_filters.NumberFilter("shop_price", lookup_expr='gte') price_max = django_filters.NumberFilter("shop_price", lookup_expr='lte') class Meta: model = Goods fields = ['price_min', 'price_max']
(3)goods/views.py

from .filters import GoodsFilter from django_filters.rest_framework import DjangoFilterBackend class GoodsListViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin,viewsets.GenericViewSet): '商品列表页' #这里必须要定义一个默认的排序,否则会报错 queryset = Goods.objects.all().order_by('id') # 分页 pagination_class = GoodsPagination serializer_class = GoodsSerializer filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend,) # 设置filter的类为我们自定义的类 filter_class = GoodsFilter
drf的搜索和排序
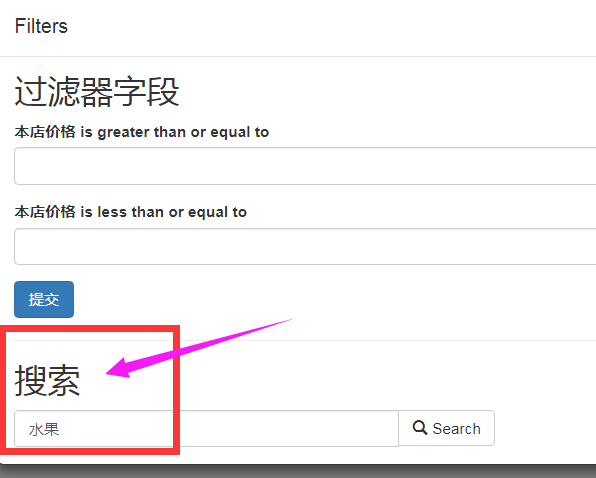
添加搜索功能
搜索的字段可以使用正则表达式

from rest_framework import filters class GoodsListViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin,viewsets.GenericViewSet): '商品列表页' #这里必须要定义一个默认的排序,否则会报错 queryset = Goods.objects.all().order_by('id') # 分页 pagination_class = GoodsPagination serializer_class = GoodsSerializer filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend,filters.SearchFilter) # 设置filter的类为我们自定义的类 filter_class = GoodsFilter #搜索,=name表示精确搜索,也可以使用各种正则表达式 search_fields = ('=name','goods_brief')
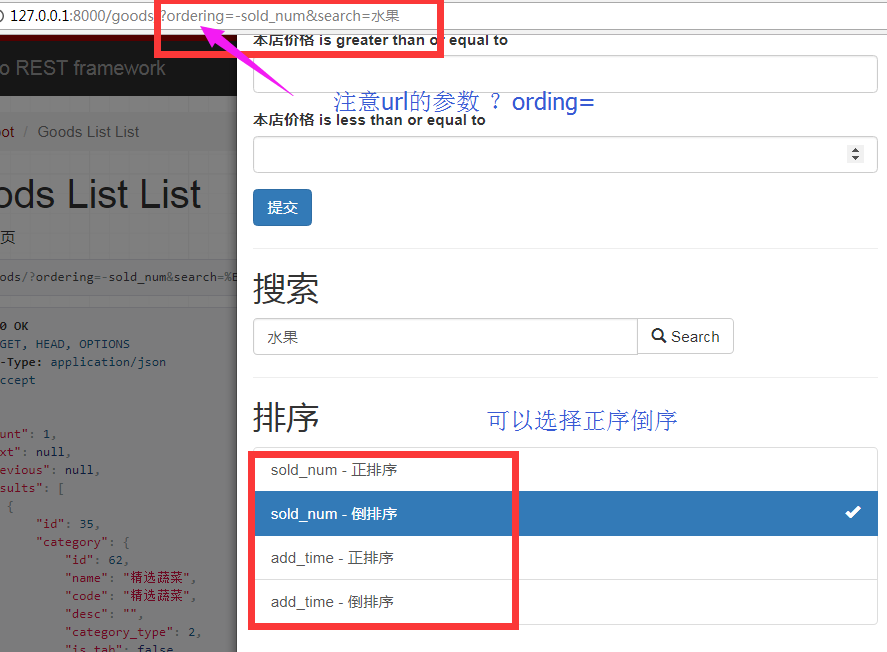
添加排序功能主要配置以下参数
filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend,filters.SearchFilter,filters.OrderingFilter)
ordering_fields = ('sold_num', 'add_time')

class GoodsListViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin,viewsets.GenericViewSet): '商品列表页' #这里必须要定义一个默认的排序,否则会报错 queryset = Goods.objects.all().order_by('id') # 分页 pagination_class = GoodsPagination serializer_class = GoodsSerializer # filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend,filters.SearchFilter) filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend, filters.SearchFilter, filters.OrderingFilter) # 设置filter的类为我们自定义的类 filter_class = GoodsFilter #搜索,=name表示精确搜索,也可以使用各种正则表达式 search_fields = ('=name','goods_brief') # 排序 ordering_fields = ('sold_num', 'add_time')
所有代码

from goods.serializers import GoodsSerializer from .models import Goods from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework import mixins,viewsets from rest_framework import generics from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination from .filters import GoodsFilter from django_filters.rest_framework import DjangoFilterBackend from rest_framework import filters class GoodsPagination(PageNumberPagination): ''' 商品列表自定义分页 ''' #默认每页显示的个数 page_size = 5 #可以动态改变每页显示的个数 page_size_query_param = 'page_size' #页码参数 page_query_param = 'page' #最多能显示多少页 max_page_size = 100 class GoodsListViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin,viewsets.GenericViewSet): '商品列表页' #这里必须要定义一个默认的排序,否则会报错 queryset = Goods.objects.all().order_by('id') # 分页 pagination_class = GoodsPagination serializer_class = GoodsSerializer # filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend,filters.SearchFilter) filter_backends = (DjangoFilterBackend, filters.SearchFilter, filters.OrderingFilter) # 设置filter的类为我们自定义的类 filter_class = GoodsFilter #搜索,=name表示精确搜索,也可以使用各种正则表达式 search_fields = ('=name','goods_brief') # 排序 ordering_fields = ('sold_num', 'add_time')

from django.conf.urls import url,include import xadmin from MxShop.settings import MEDIA_ROOT from django.views.static import serve from rest_framework.documentation import include_docs_urls from goods.views import GoodsListViewSet from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter router = DefaultRouter() #配置goods的url router.register(r'goods', GoodsListViewSet) urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', xadmin.site.urls), url(r'^media/(?P<path>.*)$', serve, {"document_root": MEDIA_ROOT}), url(r'docs/', include_docs_urls(title="慕学生鲜")), url(r'^api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework')), url('^', include(router.urls)), ]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号