python 实用编程技巧 —— 数据结构与算法
如何在列表, 字典, 集合中根据条件筛选数据
过滤列表中的负数
使用列表解析方法
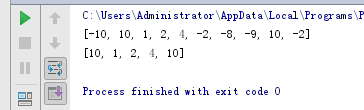
from random import randint data = [randint(-10,10) for _ in range(10)] print(data) print(list(filter(lambda x:x>=0,data)))

使用 filter 函数
from random import randint data = [randint(-10,10) for _ in range(10)] print(data) print(list(filter(lambda x:x>=0,data)))
找出分数大于90的学生
字典解析方法
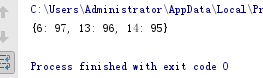
from random import randint
d = {x:randint(60,100) for x in range(1,21)}
list(filter(lambda x:x[1] > 90, d.items()))
使用 filter 函数
[filter(lambda item: item[1] >= 90, d.items())]
留下集合中的3的倍数
from random import randint
s = {randint(0,20) for _ in range(20)}
list(filter(lambda x:x%3==0, s))

如何为元组中的每个元素命名, 提高程序可读性
定义一系列数值常量或枚举类型
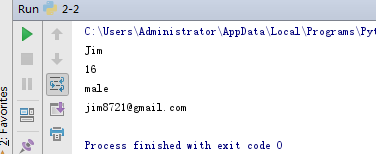
NAME, AGE, SEX, EMAIL = range(4)
student = ('Jim', 16, 'male', 'jim8721@gmail.com')
print(student[NAME])
print(student[AGE])
print(student[SEX])
print(student[EMAIL])

使用 python3 中的枚举类型
from enum import IntEnum
class StudentEnum(IntEnum):
NAME = 0
AGE = 1
SEX = 2
EMAIL = 3
print(student[StudentEnum.NAME])
print(student[StudentEnum.AGE])
print(student[StudentEnum.SEX])
print(student[StudentEnum.EMAIL])

使用标准库中 collections.namedtuple 替代内置tuple
from collections import namedtuple
Student = namedtuple('Student', ['name', 'age', 'sex', 'email'])
s2 = Student('Jim', 16, 'male', 'jim8721@gmail.com')
print(s2.name)
print(s2.age)
print(s2.sex)
print(s2.email)
如何统计序列中元素的出现频度
将序列转化为字典{元素: 频度}, 根据字典中的值排序
from random import randint
data = [randint(0,20) for _ in range(30)]
#fromkeys:用于创建并返回一个新的字典。两个参数:第一个是字典的键,第二个(可选)是传入键的值,默认为None。
c = dict.fromkeys(data,0)
for x in data:
c[x] += 1
# 如果只是想取出最大的3个,可以使用堆代替排序后再取值的方法
import heapq
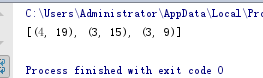
res2 = heapq.nlargest(3, ((v,k) for k,v in c.items()))
print(res2)
使用标准库collections中的Counter对象
from collections import Counter from random import randint data = [randint(0,20) for _ in range(30)] c2 = Counter(data) #找出频率出现最高的3个元素 print(c2.most_common(3))

实际运用: 词频统计
from collections import Counter
import re
txt = open('example.txt').read() # 读入文件
wordList = re.split('\W+', txt)
c2 = Counter(wordList) # 可以传入列表或者字典
res4 = c2.most_common(10)
print(res4)

如何根据字典中值的大小, 对字典中的项排序
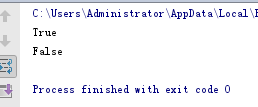
元祖进行比较,先比较第一个元素,在比较第二个元素
# 元祖进行比较,先比较第一个元素,在比较第二个元素 print((97, 'a') > (96, 'b')) print((97, 'a') > (97, 'b'))
利用zip将字典转换成元组进行排序
from random import randint
d = {x:randint(60,100) for x in 'xyzabc'}
print(d)
print(sorted(zip(d.values(),d.keys())))

传递sorted函数的key参数
from random import randint
d = {x:randint(60,100) for x in 'xyzabc'}
print(sorted(d.items(),key=lambda x:x[1]))

如何快速找到多个字典中的公共键(key)
random 函数取样
from random import randint,sample
# 取样
print(sample('abcdef',3)) # 随机去 3 个

方案一: 利用集合的交集操作
from random import randint,sample
# 取样
s1 = {x:randint(1,4) for x in sample('abcdef',randint(3,6))}
s2 = {x:randint(1,4) for x in sample('abcdef',randint(3,6))}
s3 = {x:randint(1,4) for x in sample('abcdef',randint(3,6))}
print(s1)
print(s2)
print(s3)
print('resuit ===========')
print(s1.keys() & s2.keys() & s3.keys())
方案二: 使用map和reduce
- step1 使用字典的keys方法, 得到一个字典keys的集合
- step2 使用map函数, 得到每个字典keys的集合
- step3 使用reduce函数, 取所有字典的keys集合的交集
from random import randint,sample
from functools import reduce
s1 = {x:randint(1,4) for x in sample('abcdef',randint(3,6))}
s2 = {x:randint(1,4) for x in sample('abcdef',randint(3,6))}
s3 = {x:randint(1,4) for x in sample('abcdef',randint(3,6))}
dl = [s1, s2,s3]
print(s1)
print(s2)
print(s3)
print('result======')
print(reduce(lambda a, b: a & b, map(dict.keys, dl)))

如何让字典保持排序
使用标准库collections 中的OrderedDict
为了能控制一个字典中元素的顺序,你可以使用 collections 模块中的 OrderedDict 类。 在迭代操作的时候它会保持元素被插入时的顺序
from collections import OrderedDict
d = OrderedDict()
d['foo'] = 1
d['bar'] = 2
d['spam'] = 3
d['grok'] = 4
# Outputs "foo 1", "bar 2", "spam 3", "grok 4"
for key in d:
print(key, d[key])
如何实现用户的历史记录功能(最多n条)
使用容量为n的 队列存储历史记
- 使用标准库collections中的deque, 它是一个双端循环队列
- 使用pickle模块将历史记录存储到硬盘, 以便下次启动使用(代替数据库)
from random import randint
from collections import deque
N = randint(0, 100)
history = deque([], 5)
def guess(k):
if k == N:
print('Right')
return True
if k < N:
print('%s is less-than N' % k)
else:
print('%s is greater-than N' % k)
return False
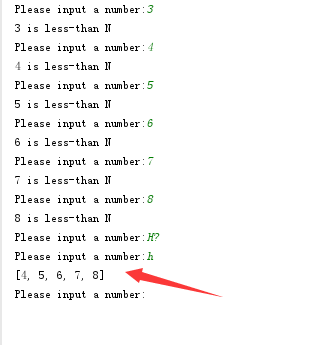
while True:
line = input('Please input a number:')
if line.isdigit():
k = int(line)
history.append(k)
if guess(k):
break
elif line == 'history' or line == 'h':
print(list(history))
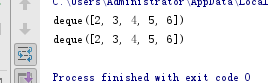
plckle 基本使用
from collections import deque
import pickle
q = deque([2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
print(q)
# 将数据存入文件
pickle.dump(q,open('history','wb'))
# 读取文件
q2 = pickle.load(open('history','rb'))
print(q2)