springAOP及事务控制
一、编写事务控制类(动态代理简化代码)
1.spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置代理Service-->
<bean id="proxyAccountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
<!--配置beanfactory-->
<bean id="beanFactory" class="com.li.factory.BeanFactory">
<property name="accountService" ref="accountService"></property>
<!--注入事务管理器-->
<property name="txManager" ref="txManager"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置Service(被代理对象)-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.li.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!--注入dao对象-->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置dao-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.li.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!--注入QueryRunner对象-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"></bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置Connection的工具类 ConnectionUtils-->
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.li.utils.ConnectionUtils">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="com.li.utils.TransactionManage">
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.工具类编写
1)连接数据库工具
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 连接的工具类,用于从数据源中获取一个连接,并实现和线程的绑定
*/
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
private DataSource dataSource; // set注入数据源
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
/**
* 获取当前线程上的连接
*/
public Connection getThreadConnection() {
try {
//1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
Connection conn = tl.get();
//2.判断当前线程上是否有链接
if (conn == null) {
//3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并从入ThreadLocal
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
//4.返回当前线程的连接
return conn;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 把连接和线程解绑
*/
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
2)事务控制管理类
/**
* 和事务管理相关的事务类:开启、提交、回滚、释放事务
*/
public class TransactionManage {
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils; //set注入
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 提交事务
*/
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 释放连接
*/
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();//还回线程池中
connectionUtils.removeConnection();//解绑
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.创建代理类
/**
* 用于创建Service的代理对象的工厂
*/
public class BeanFactory {
private IAccountService accountService;
private TransactionManage txManager;
public void setTxManager(TransactionManage txManager) {
this.txManager = txManager;
}
public final void setAccountService(IAccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
/**
* 获取Service代理对象
* @return
*/
public IAccountService getAccountService() {
return (IAccountService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 添加事务的支持
*
* @param proxy
* @param method
* @param args
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
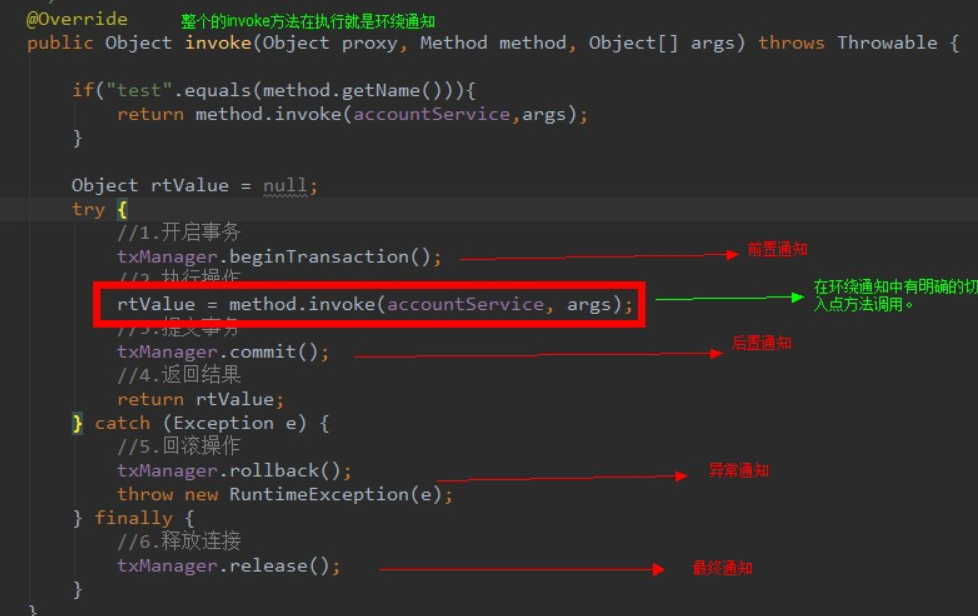
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object rtValue = null;
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
/**
*2.执行操作
* invoke:
* 1.被代理的对象
* 2.代理的方法的参数
*/
rtValue = method.invoke(accountService, args);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return rtValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
//5.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//6.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
});
}
}
4.Service对象及接口创建
import com.li.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.li.domain.Account;
import com.li.service.IAccountService;
import com.li.utils.TransactionManage;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
* 事务控制
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService{
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
return accountDao.findAllAccount();
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.saveAccount(account);
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
@Override
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
accountDao.deleteAccount(accountId);
}
@Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
//2.1根据名称查询转出账户
Account source=accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.2 根据名称查询转入账户
Account target=accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//2.3转出账户减钱
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
//2.4转入账户加钱
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
//2.5更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
int i=5/0;
//2.6更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
}
5.创建AccountDao的类和接口
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner;
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
try {
return runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account", new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try {
return runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account where id=?",new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"insert into account(name,money) values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try {
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"delete from account where id=?",accountId);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 转账
* @param accountName
* @return
*/
@Override
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
try {
List<Account> accounts=runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account where name=?", new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class), accountName);
if(accounts==null || accounts.size()==0)
{
return null;
}
if(accounts.size()>1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一");
}
return accounts.get(0);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
6.测试类
/**
* 使用junit测试配置
*
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("proxyAccountService")
private IAccountService as=null;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
as.transfer("aaa","bbb",520f);
}
}
二、SpringAOP概念
1.什么是AOP?
面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序的功能的统一维护的技术,利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑个部分的耦合降低,提高程序可重用性。
2.AOP实现方式:动态代理技术
3.AOP作用优势
作用:在程序运行期间,不修改源代码对已有的方法进行增强
优势:减少重复代码、提高开发效率、维护方便
4.AOP的相关术语
Joinpoint(连接点): 所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点(代理对象中所有的方法)。在 spring 中,这些点指的是方法,因为 spring 只支持方法类型的 连接点。
Pointcut(切入点): 所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些 Joinpoint 进行拦截的定义(被增强的方法)。
Advice(通知/增强): 所谓通知是指拦截到 Joinpoint 之后所要做的事情就是通知。
通知的类型:前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知,环绕通知
Introduction(引介): 引介是一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下, Introduction 可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方 法或 Field。
Target(目标对象): 代理的目标对象(被代理对象)。
Weaving(织入): 是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。 spring 采用动态代理织入,而 AspectJ 采用编译期织入和类装载期织入。
Proxy(代理): 一个类被 AOP 织入增强后,就产生一个结果代理类(代理对象)。
Aspect(切面): 是切入点和通知(引介)的结合。


