12 python asyncio并发编程
事件循环
asyncio是python用于解决异步io编程的一整套解决方案
执行 10 个耗时的请求
import asyncio
import time
async def get_html(url):
print("start get url")
await asyncio.sleep(2)
print("end get url")
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = [get_html("http://www.imooc.com") for i in range(10)]
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
print(time.time()-start_time)
loop.close()
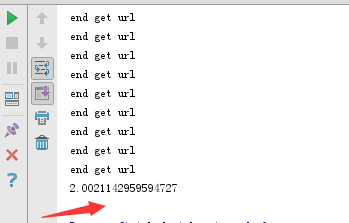
输出结果如下
获取协程的返回值
1 创建一个任务 task
2 通过调用 task.result 获取协程的返回值
import asyncio
import time
async def get_html(url):
print("start get url")
await asyncio.sleep(2)
return "zhangbiao"
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
task = loop.create_task(get_html("http://www.imooc.com"))
loop.run_until_complete(task)
print(task.result())
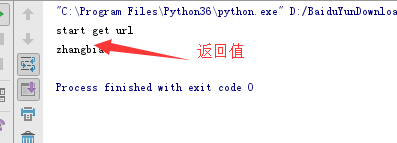
输出结果如下
执行成功进行回调处理
可以通过 add_done_callback( 任务) 添加回调,因为这个函数只接受一个回调的函数名,不能传参,我们想要传参可以使用偏函数
# 获取协程的返回值
import asyncio
import time
from functools import partial
async def get_html(url):
print("start get url")
await asyncio.sleep(2)
return "zhangbiao"
def callback(url, future):
print(url)
print("send email to bobby")
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
task = loop.create_task(get_html("http://www.imooc.com"))
task.add_done_callback(partial(callback, "http://www.imooc.com"))
loop.run_until_complete(task)
print(task.result())
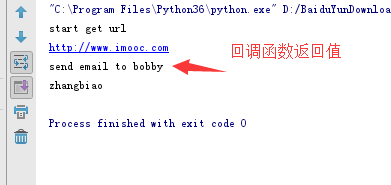
输出结果如下
wait 和 gather区别
这两个都可以添加多个任务到事件循环中
gather 比wait更加的高级
1 可以对任务进行分组
2 可以取消任务
import asyncio
import time
async def get_html(url):
print("start get url")
await asyncio.sleep(2)
print("end get url")
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = [get_html("http://www.imooc.com") for i in range(10)]
#gather和wait的区别
# tasks = [get_html("http://www.imooc.com") for i in range(10)]
# loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
group1 = [get_html("http://projectsedu.com") for i in range(2)]
group2 = [get_html("http://www.imooc.com") for i in range(2)]
group1 = asyncio.gather(*group1)
group2 = asyncio.gather(*group2)
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(group1, group2))
print(time.time() - start_time)
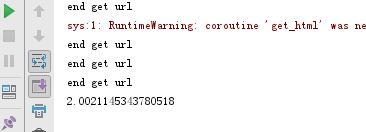
输出结果如下
task取消和子协程调用原理
程序运行时 通过 ctl +c 取消任务 调用task.cancel()取消任务
import asyncio
import time
async def get_html(sleep_times):
print("waiting")
await asyncio.sleep(sleep_times)
print("done after {}s".format(sleep_times))
if __name__ == "__main__":
task1 = get_html(2)
task2 = get_html(3)
task3 = get_html(3)
tasks = [task1, task2, task3]
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
try:
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
except KeyboardInterrupt as e:
all_tasks = asyncio.Task.all_tasks()
for task in all_tasks:
print("cancel task")
print(task.cancel())
loop.stop()
loop.run_forever()
finally:
loop.close()
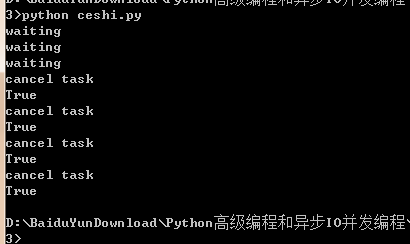
在终端
python ceshi.py # 运行成功后 按 ctl +c 取消任务
输出结果如下
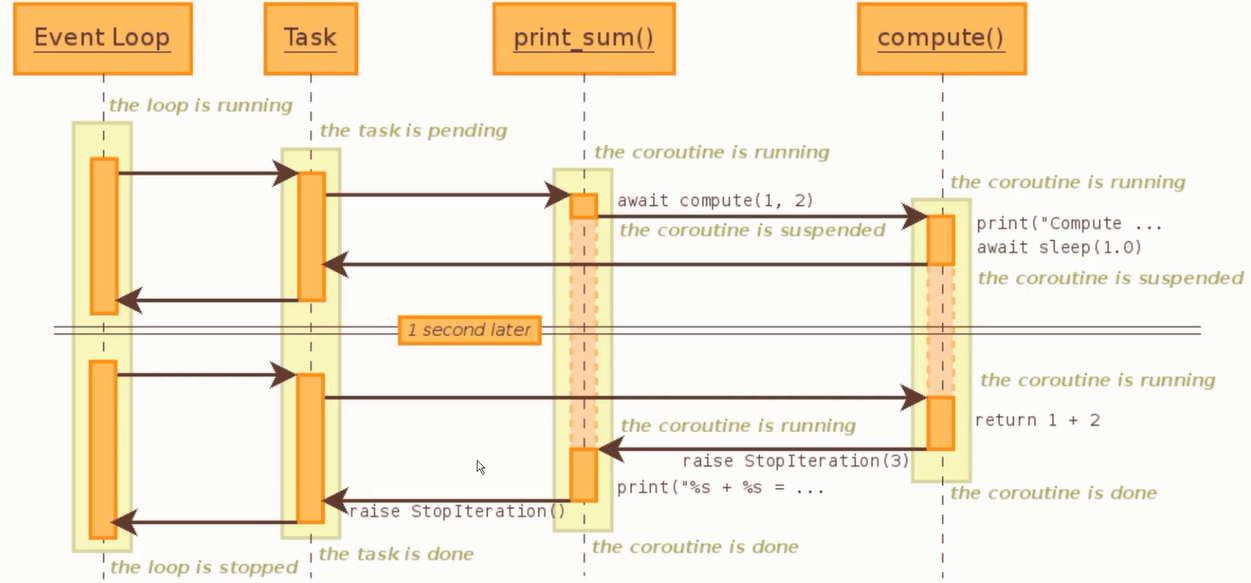
子协程调用原理图
官方的一个实例如下

从下面的原理图我们可以看到
1 当时间循环处于运行状态的时候 任务Task 处于pending(等待),会把控制权交给委托生成器print_sum
2 委托生成器print_sum 会建立一个双向通道为Task和子生成器,调用子生成器compute并把值传递过去
3 子生成器compute会通过委托生成器建立的双向通道把自己当前的状态suspending(暂停),传给Task,Task告诉loop它数据还没处理完成
4 loop会循环检测Task ,Task通过双向通道去看自生成器是否处理完成
5 子生成器处理完成后会向委托生成器抛出一个异常和计算的值,并关闭生成器
6 委托生成器再把异常抛给任务(Task),把任务关闭
7 loop停止循环
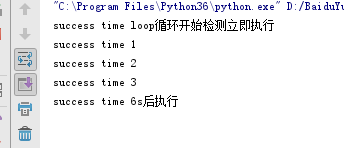
call_soon、call_at、call_later、call_soon_threadsafe
call_soon 循环开始检测时,立即执行一个回调函数
call_at 循环开始的第几秒s执行
call_later 循环开始后10s后执行
call_soom_threadsafe 立即执行一个安全的线程
import asyncio
import time
def callback(str, loop):
print("success time {}".format(str))
def stoploop(str,loop):
time.sleep(str)
loop.stop()
#call_later, call_at
if __name__ == "__main__":
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.call_soon(callback, 'loop循环开始检测立即执行', loop)
now = loop.time() # loop循环时间
loop.call_at(now+2, callback, 2, loop)
loop.call_at(now+1, callback, 1, loop)
loop.call_at(now+3, callback, 3, loop)
loop.call_later(6,callback,"6s后执行",loop)
# loop.call_soon_threadsafe(stoploop,loop)
loop.run_forever()
运行结果如下
ThreadPollExecutor 和 asyncio 完成阻塞 IO 请求
在asyncio 中集成线程池处理耗时IO
在协程中同步阻塞的写法,但有些时候不得已就是一些同步耗时的接口
可以把线程池进程到asynico模块中
tasks = []
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(3)
for url in range(20):
url = "http://shop.projectsedu.com/goods/{}/".format(url)
task = loop.run_in_executor(executor, get_url, url)
tasks.append(task)
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
完整代码如下
#使用多线程:在携程中集成阻塞io
import asyncio
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import socket
from urllib.parse import urlparse
def get_url(url):
#通过socket请求html
url = urlparse(url)
host = url.netloc
path = url.path
if path == "":
path = "/"
#建立socket连接
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# client.setblocking(False)
client.connect((host, 80)) #阻塞不会消耗cpu
#不停的询问连接是否建立好, 需要while循环不停的去检查状态
#做计算任务或者再次发起其他的连接请求
client.send("GET {} HTTP/1.1\r\nHost:{}\r\nConnection:close\r\n\r\n".format(path, host).encode("utf8"))
data = b""
while True:
d = client.recv(1024)
if d:
data += d
else:
break
data = data.decode("utf8")
html_data = data.split("\r\n\r\n")[1]
print(html_data)
client.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
import time
start_time = time.time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(3)
tasks = []
for url in range(20):
url = "http://shop.projectsedu.com/goods/{}/".format(url)
task = loop.run_in_executor(executor, get_url, url)
tasks.append(task)
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
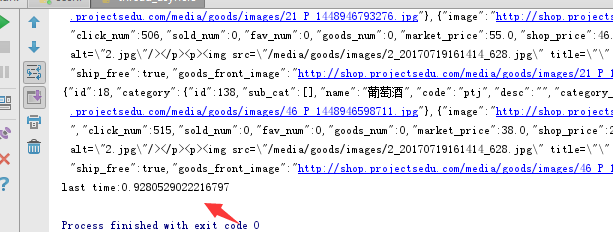
print("last time:{}".format(time.time()-start_time))
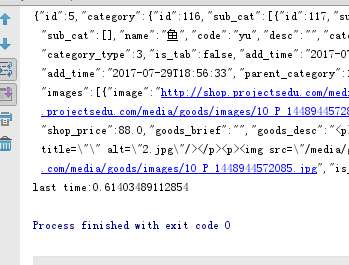
输出结果如下
不用集成也是可以的 但是要在函数的前面加上 async使同步变成异步写法

#使用多线程:在携程中集成阻塞io import asyncio from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor import socket from urllib.parse import urlparse import time async def get_html(url): #通过socket请求html url = urlparse(url) host = url.netloc path = url.path if path == "": path = "/" #建立socket连接 client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) # client.setblocking(False) client.connect((host, 80)) #阻塞不会消耗cpu #不停的询问连接是否建立好, 需要while循环不停的去检查状态 #做计算任务或者再次发起其他的连接请求 client.send("GET {} HTTP/1.1\r\nHost:{}\r\nConnection:close\r\n\r\n".format(path, host).encode("utf8")) data = b"" while True: d = client.recv(1024) if d: data += d else: break data = data.decode("utf8") html_data = data.split("\r\n\r\n")[1] print(html_data) client.close() if __name__ == "__main__": start_time = time.time() loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() tasks = [get_html("http://shop.projectsedu.com/goods/2/") for i in range(10)] loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks)) print(time.time() - start_time)
输出结果如下

asyncio 模拟 http 请求
#asyncio 没有提供http协议的接口 aiohttp
import asyncio
import socket
from urllib.parse import urlparse
async def get_url(url):
#通过socket请求html
url = urlparse(url)
host = url.netloc
path = url.path
if path == "":
path = "/"
#建立socket连接
reader, writer = await asyncio.open_connection(host,80)
writer.write("GET {} HTTP/1.1\r\nHost:{}\r\nConnection:close\r\n\r\n".format(path, host).encode("utf8"))
all_lines = []
async for raw_line in reader:
data = raw_line.decode("utf8")
all_lines.append(data)
html = "\n".join(all_lines)
return html
async def main():
tasks = []
for url in range(20):
url = "http://shop.projectsedu.com/goods/{}/".format(url)
tasks.append(asyncio.ensure_future(get_url(url)))
for task in asyncio.as_completed(tasks): # 获取执行完的任务
result = await task # 获取执行完任务的结果
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import time
start_time = time.time()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(main())
print('last time:{}'.format(time.time()-start_time))
输出结果如下
future 和 task
future 是一个结果的容器,结果执行完后在内部会回调call_back函数
task 是future的子类,可以用来激活协程
asyncio同步和通信
在多少线程中考虑安全性,需要加锁,在协程中是不需要的
import asyncio
total = 0
async def add():
global total
for _ in range(1000000):
total += 1
async def desc():
global total, lock
for _ in range(1000000):
total -= 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
tasks = [add(), desc()]
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
print(total)
输出结果如下
在有些情况在对协程中我们还是需要类似锁的机制
parse_stuff和use_stuff有共同调用的代码 get_stuff parse_stuff去请求的时候 如果get_stuff也去请求, 会触发网站的反爬虫机制. 这就需要我们像上诉代码那样加lock
get_stuff 和 use_stuff 中都调用了parse_stuff我们想在get_stuff中只请求一次,下次用缓存,所以要用到锁
import asyncio
import aiohttp
from asyncio import Lock
cache = {}
lock = Lock()
async def get_stuff(url):
async with lock: # 等价于 with await lock: 还有async for 。。。类似的用法
# 这里可以使用async with 是因为 Lock中有__await__ 和 __aenter__两个魔法方法
# 和线程一样, 这里也可以用 await lock.acquire() 并在结束时 lock.release
if url in cache:
return cache[url]
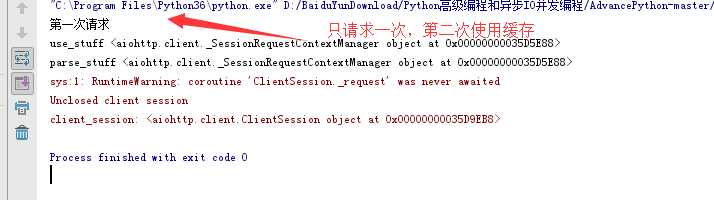
print("第一次请求")
stuff = aiohttp.request('GET', url)
cache[url] = stuff
return stuff
async def parse_stuff(url):
stuff = await get_stuff(url)
print('parse_stuff',stuff)
# do some parse
async def use_stuff(url):
stuff = await get_stuff(url)
print('use_stuff',stuff)
# use stuff to do something interesting
if __name__ == '__main__':
tasks = [parse_stuff('baidu'), use_stuff('baidu')]
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
输出结果如下
asyncio 通信 queue
协程是单线程的,所以协程中完全可以使用全局变量实现queue来相互通信,但是如果想要 在queue中定义存放有限的最大数目。 我们需要使用 :
put 和get 的前面都要加 await
from asyncio import Queue queue = Queue(maxsize=3) await queue.get() await queue.put()
aiohttp实现高并发爬虫
# asyncio爬虫, 去重, 入库 import asyncio import re import aiohttp import aiomysql from pyquery import PyQuery stopping = False start_url = 'http://www.jobbole.com' waitting_urls = [] seen_urls = set() # 实际使用爬虫去重时,数量过多,需要使用布隆过滤器 async def fetch(url, session): async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: try: async with session.get(url) as resp: print('url status: {}'.format(resp.status)) if resp.status in [200, 201]: data = await resp.text() return data except Exception as e: print(e) def extract_urls(html): # html中提取所有url urls = [] pq = PyQuery(html) for link in pq.items('a'): url = link.attr('href') if url and url.startwith('http') and url not in seen_urls: urls.append(url) waitting_urls.append(urls) return urls async def init_urls(url, session): html = await fetch(url, session) seen_urls.add(url) extract_urls(html) async def article_handler(url, session, pool): # 获取文章详情并解析入库 html = await fetch(url, session) extract_urls(html) pq = PyQuery(html) title = pq('title').text() # 为了简单, 只获取title的内容 async with pool.acquire() as conn: async with conn.cursor() as cur: await cur.execute('SELECT 42;') insert_sql = "insert into article_test(title) values('{}')".format( title) await cur.execute(insert_sql) # 插入数据库 # print(cur.description) # (r,) = await cur.fetchone() # assert r == 42 async def consumer(pool): async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: while not stopping: if len(waitting_urls) == 0: # 如果使用asyncio.Queue的话, 不需要我们来处理这些逻辑。 await asyncio.sleep(0.5) continue url = waitting_urls.pop() print('start get url:{}'.format(url)) if re.match('http://.*?jobbole.com/\d+/', url): if url not in seen_urls: # 是没有处理过的url,则处理 asyncio.ensure_future(article_handler(url, sssion, pool)) else: if url not in seen_urls: asyncio.ensure_future(init_urls(url)) async def main(loop): # 等待mysql连接建立好 pool = await aiomysql.creat_pool(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='aiomysql_test', loop=loop, charset='utf8', autocommit=True) # charset autocommit必须设置, 这是坑, 不写数据库写入不了中文数据 async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: html = await fetch(start_url, session) seen_urls.add(start_url) extract_urls(html) asyncio.ensure_future(consumer(pool)) if __name__ == '__main__': loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() asyncio.ensure_future(main(loop)) loop.run_forever()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号