PyTorch程序练习(二):循环神经网络的PyTorch实现
一、RNN实现
结构原理

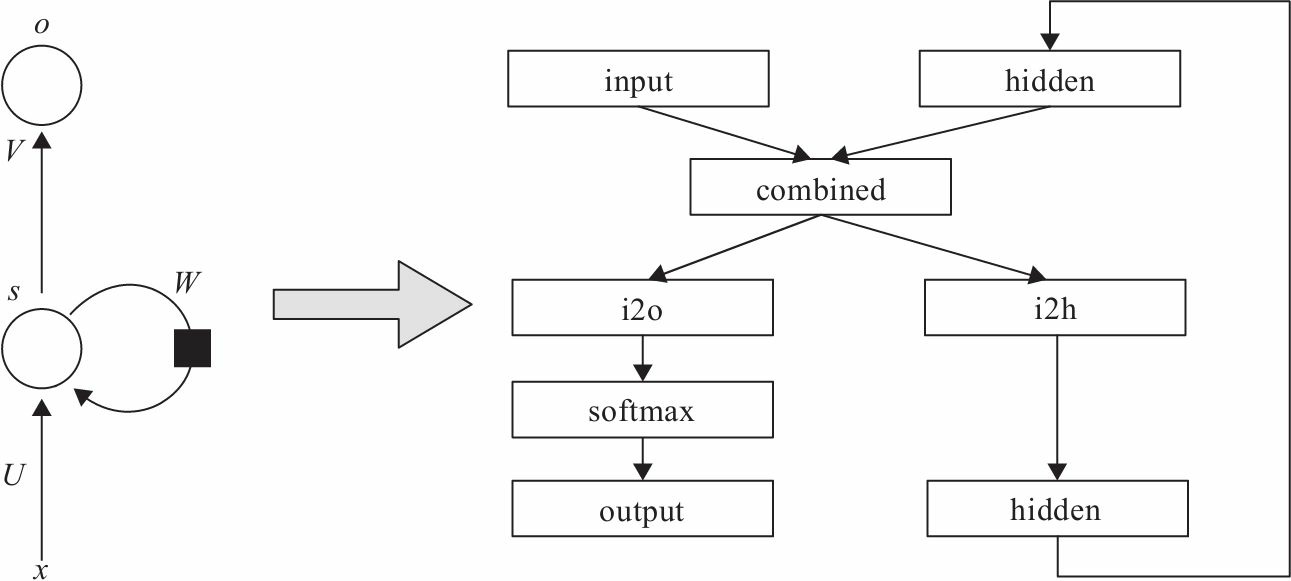
代码实现
import torch import torch.nn as nn class RNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size): super(RNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.i2h = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size) self.i2o = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, output_size) self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) def forward(self, input, hidden): combined = torch.cat((input, hidden), 1) hidden = self.i2h(combined) #全连接层 output: object = self.i2o(combined) output = self.softmax(output) return output, hidden def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size)
二、LSTM实现
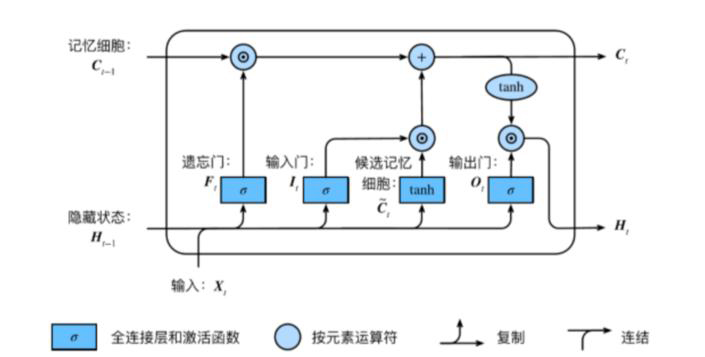
结构原理
封装好的LSTM
import torch import torch.nn as nn class LSTMTagger(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, vocab_size, tagset_size): super(LSTMTagger, self).__init__() self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim) # LSTM以word_embeddings作为输入, 输出维度为 hidden_dim 的隐藏状态值 self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim) # 线性层将隐藏状态空间映射到标注空间 self.hidden2tag = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, tagset_size) self.hidden = self.init_hidden() def init_hidden(self): # 一开始并没有隐藏状态所以要先初始化一个 # 各个维度的含义是 (num_layers, minibatch_size, hidden_dim) return (torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_dim), torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_dim)) def forward(self, sentence): embeds = self.word_embeddings(sentence) lstm_out, self.hidden = self.lstm(embeds.view(len(sentence), 1, -1), self.hidden) tag_space = self.hidden2tag(lstm_out.view(len(sentence), -1)) tag_scores = F.log_softmax(tag_space, dim=1) return tag_scores
未封装的LSTM
import torch import torch.nn as nn class LSTMCell(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, cell_size, output_size): super(LSTMCell, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.cell_size = cell_size self.gate = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, cell_size) # 门:线性全连接层 self.output = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() self.tanh = nn.Tanh() self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) def forward(self, input, hidden, cell): combined = torch.cat((input, hidden), 1) #维度上连接 f_gate = self.sigmoid(self.gate(combined)) #遗忘门 i_gate = self.sigmoid(self.gate(combined)) #输入门 o_gate = self.sigmoid(self.gate(combined)) #输出门 z_state = self.tanh(self.gate(combined)) cell = torch.add(torch.mul(cell, f_gate), torch.mul(z_state, i_gate)) """ cell长期记忆细胞:(cell·f_gate)+(z_state·i_gate) 遗忘门经过sigmoid后,值在[0,1]之间: 当f_gate趋于0时,和cell矩阵相乘后,记忆细胞为0,忘记长期记忆; 当f_gate区域1时,cell全部输入,作为长期记忆。 """ hidden = torch.mul(self.tanh(cell), o_gate) #隐藏层:长期记忆细胞cell先过一层tanh激活函数,然后和输出门o_gate矩阵相乘 output = self.output(hidden) #隐藏层作为输出层的输出 output = self.softmax(output) return output, hidden, cell def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size) def initCell(self): return torch.zeros(1, self.cell_size)
三、GRU实现
结构原理


代码实现
import torch import torch.nn as nn class GRUCell(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size): super(GRUCell, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.gate = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size) self.output = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() self.tanh = nn.Tanh() self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) def forward(self, input, hidden): combined = torch.cat((input, hidden), 1) z_gate = self.sigmoid(self.gate(combined)) #重置门 r_gate = self.sigmoid(self.gate(combined)) #更新门 combined01 = torch.cat((input, torch.mul(hidden, r_gate)), 1) h1_state = self.tanh(self.gate(combined01)) h_state = torch.add(torch.mul((1 - z_gate), hidden), torch.mul(h1_state, z_gate)) output = self.output(h_state) output = self.softmax(output) return output, h_state def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size)
四、程序分析
1、RNN(Recurrent Natural Network,循环神经网络)
PyTorch提供了两个版本的循环神经网络接口,单元版的输入是每个时间步,或循环神经网络的一个循环,而封装版的是一个序列。
2、LSTM(Long Short-TermMemory,长短时记忆网络)
LSTM是在RNN基础上增加了长时间记忆功能,具体通过增加一个状态C及利用3个门(Gate)实现对信息的更精准控制。
LSTM比标准的RNN多了3个线性变换,多出的3个线性变换的权重合在一起是RNN的4倍,偏移量也是RNN的4倍。所以,LSTM的参数个数是RNN的4倍。
除了参数的区别外,隐含状态除h0外,多了一个c0,两者形状相同,都是(num_layers*num_directions,batch,hidden_size),它们合在一起构成了LSTM的隐含状态。所以,LSTM的输入隐含状态为(h0,c0),输出的隐含状态为(hn,cn),其他输入与输出与RNN相同。
3、GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit,门控循环单元)
GRU网络结构与LSTM基本相同,主要区别是LSTM共有3个门,两个隐含状态;而GRU只有两个门,一个隐含状态。其参数是标准RNN的3倍。
很高兴本文对你有用(*^_^*),如需转载请记得标明出处哟(☆▽☆):
本文来自博客园,作者:雪与锄,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/corianderfiend/p/16583130.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步