基于list_head实现的通用内核Hash表
由于linux内核中的struct list_head已经定义了指向前驱的prev指针和指向后继的next指针,并且提供了相关的链表操作方法,因此为方便复用,本文在它的基础上封装实现了一种使用开链法解决冲突的通用内核Hash表glib_htable,提供了初始化、增加、查找、删除、清空和销毁6种操作,除初始化和销毁外,其它操作都做了同步,适用于中断和进程上下文。与一般的通用Hash表(如c++中的hash_map及某些c语言实现的泛型哈希表)有以下不同:
● 存储在glib_htable里的对象由外部而不是内部负责创建,这个对象必须直接或间接地组合了list_head成员(间接组合,包含下文中的glib_hentry即可),这里引用UML中的术语组合,意在强调不是聚合关系。
● 删除操作的语义是从Hash表移去对象的链接,但释放对象是可选的。
● 桶的个数由外部指定而不是内部维护。
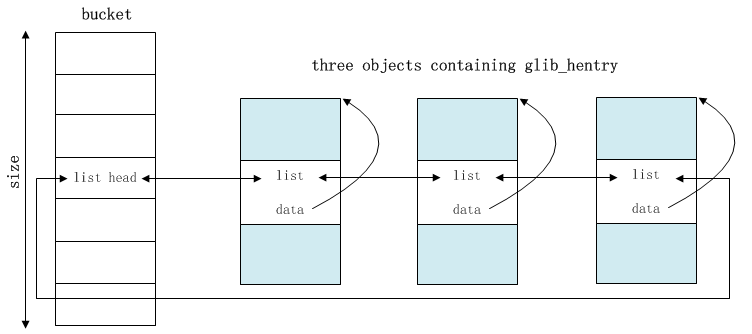
综上可见glib_htable是使用对象已存在的内嵌成员list_head来链接到Hash表中的,比一般的通用Hash表,每个表项节省了1个指针的空间,如下图所示。
结构定义
1)glib_hentry抽象了存储对象的内嵌成员,表示Hash项,也可表示整个对象,这时内嵌成员就是对象本身了,成员data表示对象关联的任意数据,用于计算hash值,当关联数据大小<=sizeof(void*)时,可直接强制转换为data存储,而不必为数据地址。
2)glib_htable抽象了Hash表,size表示桶个数,考虑到size可能很多,需要占用大块内存,所以在分配连续物理页失败的情况下,再使用vmalloc尝试分配不连续的物理页,所以引入了vmalloced表示分配方式,非零表示用vmalloc,零则用__get_free_pages;hashfun和cmpfun是实现Hash表的两个缺一不可的关键函数,cbfun用于查找成功时的回调处理,如打印、增加引用计数等,freefun用于释放对象,提供这个回调接口是为了方便从Hash表移除对象后可以释放对象,而不必由外部释放,增加了灵活性。
主要接口
以下所有操作中的第1参数ht表示glib_htable对象。
● 初始化
 int glib_htable_init(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int size, glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun, glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun); size表示Hash表桶的个数,hashfun为Hash函数,cmpfun为比较函数;成功时返回0,ht成员cbfun和freefun设置为空,失败返回ENOMEM。由于可能使用vmalloc分配内存,因此不能用于中断上下文。
int glib_htable_init(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int size, glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun, glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun); size表示Hash表桶的个数,hashfun为Hash函数,cmpfun为比较函数;成功时返回0,ht成员cbfun和freefun设置为空,失败返回ENOMEM。由于可能使用vmalloc分配内存,因此不能用于中断上下文。
● 增加
 void glib_htable_add(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num); 在一次同步内添加多个对象,he为指向对象Hash项的指针,num为个数。
void glib_htable_add(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num); 在一次同步内添加多个对象,he为指向对象Hash项的指针,num为个数。
● 查找
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_get(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_get(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data);
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_rget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_rget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data);
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg); 从上到下依次为正向查找、反向查找、正向条件查找、反向条件查找、按桶定位的正向条件查找、按桶定位的反向条件查找,data为对象关联数据,cmp为自定义的比较函数,arg为cmp所带的自定义参数,bucket为桶索引,若查找成功,则bucket更新为对象所在的桶索引。以上所有操作,当失败时返回NULL。
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg); 从上到下依次为正向查找、反向查找、正向条件查找、反向条件查找、按桶定位的正向条件查找、按桶定位的反向条件查找,data为对象关联数据,cmp为自定义的比较函数,arg为cmp所带的自定义参数,bucket为桶索引,若查找成功,则bucket更新为对象所在的桶索引。以上所有操作,当失败时返回NULL。
● 删除
 void glib_htable_del(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num);
void glib_htable_del(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num);
 void glib_htable_del_bydata(struct glib_htable *ht, const void **data, int num); 第1个按对象Hash项删除,第2个按对象关联数据删除,num表示个数,若ht成员freefun非空,则释放对象。
void glib_htable_del_bydata(struct glib_htable *ht, const void **data, int num); 第1个按对象Hash项删除,第2个按对象关联数据删除,num表示个数,若ht成员freefun非空,则释放对象。
● 清空
 void glib_htable_clear(struct glib_htable *ht); 在一次同步内删除所有的对象,若ht成员freefun非空,则释放对象。
void glib_htable_clear(struct glib_htable *ht); 在一次同步内删除所有的对象,若ht成员freefun非空,则释放对象。
● 销毁
 void glib_htable_free(struct glib_htable *ht); 仅释放所有桶占用的内存,应在glib_htable_clear后调用。由于可能使用vfree释放内存,因此不能用于中断上下文。
void glib_htable_free(struct glib_htable *ht); 仅释放所有桶占用的内存,应在glib_htable_clear后调用。由于可能使用vfree释放内存,因此不能用于中断上下文。
接口实现
其它接口实现比较简单,略过讲解。对于查找接口,如果增加一个参数来指示遍历方向,那么虽然接口总数减半,但在使用特别是在一个循环内调用时,每次都进行不必要的方向判断而降低了性能,所以对于正向和反向遍历,每个都给出一个接口,正如c库中的strchr与strrchr、c++容器中的iterator与reverse_iterator,这样一来更清晰明确。在实现上除了遍历方向不同外,其它代码都相同,因此为避免手工编码冗余,使用了3组宏来生成。
辅助函数宏生成
生成宏为DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP和DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP,展开后就有了__glib_htable_get(rget)和__glib_htable_cget(crget) 4个不加锁的函数,用于实现对应的加锁接口。glib_htable_list_get和glib_htable_list_rget分别是宏list_for_each_entry和list_for_each_entry_reverse的别名。
普通查找宏生成
调用辅助函数__glib_htable_get(rget)实现,生成宏为DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET,展开后就有了glib_htable_get(rget)接口。
条件查找宏生成
前者调用辅助函数__glib_htable_cget(rget)实现,生成宏为DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET,展开后就有了glib_htable_cget(rget)接口;后者调用辅助函数__glib_htable_cget(rget)_byidx实现,生成宏为DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX,展开后就有了glib_htable_cget(rget)_byidx接口。
完整源码下载:glib_hash,包括glib_htable.h和glib_htable.c文件。
● 存储在glib_htable里的对象由外部而不是内部负责创建,这个对象必须直接或间接地组合了list_head成员(间接组合,包含下文中的glib_hentry即可),这里引用UML中的术语组合,意在强调不是聚合关系。
● 删除操作的语义是从Hash表移去对象的链接,但释放对象是可选的。
● 桶的个数由外部指定而不是内部维护。
综上可见glib_htable是使用对象已存在的内嵌成员list_head来链接到Hash表中的,比一般的通用Hash表,每个表项节省了1个指针的空间,如下图所示。

结构定义
1 struct glib_hentry {
struct glib_hentry {
2 struct list_head list;
struct list_head list;
3 void *data;
void *data;
4 };
};
5
6 typedef unsigned int (*glib_htable_hashfun_t)(const void*,unsigned int);
typedef unsigned int (*glib_htable_hashfun_t)(const void*,unsigned int);
7 typedef int (*glib_htable_cmpfun_t)(const void*, const void*);
typedef int (*glib_htable_cmpfun_t)(const void*, const void*);
8 typedef void (*glib_htable_cbfun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);
typedef void (*glib_htable_cbfun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);
9 typedef void (*glib_htable_freefun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);
typedef void (*glib_htable_freefun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);
10
11 struct glib_htable {
struct glib_htable {
12 struct list_head *bucket;
struct list_head *bucket;
13 unsigned int size;
unsigned int size;
14 unsigned int vmalloced;
unsigned int vmalloced;
15
16 rwlock_t lock;
rwlock_t lock;
17
18 glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun;
glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun;
19 glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun;
glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun;
20 glib_htable_cbfun_t cbfun;
glib_htable_cbfun_t cbfun;
21 glib_htable_freefun_t freefun;
glib_htable_freefun_t freefun;
22 };
};
 struct glib_hentry {
struct glib_hentry {2
 struct list_head list;
struct list_head list;3
 void *data;
void *data;4
 };
};5

6
 typedef unsigned int (*glib_htable_hashfun_t)(const void*,unsigned int);
typedef unsigned int (*glib_htable_hashfun_t)(const void*,unsigned int);7
 typedef int (*glib_htable_cmpfun_t)(const void*, const void*);
typedef int (*glib_htable_cmpfun_t)(const void*, const void*);8
 typedef void (*glib_htable_cbfun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);
typedef void (*glib_htable_cbfun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);9
 typedef void (*glib_htable_freefun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);
typedef void (*glib_htable_freefun_t)(struct glib_hentry*);10

11
 struct glib_htable {
struct glib_htable {12
 struct list_head *bucket;
struct list_head *bucket;13
 unsigned int size;
unsigned int size;14
 unsigned int vmalloced;
unsigned int vmalloced;15

16
 rwlock_t lock;
rwlock_t lock;17

18
 glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun;
glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun;19
 glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun;
glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun;20
 glib_htable_cbfun_t cbfun;
glib_htable_cbfun_t cbfun;21
 glib_htable_freefun_t freefun;
glib_htable_freefun_t freefun;22
 };
};2)glib_htable抽象了Hash表,size表示桶个数,考虑到size可能很多,需要占用大块内存,所以在分配连续物理页失败的情况下,再使用vmalloc尝试分配不连续的物理页,所以引入了vmalloced表示分配方式,非零表示用vmalloc,零则用__get_free_pages;hashfun和cmpfun是实现Hash表的两个缺一不可的关键函数,cbfun用于查找成功时的回调处理,如打印、增加引用计数等,freefun用于释放对象,提供这个回调接口是为了方便从Hash表移除对象后可以释放对象,而不必由外部释放,增加了灵活性。
主要接口
以下所有操作中的第1参数ht表示glib_htable对象。
● 初始化
 int glib_htable_init(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int size, glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun, glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun);
int glib_htable_init(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int size, glib_htable_hashfun_t hashfun, glib_htable_cmpfun_t cmpfun);● 增加
 void glib_htable_add(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num);
void glib_htable_add(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num);● 查找
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_get(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_get(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data); struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_rget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_rget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data); struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg); struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg); struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_cget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg); struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_crget_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg);● 删除
 void glib_htable_del(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num);
void glib_htable_del(struct glib_htable *ht, struct glib_hentry *he, int num); void glib_htable_del_bydata(struct glib_htable *ht, const void **data, int num);
void glib_htable_del_bydata(struct glib_htable *ht, const void **data, int num);● 清空
 void glib_htable_clear(struct glib_htable *ht);
void glib_htable_clear(struct glib_htable *ht);● 销毁
 void glib_htable_free(struct glib_htable *ht);
void glib_htable_free(struct glib_htable *ht);接口实现
其它接口实现比较简单,略过讲解。对于查找接口,如果增加一个参数来指示遍历方向,那么虽然接口总数减半,但在使用特别是在一个循环内调用时,每次都进行不必要的方向判断而降低了性能,所以对于正向和反向遍历,每个都给出一个接口,正如c库中的strchr与strrchr、c++容器中的iterator与reverse_iterator,这样一来更清晰明确。在实现上除了遍历方向不同外,其它代码都相同,因此为避免手工编码冗余,使用了3组宏来生成。
辅助函数宏生成
1 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(name) \
2 static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, const void *data) \
static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, const void *data) \
3 {\
{\
4 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \
5 \
\
6 glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \
glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \
7 if(ht->cmpfun(he->data,data)){ \
if(ht->cmpfun(he->data,data)){ \
8 if(ht->cbfun) \
if(ht->cbfun) \
9 ht->cbfun(he); \
ht->cbfun(he); \
10 return he; \
return he; \
11 } \
} \
12 } \
} \
13 \
\
14 return NULL; \
return NULL; \
15 }
}
16
17 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(get)
18 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(rget)
19
20 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(name) \
21 static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
22 { \
{ \
23 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \
24 \
\
25 glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \
glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \
26 if(cmp(he, arg)){ \
if(cmp(he, arg)){ \
27 if(ht->cbfun) \
if(ht->cbfun) \
28 ht->cbfun(he); \
ht->cbfun(he); \
29 return he; \
return he; \
30 } \
} \
31 } \
} \
32 \
\
33 return NULL; \
return NULL; \
34 }
}
35
36 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(get)
37 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(rget)
 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(name) \2
 static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, const void *data) \
static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, const void *data) \3
 {\
{\4
 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \5
 \
\6
 glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \
glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \7
 if(ht->cmpfun(he->data,data)){ \
if(ht->cmpfun(he->data,data)){ \8
 if(ht->cbfun) \
if(ht->cbfun) \9
 ht->cbfun(he); \
ht->cbfun(he); \10
 return he; \
return he; \11
 } \
} \12
 } \
} \13
 \
\14
 return NULL; \
return NULL; \15
 }
}16

17
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(get)18
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET_HELP(rget)19

20
 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(name) \21
 static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
static struct glib_hentry* __glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int hash, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \22
 { \
{ \23
 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \24
 \
\25
 glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \
glib_htable_list_##name(he,&ht->bucket[hash],list){ \26
 if(cmp(he, arg)){ \
if(cmp(he, arg)){ \27
 if(ht->cbfun) \
if(ht->cbfun) \28
 ht->cbfun(he); \
ht->cbfun(he); \29
 return he; \
return he; \30
 } \
} \31
 } \
} \32
 \
\33
 return NULL; \
return NULL; \34
 }
}35

36
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(get)37
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_HELP(rget)普通查找宏生成
1 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(name) \
2 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data) \
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data) \
3 { \
{ \
4 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \
5 unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \
unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \
6 \
\
7 read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
8 he = __glib_htable_##name(ht, h, data); \
he = __glib_htable_##name(ht, h, data); \
9 read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
10 \
\
11 return he; \
return he; \
12 }
}
13
14 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(get)
15 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(rget)
 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(name) \2
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data) \
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data) \3
 { \
{ \4
 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \5
 unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \
unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \6
 \
\7
 read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \8
 he = __glib_htable_##name(ht, h, data); \
he = __glib_htable_##name(ht, h, data); \9
 read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \10
 \
\11
 return he; \
return he; \12
 }
}13

14
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(get)15
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_GET(rget)条件查找宏生成
1 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(name) \
2 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
3 { \
{ \
4 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \
5 unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \
unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \
6 \
\
7 read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
8 he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \
he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \
9 read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
10 \
\
11 return he; \
return he; \
12 }
}
13
14 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(get)
15 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(rget)
16
17 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(name) \
18 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name##_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name##_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
19 { \
{ \
20 unsigned int h; \
unsigned int h; \
21 struct glib_hentry *he = NULL; \
struct glib_hentry *he = NULL; \
22 \
\
23 read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
24 \
\
25 for (h = *bucket; h < ht->size; h = (*bucket)++){ \
for (h = *bucket; h < ht->size; h = (*bucket)++){ \
26 he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \
he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \
27 if(he) \
if(he) \
28 break; \
break; \
29 } \
} \
30 \
\
31 read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
32 \
\
33 return he; \
return he; \
34 }
}
35
36 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(get)
37 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(rget)
 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(name) \2
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name(struct glib_htable *ht, const void *data, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \3
 { \
{ \4
 struct glib_hentry *he; \
struct glib_hentry *he; \5
 unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \
unsigned int h = ht->hashfun(data,ht->size); \6
 \
\7
 read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \8
 he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \
he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \9
 read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \10
 \
\11
 return he; \
return he; \12
 }
}13

14
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(get)15
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET(rget)16

17
 #define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(name) \
#define DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(name) \18
 struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name##_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \
struct glib_hentry* glib_htable_c##name##_byidx(struct glib_htable *ht, unsigned int *bucket, int(*cmp)(const struct glib_hentry*, void*), void *arg) \19
 { \
{ \20
 unsigned int h; \
unsigned int h; \21
 struct glib_hentry *he = NULL; \
struct glib_hentry *he = NULL; \22
 \
\23
 read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_lock_bh(&ht->lock); \24
 \
\25
 for (h = *bucket; h < ht->size; h = (*bucket)++){ \
for (h = *bucket; h < ht->size; h = (*bucket)++){ \26
 he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \
he = __glib_htable_c##name(ht, h, cmp, arg); \27
 if(he) \
if(he) \28
 break; \
break; \29
 } \
} \30
 \
\31
 read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \
read_unlock_bh(&ht->lock); \32
 \
\33
 return he; \
return he; \34
 }
}35

36
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(get)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(get)37
 DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(rget)
DEFINE_GLIB_HTABLE_COND_GET_BYIDX(rget)完整源码下载:glib_hash,包括glib_htable.h和glib_htable.c文件。




 glib_htable_list_##name(he,
glib_htable_list_##name(he,

【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)