[luogu p5677] 配对统计
给定一个序列 ,定义 为好的配对当且仅当 且对于 有 。给定 组询问,每组询问给定 (),查询 中有多少好的配对。
处理好的配对
首先可以观察到,题目对于好的配对的描述其实就是说 对于 而言是整个数列中差最小的。很自然想到排序,排序后好的配对一定会相邻。需要注意的是,排序时应该采用结构体,才能保护好数列中每一个数的位置信息。其次注意原题的数据已经给出了每个数不同的限定。
排序后,设排序后的下标是 ,排序前的位置是 ,对于每个数进行判断:
- ,那么 便是一组好的配对;
- ,那么 便是一组好的配对;
- ,那么 两组均为好的配对。
需要注意的是,对于好的配对 , 不一定是好的配对!比如 , 就是好的配对,而 不是。但是在这里,如果好的配对 有 ,那么我们将 进行调换,以 的形式记录为好的配对。虽然 本质上并不是好的配对,但这种记录方式完全不会影响答案。非得这么记录也不是吃饱了撑的,这是便于后面的处理,请接着往下看。
统计好的配对
上面我们已经处理好了好的配对信息,那么接下来进入第二部分,统计好的配对。
首先我们会发现,直接将所有好的配对统计进去很难用树状数组处理。又观察到题目中所给的操作只有查询,没有增删改。不免想到HH的项链,一切似乎都告诉我们,正解应该是将查询离线。
先考虑将查询按照r第一关键字l第二关键字从小到大排序,这样,每次查询都相当于查询右边界r在不断向右挪动。
不妨假想一个数组 表示左端点 的好的配对个数。每次扫到一个询问,首先把右边界向右挪动到当前询问的右边界,挪动的过程中可能会扫过一些好的配对的右边界,此时我们考虑将这样的好的配对选中,将这样选中的好配对数量统计起来,再减去 ,也就是扣除左边界在要查询左边界之外的不符合条件的好的配对。
所以还需要提前将好对也按照右边界第一左边界第二排一下序……
下面是来自zhr的博客的图例
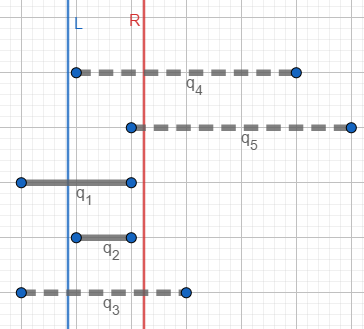
实线就是当前选中的好的配对,虚线就是未选中的好的配对(因为当前右边界还没有扫到这些配对的右边界)。同时我们可以发现 的左边界在查询左边界之外,所以实际统计数量还需要把这条线段扣去。()
数组怎么维护呢?想必聪明的你已经想到,用树状数组简单维护一下即可。
处理好的配对时间复杂度 。(排序 ,预处理好对 )
统计好的配对时间复杂度 。( 在树状数组上)
/*
* @Author: crab-in-the-northeast
* @Date: 2022-02-27 20:49:14
* @Last Modified by: crab-in-the-northeast
* @Last Modified time: 2022-02-27 22:25:20
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#define int long long
inline int read() {
int x = 0;
bool flag = true;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-')
flag = false;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
if (flag)
return x;
return ~(x - 1);
}
const int maxn = 300005;
const int maxm = 300005;
int n, m;
inline int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
struct number {
int v, pos;
const bool operator < (const number b) {
return this -> v < b.v;
}
}a[maxn];
struct pair {
int l, r;
const bool operator < (const pair b) {
if (this -> r != b.r)
return this -> r < b.r;
return this->l < b.l;
}
}p[maxn * 2];
int pcnt;
inline void insert_pair(int l, int r) {
l = a[l].pos;
r = a[r].pos;
if (l > r)
l ^= r ^= l ^= r;
p[++pcnt].l = l;
p[pcnt].r = r;
}
struct question {
int l, r, pos;
const bool operator < (const question b) {
if (this -> r != b.r)
return this -> r < b.r;
return this->l < b.l;
}
}q[maxm];
int c[maxn];
void add(int x) {
for (; x <= n; x += lowbit(x))
++c[x];
}
int query(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowbit(x))
ans += c[x];
return ans;
}
signed main() {
n = read();
m = read();
if (n == 1) {
puts("0");
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].v = read();
a[i].pos = i;
}
std :: sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
insert_pair(1, 2);
insert_pair(n - 1, n);
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
int dl = a[i].v - a[i - 1].v, dr = a[i + 1].v - a[i].v;
if (dl <= dr)
insert_pair(i, i - 1);
if (dl >= dr)
insert_pair(i, i + 1);
}
std :: sort(p + 1, p + 1 + pcnt);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
q[i].l = read();
q[i].r = read();
q[i].pos = i;
}
std :: sort(q + 1, q + 1 + m);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (; j <= pcnt && p[j].r <= q[i].r; ++j)
add(p[j].l);
ans += q[i].pos * (j - query(q[i].l - 1) - 1);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
本题最大亮点离线。

