python 实用编程技巧 —— 多线程并发相关问题与解决技巧
如何使用多线程
创建一个线程类来封装数据
from threading import Thread
from time import sleep
def handle(sid):
print('Download...(%d)' % sid)
sleep(2)
print('Convert to...(%d)' % sid)
class MyThread(Thread): # 自定义线程类
def __init__(self, sid):
# Thread.__init__(self)
super(MyThread, self).__init__() # 必须调用 父类的构造器 这是py2的语法,py3是super().__init__()
self.sid = sid # 使用类,能够更好的封装数据
def run(self): # 新建程序的入口点,和target类似
handle(self.sid) # 更常见的做法是将handle也做为这个类的方法
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = MyThread(1)
t.start()
t.join()
print('main thread')
如何实现线程间的通信
GIL
- 在每个进程中, 存在一把GIL, 该进程中的线程间共享GIL
- 多线程进行时, 只有有GIL的那个线程能运行
- 通过线程间快速 传递GIL, 达到表象上的多线程, 其实同一时间只有一个线程在工作
解决方案:
- 使用标准库中的 queue.Queue, 它是一个线程安全的队列
from threading import Thread
from queue import Queue
from time import sleep
class DownThread(Thread):
def __init__(self, sid, queue):
# Thread.__init__(self)
super(DownThread, self).__init__()
self.sid = sid
self.queue = queue
def downLoad(self, sid):
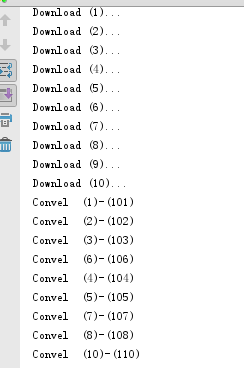
print("Download (%d)..." % sid)
sleep(2)
def run(self):
self.downLoad(self.sid)
data = self.sid + 100
self.queue.put((self.sid, data))
class ConvelThread(Thread):
def __init__(self, queue):
# Thread.__init__(self)
super(ConvelThread, self).__init__()
self.queue = queue
def convel(self, id, data):
print("Convel (%d)-(%d)" % (id, data))
def run(self):
while (True):
id , data = self.queue.get() # 元组解包的形式得到数据
if (data):
self.convel( id , data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
q = Queue()
dThreads = [DownThread(i, q) for i in range(1, 11)]
cThread = ConvelThread(q)
for t in dThreads:
t.start()
cThread.start()
for t in dThreads:
t.join()
q.put((-1, None)) # 往队列中写入-1使 转换线程结束
cThread.join()
print('MainThread')
tar包打包
import tarfile
import os
def FunTarFile(tfname):
tf = tarfile.open(tfname,'w:gz') #open打开一个tar包,‘w’打开模式为写 ‘:gz’压缩模式gzip
for fname in os.listdir('.'): #遍历当前目录的文件
if fname.endswith('.docx'):
tf.add(fname) #将此文件加入tar包
os.remove(fname) #移除此文件
tf.close()
print (tf.members) #打印tar包成员信息
if not tf.members: #判断tar包是否为空
os.remove(tfname) #如果tar包为空,删除此tar包
FunTarFile('DocxTar.tgz')
事件通知使用方法
线程间的事件通知, 可以使用标准库中 Threading.Event
- 等待事件一端调用wait, 等待事件
- 通知事件一端调用 set, 通知事件
from threading import Event,Thread
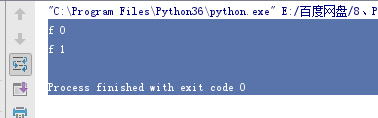
def f(e):
print('f 0')
e.wait() #事件等待,阻塞
print('f 1')
if __name__ == '__main__':
e = Event()
t = Thread(target=f, args=(e,)) #创建子线程,运行f函数
t.start() # 子线程运行
e.set() # 主线程里 事件发送


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号