hdu 2665 Kth number(划分树模板)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2665
[ poj 2104 2761 ] 改变一下输入就可以过
http://poj.org/problem?id=2104
http://poj.org/problem?id=2761
Kth number
Time Limit: 15000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 3266 Accepted Submission(s): 1090
The second line contains n integers, describe the sequence. Each of following m lines contains three integers s, t, k. [s, t] indicates the interval and k indicates the kth big number in interval [s, t]
划分树是一种基于线段树的数据结构。主要用于快速求出(在log(n)的时间复杂度内)序列区间的第k大值 。
划分树和归并树都是用线段树作为辅助的,原理是基于快排 和归并排序 的。
划分树的建树过程基本就是模拟快排过程,取一个已经排过序的区间中值,然后把小于中值的点放左边,大于的放右边。并且记录d层第i个数之前(包括i)小于中值的放在左边的数。具体看下面代码注释。
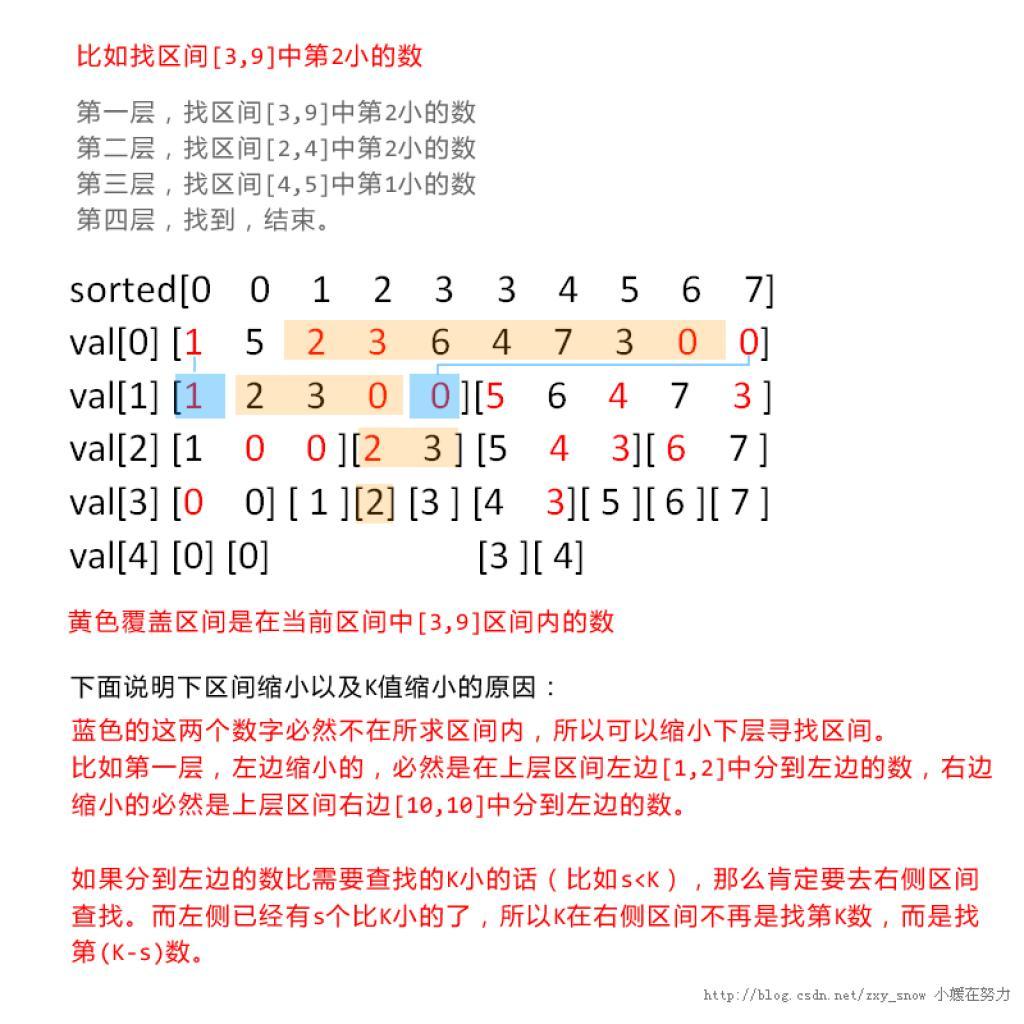
查找其实是关键,因为再因查找[l,r]需要到某一点的左右孩子时需要把[l,r]更新。具体分如下几种情况讨论: 假设要在区间[l,r]中查找第k大元素,t为当前节点,lch,rch为左右孩子,left,mid为节点t左边界和中间点。
1、sum[r]-sum[l-1]>=k,查找lch[t],区间对应为[ left+sum[l-1] , left+sum[r]-1 ]
2、sum[r]-sum[l-1]<k,查找rch[t],区间对应为[ mid+1+l-left-sum[l-1] , mid+1+r-left-sum[r] ]
上面两个关系在纸上可以推出来,对着上图更容易理解关系式;
讲解转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/pony1993/archive/2012/07/17/2594544.html
AC代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<string.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 #define N 100010 9 10 int sorted[N]; //排序完的数组 11 int toleft[30][N]; //toleft[i][j]表示第i层从1到k有多少个数分入左边 12 int tree[30][N]; //表示每层每个位置的值 13 14 void buildingTree(int l,int r,int dep) 15 { 16 if(l==r) return; 17 int mid = (l+r)>>1; 18 int i,sum = mid-l+1; //表示等于中间值而且被分入左边的个数 19 for(i=l;i<=r;i++) 20 { 21 if(tree[dep][i]<sorted[mid]) sum--; 22 } 23 int lpos=l; 24 int rpos=mid+1; 25 for(i=l;i<=r;i++) 26 { 27 if(tree[dep][i]<sorted[mid]) //比中间的数小,分入左边 28 { 29 tree[dep+1][lpos++]=tree[dep][i]; 30 } 31 else if(tree[dep][i]==sorted[mid]&&sum>0) //等于中间的数值,分入左边,直到sum==0后分到右边 32 { 33 tree[dep+1][lpos++]=tree[dep][i]; 34 sum--; 35 } 36 else //右边 37 { 38 tree[dep+1][rpos++]=tree[dep][i]; 39 } 40 toleft[dep][i] = toleft[dep][l-1] + lpos - l; //从1到i放左边的个数 41 } 42 buildingTree(l,mid,dep+1); 43 buildingTree(mid+1,r,dep+1); 44 } 45 46 //查询区间第k大的数,[L,R]是大区间,[l,r]是要查询的小区间 47 int queryTree(int L,int R,int l,int r,int dep,int k) 48 { 49 if(l==r) return tree[dep][l]; 50 int mid = (L+R)>>1; 51 int cnt = toleft[dep][r] - toleft[dep][l-1]; //[l,r]中位于左边的个数 52 if(cnt>=k) 53 { 54 int newl = L + toleft[dep][l-1] - toleft[dep][L-1]; //L+要查询的区间前被放在左边的个数 55 int newr = newl + cnt - 1; //左端点加上查询区间会被放在左边的个数 56 return queryTree(L,mid,newl,newr,dep+1,k); 57 } 58 else 59 { 60 int newr = r + toleft[dep][R] - toleft[dep][r]; 61 int newl = newr - (r - l - cnt); 62 return queryTree(mid+1,R,newl,newr,dep+1,k-cnt); 63 } 64 } 65 66 67 int main() 68 { 69 int t; 70 scanf("%d",&t); 71 while(t--) 72 { 73 int n,m,i; 74 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 75 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 76 { 77 scanf("%d",&tree[0][i]); 78 sorted[i] = tree[0][i]; 79 } 80 sort(sorted+1,sorted+1+n); 81 buildingTree(1,n,0); 82 while(m--) 83 { 84 int s,t,k; 85 scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&t,&k); 86 printf("%d\n",queryTree(1,n,s,t,0,k)); 87 } 88 } 89 return 0; 90 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号