TF-IDF、TextRank、WordCount三种方法实现英文关键词提取(python实现)
源码:https://github.com/Cpaulyz/BigDataAnalysis/tree/master/Assignment2
数据预处理
进行关键词提取之前,需要对源文件进行一系列预处理:
- 提取PDF为TXT文件
- 分句
- 分词(词干提取、词形还原)
- 过滤数字、特殊字符等,大小写转换
提取PDF
使用Apache PDFBox工具对PDF文字进行提取
依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.pdfbox</groupId>
<artifactId>pdfbox</artifactId>
<version>2.0.13</version>
</dependency>
提取工具类utils/PDFParser类代码逻辑如下
try {
// 读取PDF文件夹,将PDF格式文件路径存入一个Array中
File dir = new File("src\\main\\resources\\ACL2020");
ArrayList<String> targets = new ArrayList<String>();
for(File file:dir.listFiles()){
if(file.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".pdf")){
targets.add(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
// readPdf为提取方法
for(String path:targets){
readPdf(path);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
至此,完成将PDF文件中的文字提取,并存入.txt文件中的操作,以便后续操作,示意图如下。
分句
使用python中的nltk库进行分句
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
sens = sent_tokenize(str)
分句情况大致如下,可以看出分句情况较为准确
分词(词干提取、词形还原)
nltk提供了分词工具,API如下
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
wnl = WordNetLemmatizer()
print(wnl.lemmatize('ate', 'v'))
print(wnl.lemmatize('fancier', 'n'))
# 输出为eat fancy
但是,这种分词方法需要确定单词在的词性,好在nltk也为我们提供了方法来判断句子的词性,将其封装为方法如下
# 获取单词的词性
def get_wordnet_pos(tag):
if tag.startswith('J'):
return wordnet.ADJ
elif tag.startswith('V'):
return wordnet.VERB
elif tag.startswith('N'):
return wordnet.NOUN
elif tag.startswith('R'):
return wordnet.ADV
else:
return None
结合后进行调用,如下:
from nltk import word_tokenize, pos_tag
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
tokens = word_tokenize(sentence) # 分词
tagged_sent = pos_tag(tokens) # 获取单词词性
wnl = WordNetLemmatizer()
lemmas_sent = []
for tag in tagged_sent:
wordnet_pos = get_wordnet_pos(tag[1]) or wordnet.NOUN
lemmas_sent.append(wnl.lemmatize(tag[0], pos=wordnet_pos)) # 词形还原
结果如图

可以看出分词后的效果还不错,但仍存在问题为
-
没有剔除掉;:.,等特殊符号
-
没有剔除数字等
-
没有剔除一些如a、the、of等介词
过滤
问题1、2容易使用正则表达式进行剔除;
问题3我们通过nltk提供的英文停用词列表、以及“不妨假设长度为4以下的字符串无效”来进行剔除。
import re
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
invalid_word = stopwords.words('english')
# 预处理,如果是False就丢掉
def is_valid(word):
if re.match("[()\-:;,.0-9]+", word):
return False
elif len(word) < 4 or word in invalid_word:
return False
else:
return True
方法1 TF-IDF
TF-IDF算法提取关键词的结构化流程如下:

1.1 分句分词
同数据预处理,不再赘述
1.2 构造语料库
由于IDF的计算需要语料库的支持,我们在这里以全部文章构建一个语料库,存储在all_dic = {}中
all_dict是一个map,存储结构为(String 文章名,Map 词频<单词,词频>)
一个示例如下
{
'A Generative Model for Joint Natural Language Understanding and Generation.txt':
{'natural': 13,
'language': 24,
'understanding': 4,
'andnatural': 1,
'generation': 9,
'twofundamental': 1,
...
},
...
}
1.3 计算TF-IDF
(1)TF
词频 (term frequency, TF) 指的是某一个给定的词语在该文件中出现的次数。这个数字通常会被归一化(一般是词频除以文章总词数), 以防止它偏向长的文件。(同一个词语在长文件里可能会比短文件有更高的词频,而不管该词语重要与否。)

TF = article_dict[word] / article_word_counts
(2)IDF
逆向文件频率 (inverse document frequency, IDF) IDF的主要思想是:如果包含词条t的文档越少, IDF越大,则说明词条具有很好的类别区分能力。某一特定词语的IDF,可以由总文件数目除以包含该词语之文件的数目,再将得到的商取对数得到。

contain_count = 1 # 包含的文档总数,因为要+1,干脆直接初始值为1来做
for article1 in all_dic.keys():
if word in all_dic[article1].keys():
contain_count += 1
IDF = log(article_nums / contain_count)
(3)TF-IDF
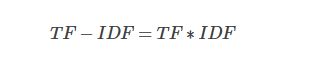
实现核心代码如下:
def TFIDF():
article_nums = len(all_dic)
for article in all_dic.keys():
article_dict: dict = all_dic[article]
article_word_counts = 0
for count in article_dict.values():
article_word_counts += count
local_dict = {}
for word in article_dict:
TF = article_dict[word] / article_word_counts
contain_count = 1 # 包含的文档总数,因为要+1,干脆直接初始值为1来做
for article1 in all_dic.keys():
if word in all_dic[article1].keys():
contain_count += 1
IDF = log(article_nums / contain_count)
local_dict[word] = TF * IDF
all_dic[article] = local_dict # 用TFIDF替代词频
1.4 输出结果
值得一提的是,TF-IDF的基于语料库的关键词算法,我们在将ACL2020的全部文章作为语料库进行提取,因此提取到的TF-IDF值是相对于文章内部的关键词权重。
因此,通过这种方法,我们生成的是每篇文章的关键词而非语料库的关键词。
在这里,我们选取每篇文章中TF-IDF最高的单词及其权重输出到method1_dict.txt中,权重表示的是TF-IDF值,排序为按照文章标题的字母排序。
unlabelled 0.03366690429509488
database 0.025963153344621098
triplet 0.06007324859328521
anaphor 0.054325239855360946
sparse 0.05140787295501171
dialog 0.02857688733696682
evaluator 0.047046849916043215
article 0.03181976626426247
dialogue 0.05009864522556742
false 0.05046963249913187
explanation 0.06756267918534663
keyphrases 0.07257334117762049
switch 0.02057258339292402
response 0.03487928535131968
hcvae 0.01490817643452481
response 0.01691069785427619
fragment 0.036740214670107636
concept 0.10144398960055125
node 0.026861943279698357
type 0.021568639909022032
hierarchy 0.04174740425673965
legal 0.09062083506033958
confidence 0.03208193690887942
question 0.018326715354972434
follow-up 0.0768915254934173
graph 0.030139792811985255
quarel 0.03142980753777034
instruction 0.04310656492734328
summary 0.023522349291620226
mutual 0.021794659657633334
malicious 0.03361252033133951
nucleus 0.03062106234461863
supervision 0.02716542294214428
relation 0.026017607441275774
calibrator 0.053113533081036744
centrality 0.06527959271708282
question 0.015813880735872966
slot 0.04442739804723785
graph 0.017963145985978687
taxonomy 0.05263359765861765
question 0.01694100733341999
transformer 0.019573842786351815
response 0.027652528223249546
topic 0.04541019920353925
paraphrase 0.024098507886884227
方法2 TextRank
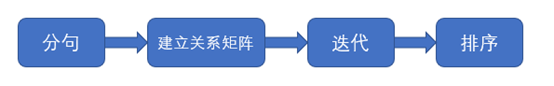
TextRank算法提取关键词的结构化流程如下
2.1 分句
同预处理部分的分句处理,不再赘述
2.2 建立关系矩阵
建立关系矩阵Mn*n,其中n为单词数量(相同单词仅记一次),Mij表示j到i存在权重为Mij的关系。
关系的定义如下:
取窗口大小为win,则在每个分句中,去除停用词、标点、无效词后,每个单词与距离为win以内的单词存在联系
为了方便表示关系矩阵,这里以一个(String word, Array relative_words)的Map来进行表示存在word→relative_words的关系,例子如下(来源网络http://www.hankcs.com/nlp/textrank-algorithm-to-extract-the-keywords-java-implementation.html)
句分词 = [程序员, 英文, 程序, 开发, 维护, 专业, 人员, 程序员, 分为, 程序, 设计, 人员, 程序, 编码, 人员, 界限, 特别, 中国, 软件, 人员, 分为, 程序员, 高级, 程序员, 系统, 分析员, 项目, 经理]
之后建立两个大小为5的窗口,每个单词将票投给它身前身后距离5以内的单词:
{开发=[专业, 程序员, 维护, 英文, 程序, 人员],
软件=[程序员, 分为, 界限, 高级, 中国, 特别, 人员],
程序员=[开发, 软件, 分析员, 维护, 系统, 项目, 经理, 分为, 英文, 程序, 专业, 设计, 高级, 人员, 中国],
分析员=[程序员, 系统, 项目, 经理, 高级],
维护=[专业, 开发, 程序员, 分为, 英文, 程序, 人员],
系统=[程序员, 分析员, 项目, 经理, 分为, 高级],
项目=[程序员, 分析员, 系统, 经理, 高级],
经理=[程序员, 分析员, 系统, 项目],
分为=[专业, 软件, 设计, 程序员, 维护, 系统, 高级, 程序, 中国, 特别, 人员],
英文=[专业, 开发, 程序员, 维护, 程序],
程序=[专业, 开发, 设计, 程序员, 编码, 维护, 界限, 分为, 英文, 特别, 人员],
特别=[软件, 编码, 分为, 界限, 程序, 中国, 人员],
专业=[开发, 程序员, 维护, 分为, 英文, 程序, 人员],
设计=[程序员, 编码, 分为, 程序, 人员],
编码=[设计, 界限, 程序, 中国, 特别, 人员],
界限=[软件, 编码, 程序, 中国, 特别, 人员],
高级=[程序员, 软件, 分析员, 系统, 项目, 分为, 人员],
中国=[程序员, 软件, 编码, 分为, 界限, 特别, 人员],
人员=[开发, 程序员, 软件, 维护, 分为, 程序, 特别, 专业, 设计, 编码, 界限, 高级, 中国]}
实现部分代码如下
def add_to_dict(word_list, windows=5):
valid_word_list = [] # 先进行过滤
for word in word_list:
word = str(word).lower()
if is_valid(word):
valid_word_list.append(word)
# 根据窗口进行关系建立
if len(valid_word_list) < windows:
win = valid_word_list
build_words_from_windows(win)
else:
index = 0
while index + windows <= len(valid_word_list):
win = valid_word_list[index:index + windows]
index += 1
build_words_from_windows(win)
# 根据小窗口,将关系建立到words中
def build_words_from_windows(win):
for word in win:
if word not in words.keys():
words[word] = []
for other in win:
if other == word or other in words[word]:
continue
else:
words[word].append(other)
2.3 迭代
TextRank的计算公式类似PageRank

迭代的终止条件有以下两种
-
max_diff < 指定阈值,说明已收敛
-
max_iter > 指定迭代次数,说明迭代次数达到上限
代码实现如下
def text_rank(d=0.85, max_iter=100):
min_diff = 0.05
words_weight = {} # {str,float)
for word in words.keys():
words_weight[word] = 1 / len(words.keys())
for i in range(max_iter):
n_words_weight = {} # {str,float)
max_diff = 0
for word in words.keys():
n_words_weight[word] = 1 - d
for other in words[word]:
if other == word or len(words[other]) == 0:
continue
n_words_weight[word] += d * words_weight[other] / len(words[other])
max_diff = max(n_words_weight[word] - words_weight[word], max_diff)
words_weight = n_words_weight
print('iter', i, 'max diff is', max_diff)
if max_diff < min_diff:
print('break with iter', i)
break
return words_weight
2.4 输出结果
选取前30个关键词,输出结果如下,本方法中权重表示TextRank计算出来的值,保存在method2_dict.txt中
model 176.5304347133946
question 85.40181168045564
response 62.507994652932325
data 60.65722815422958
method 59.467011421798766
result 58.625521805302576
show 58.328949197586205
graph 57.56085447050974
answer 56.016412290514324
generate 53.04744866326927
example 52.68958963476476
training 52.109756756305856
also 51.35655567676399
input 50.69980375572206
word 50.52677865990237
train 49.34118286080509
representation 48.497427796293245
sentence 48.21207111035171
dataset 48.07840701700186
work 47.57844139247928
system 47.03771276235998
propose 46.88347913956473
task 46.518530285062205
performance 45.70988317875179
base 45.675096486932375
different 44.92213315873288
score 43.76950706001539
test 42.996530025663326
give 42.40794849944198
information 42.39192128940212
方法3 WordCount
最后一种方法是朴素的词频计算法,思想很简单,就是计算词频,认为出现次数越多,越可能是关键词,结构化流程如下:

3.1 分词分句
同预处理部分,不再赘述
3.2 统计词频
使用一个Map来表示(单词,词频)
dic = {}
def add_to_dict(word_list):
for word in word_list:
word = str(word).lower()
if is_valid(word):
if word in dic.keys():
dic[word] += 1
else:
dic[word] = 1
3.3 输出结果
选取前30个关键词,输出结果如下,本方法中权重表示词频,保存在method3_dict.txt中
model 1742
question 813
response 579
graph 515
data 490
method 464
show 456
result 447
answer 445
representation 408
generate 398
example 394
training 393
word 387
dataset 377
sentence 368
input 365
propose 360
train 351
test 349
system 345
also 342
task 330
performance 327
score 325
different 315
work 312
document 304
base 294
information 293


