Blazor笔记-Form components
更新记录#
注意:非教程。纯笔记,日常查询用的。需要教程的小伙伴找几本书看看即可哈哈,有Vue基础的话非常快,概念都是通的。非工作需要不建议深入学习Blazor,深入Vue吧,用的多,哈哈。完整目录地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cqpanda/p/17596348.html
点击查看
2024年3月7日 发布。
2023年8月1日 迁移笔记到博客。
Forms#
Handling user input with forms is the cornerstone of many common applications. Applications use forms to enable users to log in, to update a profile, to enter sensitive information, and to perform many other data-entry tasks. Blazor makes it easy to create and manage them using C#. With Blazor's data binding capabilities, form validation, and other features, you can quickly create dynamic and interactive forms that help users input and submit data.
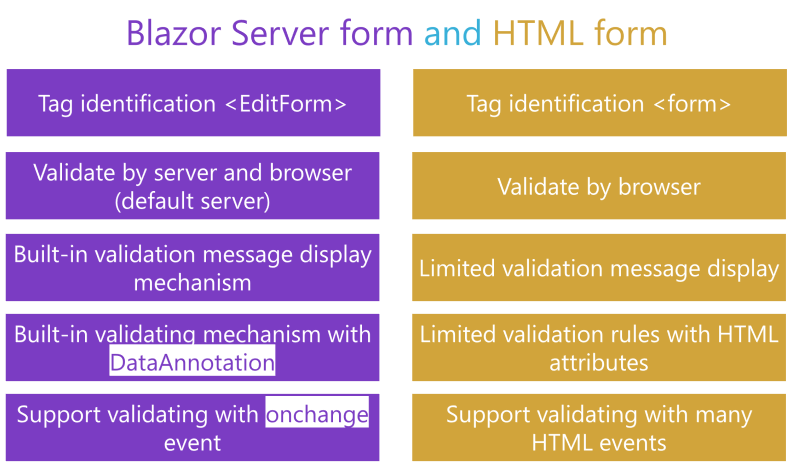
Blazor form and HTML form#
EditForm is a component that is used to create forms in Blazor applications, while HTML form is a standard way of creating forms in HTML. The EditForm component in Blazor provides features such as form validation, disabling a form control, and data binding. It allows developers to easily create forms that are tightly integrated with their Blazor application.
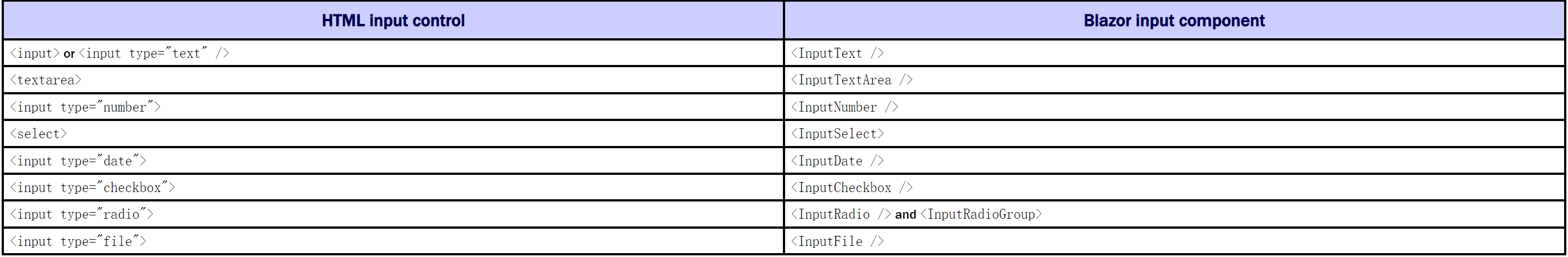
Blazor Form components#
EditForm
InputBase<>
InputCheckbox
InputDate<TValue>
InputNumber<TValue>
InputSelect<TValue>
InputText
InputTextArea
InputRadio
InputRadioGroup
ValidationMessage
ValidationSummary
对应关系:
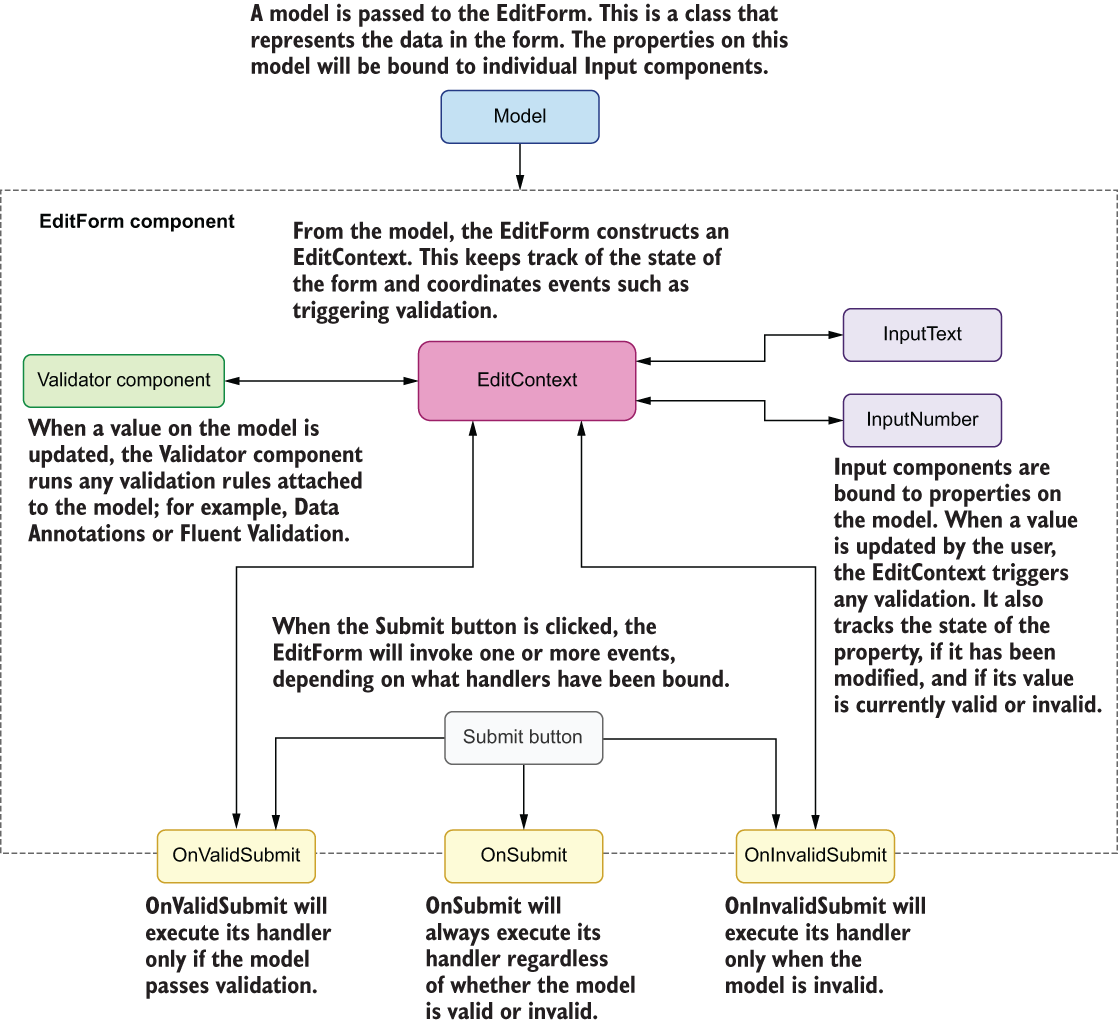
EditForm#
EditForm renders as a form tag, but it has a lot more functionalities.
<EditForm Model="BlazorFormModel" OnSubmit="_ => BlazorFormSubmitted = true">
<fieldset>
<legend>Blazor form</legend>
<InputText @bind-Value="BlazorFormModel.BlazorFormResult" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</fieldset>
</EditForm>
<EditForm Model="personmodel" OnValidSubmit="validSubmit">
...
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</EditForm>
@code {
Person personmodel = new Person();
private Task validSubmit()
{
//Do database stuff
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
Form with Bind
<EditForm Model="FormModel" OnSubmit="HandleFormSubmit">
<InputText @bind-Value="FormModel.InputText" />
<button>Submit</button>
</EditForm>
@code {
public class SimpleBlazorFormModel
{
public string InputText { get; set; } = "Blazor School";
}
public SimpleBlazorFormModel FormModel { get; set; } = new();
public void HandleFormSubmit()
{
// Do something with the form data
}
}
Blazor form events#
EditForm has the following events:
• OnValidSubmit gets triggered when the data in the form validates correctly (we will come back to validation in just a bit).
• OnInvalidSubmit gets triggered if the form does not validate correctly.
• OnSubmit gets triggered when the form is submitted, regardless of whether the form validates correctly or not. Use OnSubmit if you want to control the validation yourself.
InputBase<>#
All the Blazor input classes derive from the InputBase class. It has a bunch of things we can use for all the input components
InputBase handles AdditionalAttributes, which means that if we add any other attributes to the tag, they will automatically get transferred to the output. This means that the components derived from this class can leverage any HTML attributes since they will be part of the output.
InputCheckbox#
The InputCheckbox component will render as <input type="checkbox">
InputDate<TValue>#
The InputDate component will render as <input type="date">. We can use DateTime and DateTimeOffset as values for the InputDate component.
There is no way to format the date; it will use the web browser’s current setting. This behavior is by design and is part of the HTML5 spec.
InputNumber<TValue>#
The InputNumber component will render as <input type="number">. We can use Int32, Int64, Single, Double, and Decimal as values for the InputNumber component
InputSelect<TValue>#
The InputSelect component will render as <select>. We will create InputSelect later in this chapter, so I won’t go into further detail here.
InputText#
The InputText component will render as <input type="text">.
InputTextArea#
The InputSelect component will render as <textarea>. In this chapter, we will build our own version of this control.
InputRadio#
The InputRadio component will render as <input type="radio">.
InputRadioGroup#
The InputRadioGroup component will render as <Input type="radio">.
InputFile#
The InputFile component will render as <Input type="file">. This component will make it easier to get the file data. It will supply us with a stream for each file’s content.
ValidationMessage#
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => model.Name)"/>
Binding elements#
Binding to HTML elements
<input type="text" @bind="Variable"/>
<input type="text" @bind="Variable" @bind:event="oninput"/>
<input type="text" @bind:get="SomeText" @bind:set="SetAsync" />
<input type="text" @bind="SomeText" @bind:after="AfterAsync" />
<input type="text" @bind="SomeNumber" @bind:culture="GBCulture" />
<input type="text" @bind="SomeDate" @bind:format="MM/dd/yyyy" />
<input type="text" @bind="SomeDate" @bind:format="yyyy-MM-dd" />
Binding to components
<InputText @bind-Value="text" />
<InputText @bind-Value:get="text" @bind-Value:set="(value) => {text=value;}" />
<InputText @bind-Value:get="text" @bind-Value:set="Set" />
<InputText @bind-Value:get="text" @bind-Value:set="SetAsync" />
<InputText @bind-Value="text" @bind-Value:after="() => { }" />
<InputText @bind-Value="text" @bind-Value:after="After" />
<InputText @bind-Value="text" @bind-Value:after="AfterAsync" />
Disable a form control#
Use the HTML disabled attribute
<InputText class="form-control" @bind-Value="FormModel.ExampleString" disabled="true" />
Use the Blazor @bind-disabled directive
<InputText class="form-control" @bind-Value="FormModel.ExampleString" @bind-disabled="DisableFormControl"/>
@code {
public bool DisableFormControl { get; set; } = false;
...
}
表单验证使用Blazored.FluentValidation#
安装包#
https://github.com/Blazored/FluentValidation
dotnet add package Blazored.FluentValidation
在中引入命名空间
_Imports.razor
@using FluentValidation
@using Blazored.FluentValidation
基本使用(同步验证)#
<EditForm Model="@_person" OnValidSubmit="@SubmitValidForm">
<FluentValidationValidator />
@*如果要集中显示验证错误信息*@
<ValidationSummary />
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="Name" class="font-weight-bold text-secondary">姓名:</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="@_person.Name" class="form-control" id="Name" />
@*显示单个表单元素的错误信息*@
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => _person.Name)" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="Age" class="font-weight-bold text-secondary">年龄:</label>
<InputNumber @bind-Value="@_person.Age" class="form-control" id="Age" />
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => _person.Age)" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="Email" class="font-weight-bold text-secondary">邮箱:</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="@_person.EmailAddress" class="form-control" id="Email" />
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => _person.EmailAddress)" />
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" disabled="@(IsSending == true)">@((MarkupString)(IsSending == true ? "发送中" : "保存"))</button>
<button type="reset" class="btn btn-warning">清空</button>
</EditForm>
@code {
/// <summary>
/// 是否发送中
/// </summary>
public bool IsSending { get; set; } = false;
/// <summary>
/// 需要验证的模型
/// </summary>
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string EmailAddress { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 模型验证规则设置
/// </summary>
public class PersonValidator : AbstractValidator<Person>
{
public PersonValidator()
{
RuleFor(p => p.Name).NotEmpty().WithMessage("名字是必须的啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Name).MaximumLength(50).WithMessage("名字必须小于50个字符啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Name).MinimumLength(5).WithMessage("名字必须大于于5个字符啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Age).NotEmpty().WithMessage("年龄不可以为空");
RuleFor(p => p.Age).GreaterThan(0).WithMessage("年龄必须大于0岁啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Age).LessThanOrEqualTo(200).WithMessage("年龄必须小于200岁啦");
RuleFor(p => p.EmailAddress).NotEmpty().WithMessage("邮箱地址不可以为空");
RuleFor(p => p.EmailAddress).EmailAddress().WithMessage("必须提供一个有效的邮箱地址啦");
}
}
private Person _person = new();
private async Task SubmitValidForm()
{
IsSending = true;
//flush changes
await Task.Delay(1);
//模拟处理中
await Task.Delay(2000);
Console.WriteLine(_person.Name);
Console.WriteLine(_person.Age);
Console.WriteLine(_person.EmailAddress);
IsSending = false;
}
}
禁用验证#
默认情况下,会使用反射为所有的表单进行注入验证,可以设置禁用验证。
<FluentValidationValidator DisableAssemblyScanning="@true" />
基本使用(异步验证)(Async Validation)#
<EditForm Model="@_person" OnValidSubmit="@SubmitValidForm">
<FluentValidationValidator @ref="_fluentValidationValidator" />
@*如果要集中显示验证错误信息*@
<ValidationSummary />
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="Name" class="font-weight-bold text-secondary">姓名:</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="@_person.Name" class="form-control" id="Name" />
@*显示单个表单元素的错误信息*@
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => _person.Name)" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="Age" class="font-weight-bold text-secondary">年龄:</label>
<InputNumber @bind-Value="@_person.Age" class="form-control" id="Age" />
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => _person.Age)" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="Email" class="font-weight-bold text-secondary">邮箱:</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="@_person.EmailAddress" class="form-control" id="Email" />
<ValidationMessage For="@(() => _person.EmailAddress)" />
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" disabled="@(IsSending == true)">@((MarkupString)(IsSending == true ? "发送中" : "保存"))</button>
<button type="reset" class="btn btn-warning">清空</button>
</EditForm>
@code {
/// <summary>
/// 是否发送中
/// </summary>
public bool IsSending { get; set; } = false;
/// <summary>
/// 验证器的引用
/// </summary>
private FluentValidationValidator? _fluentValidationValidator;
/// <summary>
/// 需要验证的模型
/// </summary>
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string EmailAddress { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 模型验证规则设置
/// </summary>
public class PersonValidator : AbstractValidator<Person>
{
public PersonValidator()
{
RuleFor(p => p.Name).NotEmpty().WithMessage("名字是必须的啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Name).MaximumLength(50).WithMessage("名字必须小于50个字符啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Name).MinimumLength(5).WithMessage("名字必须大于于5个字符啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Age).NotEmpty().WithMessage("年龄不可以为空");
RuleFor(p => p.Age).GreaterThan(0).WithMessage("年龄必须大于0岁啦");
RuleFor(p => p.Age).LessThanOrEqualTo(200).WithMessage("年龄必须小于200岁啦");
RuleFor(p => p.EmailAddress).NotEmpty().WithMessage("邮箱地址不可以为空");
RuleFor(p => p.EmailAddress).EmailAddress().WithMessage("必须提供一个有效的邮箱地址啦");
}
}
private Person _person = new();
private async Task SubmitValidForm()
{
IsSending = true;
//flush changes
await Task.Delay(1);
if (await _fluentValidationValidator!.ValidateAsync())
{
//模拟处理中
await Task.Delay(2000);
Console.WriteLine(_person.Name);
Console.WriteLine(_person.Age);
Console.WriteLine(_person.EmailAddress);
}
IsSending = false;
}
}
作者:重庆熊猫
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/cqpanda/p/17596415.html
版权:本作品采用「不论是否商业使用都不允许转载,否则按3元1字进行收取费用」许可协议进行许可。
本文来自博客园,作者:重庆熊猫,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/cqpanda/p/17596415.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现