python 实用编程技巧 —— 带额外状态信息的回调函数
带额外状态信息的回调函数
问题
你的代码中需要依赖到回调函数的使用(比如事件处理器、等待后台任务完成后的回调等), 并且你还需要让回调函数拥有额外的状态值,以便在它的内部使用到。
解决方案
调用回调函数的函数
# 异步回调
def apply_async(func, args, *, callback):
# Compute the result
result = func(*args)
# Invoke the callback with the result
callback(result)
def print_result(result):
print('Got:', result)
def add(x, y):
return x + y
res = apply_async(add, (2, 3), callback=print_result)
apply_async(add, ('hello', 'world'), callback=print_result)
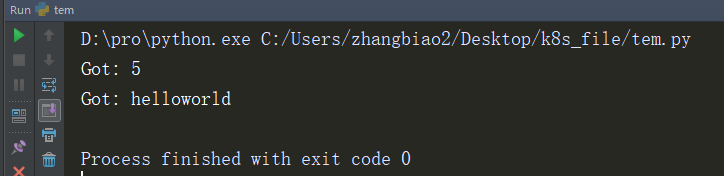
注意到 print_result() 函数仅仅只接受一个参数 result 。不能再传入其他信息。 而当你想让回调函数访问其他变量或者特定环境的变量值的时候就会遇到麻烦。
为了让回调函数访问外部信息,一种方法是使用一个绑定方法来代替一个简单函数。 比如,下面这个类会保存一个内部序列号,每次接收到一个 result 的时候序列号加1
# 异步回调
class ResultHandler:
def __init__(self):
self.sequence = 0
def handler(self, result):
self.sequence += 1
print('[{}] Got: {}'.format(self.sequence, result))
def apply_async(func, args, *, callback):
# Compute the result
result = func(*args)
# Invoke the callback with the result
callback(result)
return 'ok'
def add(x, y):
return x + y
if __name__ == '__main__':
r = ResultHandler()
res = apply_async(add, (2, 3), callback=r.handler)
res = apply_async(add, ('hello', 'world'), callback=r.handler)
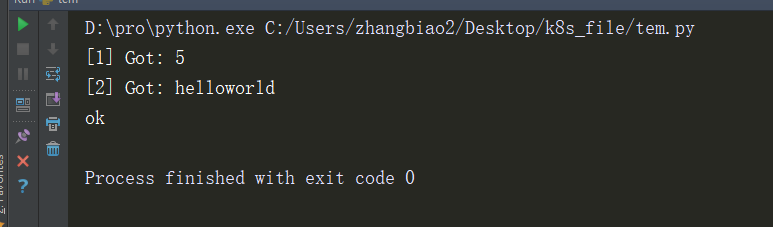
第二种方式,作为类的替代,可以使用一个闭包捕获状态值,例如:
# 异步回调
def make_handler():
sequence = 0
def handler(result):
nonlocal sequence
sequence += 1
print('[{}] Got: {}'.format(sequence, result))
return handler
def apply_async(func, args, *, callback):
# Compute the result
result = func(*args)
# Invoke the callback with the result
callback(result)
return 'ok'
def add(x, y):
return x + y
if __name__ == '__main__':
handler = make_handler()
res = apply_async(add, (2, 3), callback=handler)
res = apply_async(add, ('hello', 'world'), callback=handler)
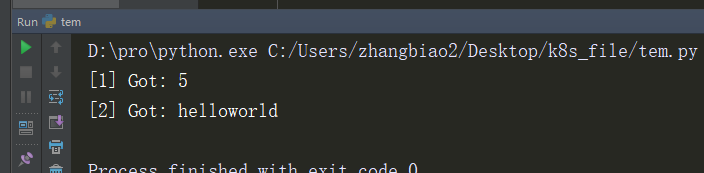
还有另外一个更高级的方法,可以使用协程来完成同样的事情
# 异步回调
def make_handler():
sequence = 0
while True:
result = yield
sequence += 1
print('[{}] Got: {}'.format(sequence, result))
def apply_async(func, args, *, callback):
# Compute the result
result = func(*args)
# Invoke the callback with the result
callback(result)
return 'ok'
def add(x, y):
return x + y
if __name__ == '__main__':
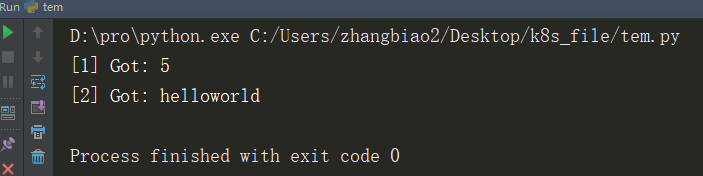
handler = make_handler()
next(handler)
res = apply_async(add, (2, 3), callback=handler.send)
res = apply_async(add, ('hello', 'world'), callback=handler.send)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号