(HDOJ 1012)u Calculate e
u Calculate e
Problem Description
A simple mathematical formula for e is
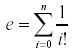
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using relatively small values of n.
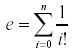
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using relatively small values of n.
Output
Output the approximations of e generated by the above formula for the values of n from 0 to 9. The beginning of your output should appear similar to that shown below.
Sample Output
n e
- -----------
0 1
1 2
2 2.5
3 2.666666667
4 2.708333333
Source
Recommend
JGShining
AC code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
long int f(int n)
{
if(n==0||n==1)
return 1;
else
return n*f(n-1);
}
double sum(int n)
{
int i;
double s=0.000000000;
for(i=0; i<=n;i++)
{
s+=(double)1/f(i);
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
int i;
printf("n e\n");
printf("- -----------\n");
for(i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
if(i==0)
{
printf("%d %d\n",i,1);
}
else if(i==1)
{
printf("%d %d\n",i,2);
}
else if(i==2)
{
printf("%d %.1f\n",i,2.5);
}
else
{
printf("%d %.9lf\n",i,sum(i));
}
}
return 0;
#include<math.h>
long int f(int n)
{
if(n==0||n==1)
return 1;
else
return n*f(n-1);
}
double sum(int n)
{
int i;
double s=0.000000000;
for(i=0; i<=n;i++)
{
s+=(double)1/f(i);
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
int i;
printf("n e\n");
printf("- -----------\n");
for(i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
if(i==0)
{
printf("%d %d\n",i,1);
}
else if(i==1)
{
printf("%d %d\n",i,2);
}
else if(i==2)
{
printf("%d %.1f\n",i,2.5);
}
else
{
printf("%d %.9lf\n",i,sum(i));
}
}
return 0;
}
作者:cpoint
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利.


