线程间通信
线程之间需要一些协调通信,来共同完成一件任务。Java多线程中,线程之间通信最常用的两个方法是wait()与notify()
使用wait()与notify()实现线程间的通信,需注意:
①wait()与notify()必须配合synochnized关键字使用
②wait()会释放锁,notify()不会释放锁
1.不使用notify()与wait()实现通信:
参照demo1
public class TestWaitNotify {
private volatile static List list = new ArrayList();
public void add(){
list.add("bjsxt");
}
public int size(){
return list.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final TestWaitNotify list1 = new TestWaitNotify();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){
list1.add();
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "添加了一个元素..");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(true){
if(list1.size() == 5){
System.out.println("当前线程收到通知:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " list size = 5 线程停止..");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
运行结果:
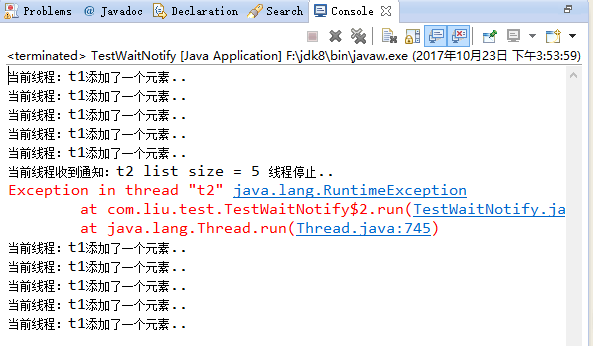
demo1总结:该方式确实实现了线程间的通信,但是用法比较传统,使用不够灵活;
2.使用wait()与notify()方法实现线程间通信
代码参照demo2:
public class TestWaitNotify2 {
private volatile static List list = new ArrayList();
public void add(){
list.add("bjsxt");
}
public int size(){
return list.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final TestWaitNotify2 list2 = new TestWaitNotify2();
// 1 实例化出来一个 lock
// 当使用wait 和 notify 的时候 , 一定要配合着synchronized关键字去使用
final Object lock = new Object();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){
list2.add();
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "添加了一个元素..");
Thread.sleep(500);
if(list2.size() == 5){
System.out.println("已经发出通知..");
lock.notify();
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
if(list2.size() != 5){
try {
//System.out.println("t2进入...");
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "收到通知线程停止..");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}, "t2");
t2.start();
t1.start();
}
}
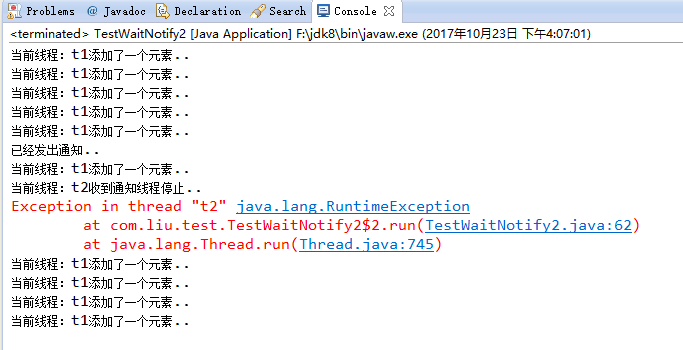
运行结果:

demo2总结:
通过wait()与notify()虽然实现了线程间通信,但是不能实现实时通信,因为wait()方法释放锁,可是notify()不释放锁,只有等t1线程执行完了,t2线程才能拿到锁执行;
3.通过countDownLatch实现线程间实时通信
demo3代码如下:
public class TestWaitNotify2 {
private volatile static List list = new ArrayList();
public void add(){
list.add("bjsxt");
}
public int size(){
return list.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final TestWaitNotify2 list2 = new TestWaitNotify2();
// 1 实例化出来一个 lock
// 当使用wait 和 notify 的时候 , 一定要配合着synchronized关键字去使用
//final Object lock = new Object();
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
//synchronized (lock) {
for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){
list2.add();
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "添加了一个元素..");
Thread.sleep(500);
if(list2.size() == 5){
System.out.println("已经发出通知..");
countDownLatch.countDown();
//lock.notify();
}
}
//}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
//synchronized (lock) {
if(list2.size() != 5){
try {
//System.out.println("t2进入...");
//lock.wait();
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "收到通知线程停止..");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
//}
}, "t2");
t2.start();
t1.start();
}
}
运行结果:
demo3总结:通过countDownLatch的awit()与countDown()方法(类似wait与notify)实现了线程间的实时通信,使用起来更灵活;





