缓冲流、转换流、序列化流
一、缓冲流
1.概念:
缓冲流的基本原理,是在创建流对象时,会创建一个内置的默认大小的缓冲区数组,通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率。
2.分类:
-
-
字符缓冲流:
BufferedReader,
-
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in):创建一个 新的缓冲输入流。 -
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建一个新的缓冲输出流。
public class BufferedDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { // 记录开始时间 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 创建流对象 try ( BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("jdk9.exe")); //创建字节缓冲输入流 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy.exe"));//创建字节缓冲输出流 ){ // 读写数据 int len; byte[] bytes =new byte[1*1024]; while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) { bos.write(bytes,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 记录结束时间 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("缓冲流复制时间:"+(end - start)+" 毫秒"); } }
4. 字符缓冲流
-
-
public BufferedWriter(Writer out): 创建一个新的缓冲输出流。
特有的方法:
-
-
BufferedWriter:
public void newLine(): 写一行行分隔符,由系统属性定义符号。 -
例1:
public class BufferedReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建流对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("in.txt")); // 定义字符串,保存读取的一行文字 String line = null; // 循环读取,读取到最后返回null while ((line = br.readLine())!=null) { System.out.print(line); System.out.println("------"); } // 释放资源 br.close(); } }
例2:
public static void writer1() { //文件字符输出流 File str =new File("2.txt"); BufferedWriter writer; try { writer =new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(str)); //操作 //写法一 /*String str1 ="I love you 蔡徐坤"; char[] aa =str1.toCharArray(); //字符串->>字符数组 writer.write(aa,0,aa.length);*/ //写法二 /*String str1 ="I love you 蔡徐坤"; writer.write(str1,0,str1.length());*/ //写法三 writer.append("唱跳 Rop"); writer.newLine(); //换行符 writer.append("蔡徐坤"); writer.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } }
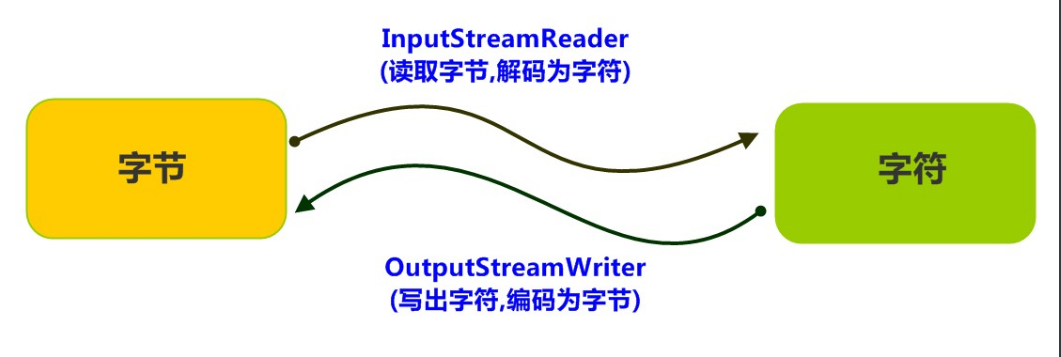
二、转换流
1.
解码:字节(看不懂的)-->字符(能看懂的)
2.InputStreamReader类
构造方法:
-
-
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName): 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt")); InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt") , "GBK");
3.OutputStreamWriter类
构造方法:
-
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in): 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。 -
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in, String charsetName): 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
OutputStreamWriter isr = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("out.txt")); OutputStreamWriter isr2 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("out.txt") , "GBK");
三、序列化流

1.ObjectOutputStream
-
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建一个指定OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream。
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("employee.txt"); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
-
该类必须实现
java.io.Serializable接口,Serializable是一个标记接口,不实现此接口的类将不会使任何状态序列化或反序列化,会抛出NotSerializableException。 -
该类的所有属性必须是可序列化的。如果有一个属性不需要可序列化的,则该属性必须注明是瞬态的,使用
transient关键字修饰。
2.ObjectInputStream类
构造方法:
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("employee.txt"); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);
四、打印流
1.PrintStream类
构造方法:
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("ps.txt");