6- scrapy框架高级
如何实现翻页请求

实现翻页请求
通过爬取腾讯招聘的页面的招聘信息,学习如何实现翻页请求
http://hr.tencent.com/position.php
找到下一页的地址
通过yield scrapy.Request(下一页的地址,callback=self.parse)构造一个url地址的request请求对象传递给调度器

需要爬取的东西
1 获取每个职位的分组,用于遍历
2 获取每个职位的名称
3 获取每个职位的工作地点
4 获取每个职位的工作职责
创建一个项目:
scrapy startproject tencent
创建一个名为itcast的爬虫,并指定爬取域的范围:
scrapy genspider t_spider tencent.com
在setting中设置日志的等级,不需要显示太多的日志信息
LOG_LEVEL='WARNING'
在t_spider.py中将start_urls的值修改为需要爬取的第一个url "http://hr.tencent.com/position.php"
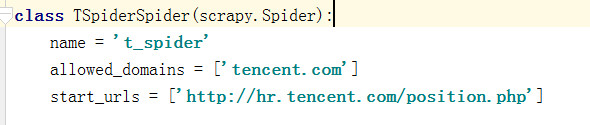
可以在parse方法中通过response从网页上提取数据

# 把详情页的url传递给调度器 yield scrapy.Request(item['detail_href'],callback=self.detail_url) # 把下一页的地址传给调度器 yield scrapy.Request(next_url, callback=self.parse)
yield scrapy.Request可以发送url地址yield item可以把清洗过的数据交给管道

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy class TSpiderSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 't_spider' allowed_domains = ['tencent.com'] start_urls = ['http://hr.tencent.com/position.php'] def parse(self, response): # 获取职位的分组信息 # 第一个和最后一个tr不需要 tr_list = response.xpath('//table[@class="tablelist"]//tr')[1:-1] # 遍历分组,拿到想要的数据 for tr in tr_list: # 定义一个字典用于存储清洗过的数据 item = {} # 获取职位的名称 # item['possition_name'] = tr.xpath('.//td[1]/a/text()').extract_first() # item['catagroy'] = tr.xpath('.//td[2]/text()').extract_first() # 上面的内容详情页里面有所以在详情页面中获取 # 获取每个职位的详情的的url item['detail_href'] ='http://hr.tencent.com/'+ tr.xpath('.//td[1]/a/@href').extract_first() # 把详情页的url传递给调度器 yield scrapy.Request(item['detail_href'],callback=self.detail_url) # 获取下一页的url next_url = response.xpath('//a[@id="next"]/@href').extract_first() if next_url != 'javascript:;': next_url='http://hr.tencent.com/'+next_url yield scrapy.Request(next_url, callback=self.parse) # print(item) def detail_url(self, response): item = {} item['possition_name'] = response.xpath('.//tr[@class="h"]/td/text()').extract_first() item['catagroy'] = response.xpath('.//tr[@class="c bottomline"]/td[2]/text()').extract_first() item['duty_list'] = response.xpath('.//ul[@ class="squareli"]/li/text()').extract_first() yield item
在pipelines.py中打印传送过来的值
class TencentPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): # 打印传送的值 print(item) return item
在setting中把PIP_INLINE的注释打开

运行爬虫t_spider
scrapy crawl t_spider
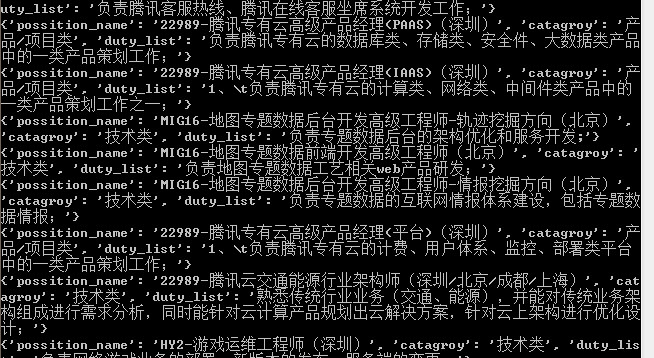
通过爬取阳光热线问政平台来学习item的使用
目标:所有的投诉帖子的编号、帖子的url、帖子的标题和内容
url: http://wz.sun0769.com/index.php/question/questionType?type=4&page=0
创建项目yanggaung
scrapy startproject yangguang
创建一个名为yg的爬虫,并指定爬取域的范围:
scrapy genspider yg sun0769.com
在setting中设置日志的等级,不需要显示太多的日志信息
LOG_FILE= 'WARNING'
在setting中添加USER_AGENT
USER_AGENT = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/61.0.3163.100 Safari/537.36'
在items的文件中
import scrapy class YangguangItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() num = scrapy.Field() title = scrapy.Field() href = scrapy.Field() handle_stats = scrapy.Field() #处理状态 author_name = scrapy.Field() #发帖人名字 publish_time = scrapy.Field() #发帖时间 content_img = scrapy.Field() #帖子图片 content_text = scrapy.Field() #帖子文本
在yg_spider.py中将start_urls的值修改为需要爬取的第一个url http://wz.sun0769.com/index.php/question/questionType?type=4&page=0

可以在parse方法中通过response从网页上提取数据

调用在items的文件中定义好的字典
from yangguang.items import YangguangItem
直接使用就行
item = YangguangItem()
# 获取编号
item['num'] = tr.xpath('.//td[1]/text()').extract_first()
# 获取标题
item['title'] = tr.xpath('.//td[2]/a[2]/@title').extract_first()
# 获取帖子的链接
item['href'] = tr.xpath('.//td[2]/a[2]/@href').extract_first()
# 获取处理的状态
item['handle_stats'] = tr.xpath('.//td[3]/span/text()').extract_first()
# 作者的名字
item['author_name'] = tr.xpath('.//td[4]/text()').extract_first()
# 发布时间
item['publish_time'] = tr.xpath('.//td[5]/text()').extract_first()
完整代码:

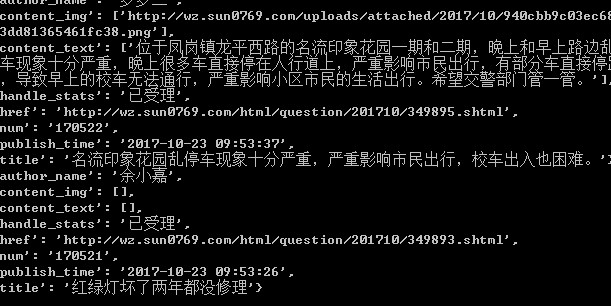
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from yangguang.items import YangguangItem class YgSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'yg' allowed_domains = ['sun0769.com'] start_urls = ['http://wz.sun0769.com/index.php/question/questionType?type=4&page=0'] def parse(self, response): # 获取分组的信息 tr_list=response.xpath('//div[@class="greyframe"]//table[2]//table/tr') # 遍历分组获取数据 for tr in tr_list: item = YangguangItem() # 获取编号 item['num'] = tr.xpath('.//td[1]/text()').extract_first() # 获取标题 item['title'] = tr.xpath('.//td[2]/a[2]/@title').extract_first() # 获取帖子的链接 item['href'] = tr.xpath('.//td[2]/a[2]/@href').extract_first() # 获取处理的状态 item['handle_stats'] = tr.xpath('.//td[3]/span/text()').extract_first() # 作者的名字 item['author_name'] = tr.xpath('.//td[4]/text()').extract_first() # 发布时间 item['publish_time'] = tr.xpath('.//td[5]/text()').extract_first() # 获取下一页的url 地址 next_url = response.xpath('.//a[text()=">"]/@href').extract_first() if next_url is not None: yield scrapy.Request(next_url,callback=self.parse) # 构造详情页的Request请求 yield scrapy.Request( item['href'], callback=self.parse_detail, meta={'item':item}, # 传送的数据必须是字典的格式 ) # print(item) def parse_detail(self,response): item = response.meta['item'] item['content_img']=response.xpath('//div[@class="textpic"]/img/@src').extract() item['content_text']=response.xpath('//div[@class="c1 text14_2"]/div[@class="contentext"]/text()').extract() yield item
在piplines中打印出来
class YangguangPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
print(item)
运行爬虫yg
scrapy crawl yg

图片和content有好多字符要处理
在piplines.py中处理这些数据
import json
class YangguangPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
item["content_img"] = ["http://wz.sun0769.com"+i for i in item["content_img"]]
item["content_text"] = [i.replace("\xa0","").replace("\t","") for i in item["content_text"]]
item["content_text"] = [i for i in item["content_text"] if len(i)>0]
print(item)
# with open("yangguang.txt","a",encoding="utf-8") as f:
# f.write(json.dumps(dict(item),ensure_ascii=False))
# return item
再次运行爬虫处理过后的数据:
Scrapy深入之scrapy shell
Scrapy shell是一个交互终端,我们可以在未启动spider的情况下尝试及调试代码,也可以用来测试XPath表达式
使用方法:
scrapy shell http://www.itcast.cn/channel/teacher.shtml
response.url:当前响应的url地址
response.request.url:当前响应对应的请求的url地址
response.headers:响应头
response.body:响应体,也就是html代码,默认是byte类型
response.requests.headers:当前响应的请求头
Scrapy中CrawlSpider
回头看:
之前的代码中,我们有很大一部分时间在寻找下一页的url地址或者是内容的url地址上面,这个过程能更简单一些么?
思路:
1、从response中提取所有的a标签对应的url地址
2、自动的构造自己requests请求,发送给引擎
上面的功能可以做的更好:
满足某个条件的url地址,我们才发送给引擎,同时能够指定callback函数
需求:爬取csdn上面所有的博客专家及其文章的文章
Url地址:http://blog.csdn.net/experts.html
目标:通过csdn爬虫了解crawlspider的使用
创建项目的名字
scrapy startproject csdn
生成crawlspider的命令
cd csdn
scrapy genspider -t crawl scdn_spider scdn.com
在scdn_spider中写上对应的匹配规则
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule class ScdnSpiderSpider(CrawlSpider): name = 'scdn_spider' allowed_domains = ['blog.csdn.net'] start_urls = ['http://blog.csdn.net/SunnyYoona'] rules = ( # 获取博客专家的地址 Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'blog.csdn.net/\w+$'), follow=True), # 获取博客专家的翻页地址 Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'channelid=\d+&page=\d+$'),follow=True), # 获取详情页的地址 Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'/\w+/article/details/\d+'), callback='parse_item'), # 博客列表页 翻页 Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'/\w+/article/list/\d+$'),follow=True), ) def parse_item(self, response): item = {} item["title"] = response.xpath("//h1/text()").extract_first() item["publish_date"] = response.xpath("//span[@class='time']/text()").extract_first() item["article_tag"] = response.xpath("//ul[@class='article_tags clearfix csdn-tracking-statistics']//text()").extract() # print(item) yield item
在piplines中对数据进一步处理
import re
class CsdnPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
item["article_tag"] = [re.sub(r'\s|/','',i) for i in item["article_tag"]]
item["article_tag"] = [i for i in item["article_tag"] if len(i) > 0 and i!='标签:']
print(item)
# return item



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号