nodejs -- Buffer
Buffer 对象的基本概念
Buffer对象是一个典型的JavaScript与C++的结合模块,它性能相关的部分由C++来实现,非性能相关的部分由JavaScript来实现。
JS引擎本身是没有操作文件和数据权限的,但是Node可以直接运行在服务端,也就是说如果实现了与C++底层的对接,就可以去间接的去操作系统文件和数据了。在Node中,通过process对象提供的binging方法就可以完成JS与C++的对接。从源码也可以看出,关于Buffer.js的第一句代码:
const binding = process.binding('buffer');
// 在Node中不仅仅是Buffer对象,还有fs等对象都是这样实现和C++对接的。
Buffer对象有点类似js中的数组,但是它的元素是16进制的两位数,即为0到255的数值(8位无符号整形Uint8Array),并且可以通过length属性访问其长度。
- 值得注意的是,当给buffer元素指定一个小于0或者大于255或者是小数的时候会有一些特别的地方:
* 如果元素赋值小于0,那么该值逐次加上256,直到得到一个0到255的整数。
* 如果元素赋值大于255,那么该值会逐次减去256,直到得到一个0到255的整数。
* 如果是元素赋值是一个小数,那么会舍去小数部分,然后执行上面的两条规则。
Buffer的内存分配原理
Node中Buffer对象的内存分配不是在V8的堆内存中,而是Node在C++层面实现内存申请的。然后申请来的内存是在JavaScript的层面上进行管理的。
为了高效的管理内存,Node采用了slab动态内存管理机制。大可不必在乎这几个字符是什么意思,你就简单的去理解成:slab就是一个分配好的内存区域,也就是你使用Buffer对象传入一个指定的size就申请了一块内存。然后slab具有下面的3种状态:
- empty: 初次被创建,还没有被分配数据
- partial: 部分空间被分配,并没有完全分配
- full: 完全被分配
- 另外Node会根据当前申请的内存大小将Buffer对象进行分类,如果(这里以第一次申请为例)申请的内存大小小于4k,那么就会存入初始化的slab单元中,即查阅各种资料所谓的8k池,当接下来继续申请的内存大小仍然小于4k并且当前第一个初始化的8k池空间足够的情况下就会继续存入第一个初始化的8k池。
- 打个比方:如果被初始化的8k池的空间剩余2k,这个时候再去申请一个大于2k并且小于4k的内存空间,就会去新申请一个slab单元空间,上次初始化的slab单元的剩余2k内存就会被浪费掉,无法再使用。
- 如果申请的内存大于4k那么就不会走8k池,而是node直接通过C++层面去申请一个独占的slab单元空间。
- 最后说明一下:无论是哪种情况,最后得到的Buffer对象都是JavaScript层面的,也就是可以被V8的垃圾回收机制所管理。这中间其实Node做了大量的工作,最主要的就是把JS和C++结合起来。
上面这段话也是我个人理解了好久总结的,可能还是有不对的地方,其中一个点就非常让人疑惑,命名是8k的大小,为什么用4k作为分界点。源码上也是这么体现的。或许是人为规定?
以下是使用8k池的API和条件:
- Buffer.allocUnsafe 传入的数据大小 (0 < size < 4 * 1024)
- Buffer.concat 传入的数据大小 (0 < size < 4 * 1024)
- Buffer.from 参数不为一个 ArrayBuffer 实例 并且 传入的数据大小 (0 < size < 4 * 1024)
另外还有个不再使用的 new Buffer() 方式,同样参数不可以是 ArrayBuffer 实例。
其实我也不明白为什么出现了slab这种动态内存管理机制,按照字面说明的意思就是使用这种机制,可以更高效。我想象了一下,如果再去对根本原因追究下去可能就会要去接触更底层的知识。反之我想了想,即使我去了解了这种机制,应该也没有太多的意义,所以这里就不再追寻下去了。
关于我是怎么知道上面这些的?
可以看几段关键的Buffer.js源码,其实无论使用哪个方法初始化Buffer对象最终都会走进这几个函数:
Buffer.poolSize = 8 * 1024; // 设定8k池
// 分别对应 8k 已使用的大小partial 和ArrayBuffer对象
var poolSize, poolOffset, allocPool;
class FastBuffer extends Uint8Array {
constructor(arg1, arg2, arg3) {
super(arg1, arg2, arg3);
}
}
// 下面的Buffer也就是Buffer的构造函数,这里没有复制
// 你只需要知道Buffer是构造函数,不是凭空出来的就行
FastBuffer.prototype.constructor = Buffer;
Buffer.prototype = FastBuffer.prototype;
/*
这个函数便是直接通过C++层面来申请内存
*/
function createUnsafeBuffer(size) {
//FastBuffer继承自Uint8Array,这里并没有复制这段代码
//你只需要知道这一点足够了。
//通过这段代码就知道为什么Buffer储存的是8位
return new FastBuffer(createUnsafeArrayBuffer(size));
}
// 调用 ArrayBuffer 构造接口
function createUnsafeArrayBuffer(size) {
zeroFill[0] = 0;
try {
return new ArrayBuffer(size);
} finally {
zeroFill[0] = 1;
}
}
// 作用:对上面的变量进行初始化,allocPool 作为中间变量指向ArrayBuffer实例。
function createPool() {
poolSize = Buffer.poolSize;
allocPool = createUnsafeArrayBuffer(poolSize);
poolOffset = 0; // 用来存储使用量
}
createPool(); // 一上来就初始化一个8k池,这样更可以更高效的进行第一次内存的申请
function allocate(size) {
if (size <= 0) {
return new FastBuffer();
}
// 这里可以明确看出来,什么情况走8k池
// Buffer.poolSize >>> 1 相当于 parseFlot(a/2)
// 例如 9 >>> 1 = 4
if (size < (Buffer.poolSize >>> 1)) {
if (size > (poolSize - poolOffset))
createPool();
var b = new FastBuffer(allocPool, poolOffset, size);
poolOffset += size;
alignPool();
return b;
} else {
// 如果调用这个函数的API申请的内存大小大于4k
// 就会直接去C++层面申请内存
return createUnsafeBuffer(size);
}
}
可以看出如果走的是createUnsafeBuffer()则不会经过8k池,若走 allocate() 函数,当传入的数据大小小于 Buffer.poolSize 有符号右移 1 位后的结果(相当于将该值除以 2 再向下取整,为 4 KB),才会使用到 8KB 池(若当前池剩余空间不足,则创建一个新的slab单元,并将allocPool指向新池)。
关于更多API源码可以参阅 Buffer.js
原理图示
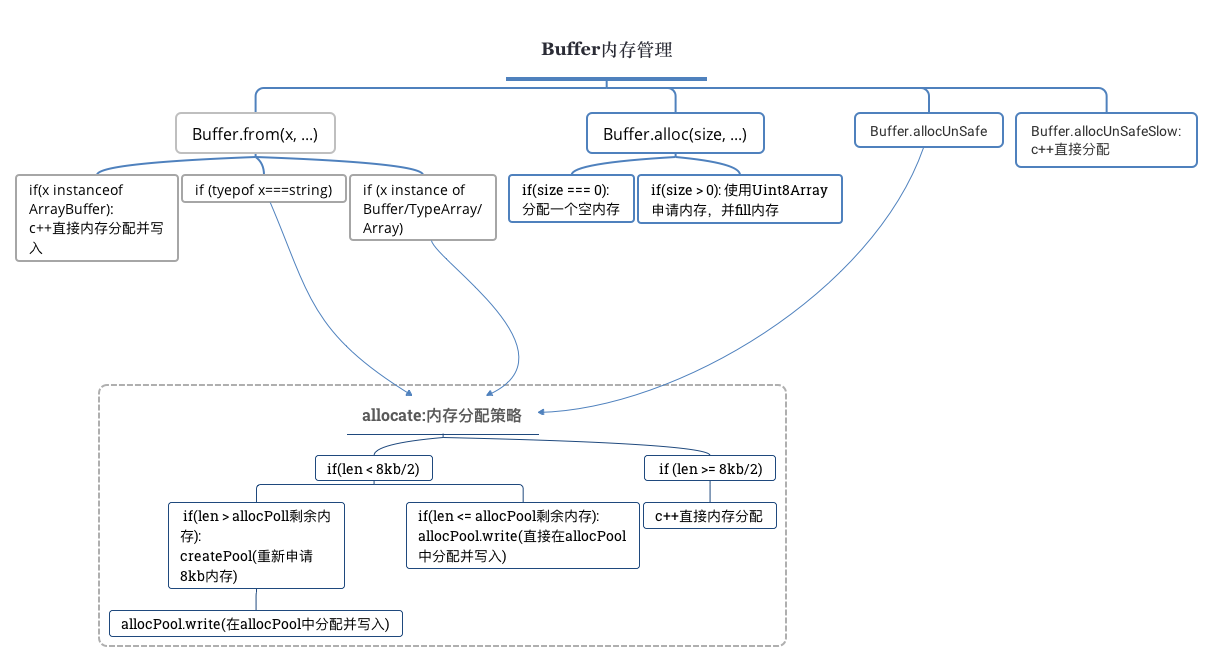
Buffer 对象的API中文文档 (7.x)
凡是相关API源码中出现的 assertSize(size) 方法都是做这么一件事:判断参数size的类型以及大小,会对小于0以及大于最大长度和非数字进行抛出异常处理。
buffer的初始化方式
- 在Node 6.0以前,直接使用new Buffer,但是这种方式存在两个问题:
* 参数复杂: 内存分配,还是内存分配+内容写入,需要根据参数来确定
* 安全隐患: 分配到的内存可能还存储着旧数据,这样就存在安全隐患
// 本来只想申请一块内存,但是里面却存在旧数据
const buf1 = new Buffer(10) // <Buffer 90 09 70 6b bf 7f 00 00 50 3a>
// 一不小心,旧数据就被读取出来了
buf1.toString() // '�\tpk�\u0000\u0000P:'
为了解决上述问题,Buffer提供了Buffer.from、Buffer.alloc、Buffer.allocUnsafe、Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow四个方法来申请内存。
Class Method: Buffer.alloc(size[, fill[, encoding]])
用来申请指定大小的内存空间
- size,指定buffer的长度,但不能超过buffer.kMaxLength,若不是数字则报错。
- fill,指定初始化buffer的值,默认为0。
- encoding,如果fill是字符串,则该参数指定fill的编码,默认'utf8'。
// 申请5个字节的内存
const buf = Buffer.alloc(5);
// Prints: <Buffer 00 00 00 00 00>
// 默认使用0进行填充
console.log(buf);
const buf = Buffer.alloc(5, 'a');
// Prints: <Buffer 61 61 61 61 61>
console.log(buf);
const buf = Buffer.alloc(11, 'aGVsbG8gd29ybGQ=', 'base64');
// Prints: <Buffer 68 65 6c 6c 6f 20 77 6f 72 6c 64>
console.log(buf);
源码:
Buffer.alloc = function(size, fill, encoding) {
assertSize(size);
if (size > 0 && fill !== undefined) {
if (typeof encoding !== 'string')
encoding = undefined;
return createUnsafeBuffer(size).fill(fill, encoding);
}
return new FastBuffer(size);
};
Class Method: Buffer.allocUnsafe(size)
size参数指定buffer的大小,该方法返回一个没有初始化的buffer,因此可能还保留有敏感的数据,造成信息的泄漏,建议使用buffer.fill(0)函数初始化buffer。
const buf = Buffer.allocUnsafe(10);
// Prints: (contents may vary): <Buffer a0 8b 28 3f 01 00 00 00 50 32> 可以看出是有数据的!
console.log(buf);
buf.fill(0);
// Prints: <Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>
console.log(buf);
源码:
Buffer.allocUnsafe = function(size) {
assertSize(size);
return allocate(size);
};
Class Method: Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow(size)
直接通过c++进行内存分配;不会进行旧值填充。除了这两点与Buffer.allocUnsafe(size)的其他特性一样。
// 从c++模块层面直接申请内存
const buf4 = Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow(10);
console.log(buf4); //<Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 86 00> // 不一定是什么数据
源码:
Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow = function(size) {
assertSize(size);
return createUnsafeBuffer(size);
};
Class Method: Buffer.from(array)
接收一个数组作为参数,会将数组内的值转化为16进制。
const bufArr = Buffer.from([1,2,3]);
console.log(bufArr); // <Buffer 01 02 03>
源码:
function fromArrayLike(obj) {
const length = obj.length;
const b = allocate(length);
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++)
b[i] = obj[i];
return b;
}
function fromObject(obj) {
if (isUint8Array(obj)) {
const b = allocate(obj.length);
if (b.length === 0)
return b;
binding.copy(obj, b, 0, 0, obj.length);
return b;
}
if (obj) {
if ('length' in obj || isArrayBuffer(obj.buffer) ||
isSharedArrayBuffer(obj.buffer)) {
if (typeof obj.length !== 'number' || obj.length !== obj.length) {
return new FastBuffer();
}
return fromArrayLike(obj);
}
if (obj.type === 'Buffer' && Array.isArray(obj.data)) {
return fromArrayLike(obj.data);
}
}
throw new TypeError(kFromErrorMsg);
}
Class Method: Buffer.from(arrayBuffer[, byteOffset[, length]])
接收一个arrayBuffer实例并且初始化,二者会共享内存。
- arrayBuffer: ArrayBuffer或者TypedArray的实例
- byteOffset: 接收一个整数,默认值0,用来指定从哪里开始复制arrayBuffer的数据。
- length: 接收一个整数,用来指定复制数据的长度,默认值是 总长度 - byteOffset。
let arrBuf = new ArrayBuffer(12);
let arr32 = new Uint32Array(arrBuf);
arr16[0] = 600;
let bf = Buffer.from(arr32);
console.log(bf); // <Buffer 58 00 00> 这里buffer的长度只有3,这是因为32为无符号整形每个站四个字节
// 也可以直接声明长度为多少 TypeArray 对象
let arr8 = new Uint8Array(10);
arr8[0] = 1000;
let bf = Buffer.from(arr8);
console.log(bf); // <Buffer e8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>
源码:
function fromArrayBuffer(obj, byteOffset, length) {
byteOffset = internalUtil.toInteger(byteOffset);
const maxLength = obj.byteLength - byteOffset;
if (maxLength < 0)
throw new RangeError("'offset' is out of bounds");
if (length === undefined) {
length = maxLength;
} else {
length = internalUtil.toLength(length);
if (length > maxLength)
throw new RangeError("'length' is out of bounds");
}
return new FastBuffer(obj, byteOffset, length);
}
Class Method: Buffer.from(buffer)
将已经有的buffer复制一份到新的buffer对象,不再是共享同一块内存。
- buffer: 接收一个 buffer 对象,作为参数。
const buf1 = Buffer.from('buffer');
const buf2 = Buffer.from(buf1);
buf1[0] = 0x61;
// Prints: auffer
console.log(buf1.toString());
// Prints: buffer
console.log(buf2.toString());
源码同上。
Class Method: Buffer.from(string[, encoding])
接收一个字符串作为参数,转换为buffer对象.
- string: 字符串参数
- encoding: 可选,用来指定转换为buffer对象后的编码格式,默认'utf8'。
const buf1 = Buffer.from('this is a tést');
// Prints: this is a tést 默认 utf8
console.log(buf1.toString());
// Prints: this is a tC)st
console.log(buf1.toString('ascii'));
const buf2 = Buffer.from('7468697320697320612074c3a97374', 'hex');
// Prints: this is a tést // 指定为16进制格式
console.log(buf2.toString());
源码:
function fromString(string, encoding) {
if (typeof encoding !== 'string' || encoding === '')
encoding = 'utf8';
if (!Buffer.isEncoding(encoding))
throw new TypeError('"encoding" must be a valid string encoding');
if (string.length === 0)
return new FastBuffer();
var length = byteLength(string, encoding);
if (length >= (Buffer.poolSize >>> 1))
return binding.createFromString(string, encoding);
if (length > (poolSize - poolOffset))
createPool();
var b = new FastBuffer(allocPool, poolOffset, length);
var actual = b.write(string, encoding);
if (actual !== length) {
// byteLength() may overestimate. That’s a rare case, though.
b = new FastBuffer(allocPool, poolOffset, actual);
}
poolOffset += actual;
alignPool();
return b;
}
Buffer 的属性
Class Property: Buffer.poolSize: 缓冲区大小,默认8k。
Class Property: buffer.kMaxLength: 缓冲区最大值,32位系统为1GB,64位系统为2GB。
可以使用 buf.length 查看Buffer对象的字节长度,这里需要注意的是字符长度不同于字节长度,比如一个中文代表一个字符长度,但是在utf8编码格式下有3个字节长度。
const buf1 = Buffer.from('爱');
console.log(buf1.length); // 3
console.log(buf1); // <Buffer e7 88 b1>
Buffer 的常用方法
Buffer对象提供了一些常用的工具方法,下面对一些常用的API进行记录和总结,方便日后查用。(基于7.x文档)
buf.toString([encoding[, start[, end]]])
将Buffer对象转为字符串
- encoding: 指定要转换为字符串的编码格式,默认为utf8。
- start: 指定Buffer起始位置,包括起始位置。
- end: 指定Buffer的结束位置,不包括结束位置。
const buf1 = Buffer.allocUnsafe(26);
for (let i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++) {
// 97 is the decimal ASCII value for 'a'
buf1[i] = i + 97;
}
// Prints: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
console.log(buf1.toString('ascii'));
// Prints: abcde
console.log(buf1.toString('ascii', 0, 5));
const buf2 = Buffer.from('tést');
// Prints: 74c3a97374
console.log(buf2.toString('hex'));
// Prints: té
console.log(buf2.toString('utf8', 0, 3));
// Prints: té
console.log(buf2.toString(undefined, 0, 3));
Class Method: Buffer.byteLength(string[, encoding])
获取字符串的实际的字节长度
- string: 要获取的字符串
- encoding: 可选,以指定的编码格式,默认utf8
const str = '把妹儿';
let len = Buffer.byteLength(str);
console.log(`${str} 的长度是${str.length},字节长度是${len}`);
// 把妹儿 的长度是3,字节长度是9
Class Method: Buffer.compare(buf1, buf2)
比较当前缓冲区和另一个缓冲区的大小,相等返回0,小于返回-1,大于返回1。
const buf1 = Buffer.from('1234');
const buf2 = Buffer.from('0123');
const arr = [buf1, buf2];
// Prints: [ <Buffer 30 31 32 33>, <Buffer 31 32 33 34> ]
// (This result is equal to: [buf2, buf1])
console.log(arr.sort(Buffer.compare));
let buf1 = Buffer.from('abc');
let buf2 = Buffer.from('abcb');
let result = Buffer.compare(buf1, buf2);
console.log(result); // -1
Class Method: Buffer.concat(list[, totalLength])
将多个buffer合并在一起,并返回一个新的buffer实例,参数totalLength为指定的buffers的长度总和,如果不提供该值,函数内部会循环去获取每一个buffer的长度,然后进行拼接,因此为了速度,最好指定一个总长度。
const buf1 = Buffer.alloc(10);
const buf2 = Buffer.alloc(14);
const buf3 = Buffer.alloc(18);
const totalLength = buf1.length + buf2.length + buf3.length;
// Prints: 42
console.log(totalLength);
const bufA = Buffer.concat([buf1, buf2, buf3], totalLength);
// Prints: <Buffer 00 00 00 00 ...>
console.log(bufA);
// Prints: 42
console.log(bufA.length);
Class Method: Buffer.isBuffer(obj)
判断一个对象是否为Buffer对象,是返回true,非返回false。
Class Method: Buffer.isEncoding(encoding)
判断是否为可用的编码格式,如果可用返回true,否则返回false。
let orIf = Buffer.isEncoding('utf-16le');
console.log(orIf); // true
// 源码
Buffer.isEncoding = function(encoding) {
switch ((encoding + '').toLowerCase()) {
case 'hex':
case 'utf8':
case 'utf-8':
case 'ascii':
case 'binary':
case 'base64':
case 'ucs2':
case 'ucs-2':
case 'utf16le':
case 'utf-16le':
case 'raw':
return true;
default:
return false;
}
};
buffer.transcode(source, fromEnc, toEnc)
此方法不属于全局方法,使用之前需要 require('buffer'),用于将指定的Buffer对象从一种编码格式转换为另外一种。暂时没发现有什么用...,当指定的编码无法转换的时候会使用 ? 代替。
const buffer = require('buffer');
const newBuf = buffer.transcode(Buffer.from('€'), 'utf8', 'ascii');
console.log(newBuf.toString('ascii'));
// Prints: '?'
buf[index]
通过下标获取或者设置Buffer对象对应的单个字节。
const str = 'Node.js';
const buf = Buffer.allocUnsafe(str.length);
for (let i = 0; i < str.length ; i++) {
buf[i] = str.charCodeAt(i);
}
// Prints: Node.js
console.log(buf.toString('ascii'));
buf.compare(target[, targetStart[, targetEnd[, sourceStart[, sourceEnd]]]])
与Buffer.compare()功能一样,但是可以指定目标和源目标的起始和结束位置。
- target: 要比较的Buffer对象。
- targetStart: buf的起始位置,默认值为0。
- targetEnd: buf的结束位置,当targetStart为undefined的时候,不包括结束位置,默认值为buf.length。
- sourceStart: 源Buffer对象的起始位置,当targetStart为undefined的时候,默认值为0。
- sourceEnd: 源Buffer对象的结束位置,不包括结束位置,当targetStart为undefined的时候,默认值为source.length。
- 如果target与source相等,那么返回0。
- 如果target比较source在前面,那么返回1。
- 如果target比较source在后面,那么返回-1。
const buf1 = Buffer.from('ABC');
const buf2 = Buffer.from('BCD');
const buf3 = Buffer.from('ABCD');
// Prints: 0
console.log(buf1.compare(buf1));
// Prints: -1
console.log(buf1.compare(buf2));
// Prints: -1
console.log(buf1.compare(buf3));
// Prints: 1
console.log(buf2.compare(buf1));
// Prints: 1
console.log(buf2.compare(buf3));
// Prints: [ <Buffer 41 42 43>, <Buffer 41 42 43 44>, <Buffer 42 43 44> ]
// (This result is equal to: [buf1, buf3, buf2])
console.log([buf1, buf2, buf3].sort(Buffer.compare));
buf.copy(target[, targetStart[, sourceStart[, sourceEnd]]])
将buf的数据拷贝到target上面,是将数据进行复制,所以是两个不同的内存空间。
- target: 被粘贴的目标Buffer对象。
- targetStart: 被粘贴目标的起始位置。
- sourceStart: 源Buffer对象的起始位置。
- sourceEnd: 源Buffer对象的结束位置,不包括结束位。
const buf1 = Buffer.allocUnsafe(26);
const buf2 = Buffer.allocUnsafe(26).fill('!');
for (let i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++) {
// 97 is the decimal ASCII value for 'a'
buf1[i] = i + 97;
}
buf1.copy(buf2, 8, 16, 20);
// Prints: !!!!!!!!qrst!!!!!!!!!!!!!
console.log(buf2.toString('ascii', 0, 25));
测方法还可以从将自己的数据复制给自己:
const buf = Buffer.allocUnsafe(26);
for (let i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++) {
// 97 is the decimal ASCII value for 'a'
buf[i] = i + 97;
}
buf.copy(buf, 0, 4, 10);
// Prints: efghijghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
console.log(buf.toString());
buf.entries()
对当前Buffer对象创建并返回一个iterator接口,这样就可以使用for...of...循环进行遍历,返回对应的键值对。
const buf = Buffer.from('buffer');
// Prints:
// [0, 98]
// [1, 117]
// [2, 102]
// [3, 102]
// [4, 101]
// [5, 114]
for (const pair of buf.entries()) {
console.log(pair);
}
buf.equals(otherBuffer)
用来比较两个Buffer对象是否相等,返回值为布尔值。
const buf1 = Buffer.from('ABC');
const buf2 = Buffer.from('414243', 'hex');
const buf3 = Buffer.from('ABCD');
// Prints: true
console.log(buf1.equals(buf2));
// Prints: false
console.log(buf1.equals(buf3));
buf.fill(value[, offset[, end]][, encoding])
以指定的内容填充Buffer对象。如果传入参数不是一个字符串或者整数,那么会强制转换为32位无符号整型Uint32。如果填充的数据是个多字节的,那么只会取出第一个字节进行填充。
- value: 要填充的内容。
- offset: 可以指定起始填充位置。
- end: 指定结束填充位置。
- encoding: 指定填充字符的编码,默认为utf8。
const b = Buffer.allocUnsafe(50).fill('h');
// Prints: hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
console.log(b.toString());
// Prints: <Buffer c8 a2 c8>
console.log(Buffer.allocUnsafe(3).fill('\u0222'));
buf.indexOf(value[, byteOffset][, encoding])
用来查找指定value的起始位置,如果找到了返回当前位置,如果没找到就返回-1,和字符串的indexOf行为类似。
- value: 可以接收 字符串、Buffer对象、整数类型。
- byteOffset: 指定查找的起始位置,默认0。
- encoding: 如果参数是字符串,可以指定其编码类型,默认utf8。
const buf = Buffer.from('this is a buffer');
// Prints: 0
console.log(buf.indexOf('this'));
// Prints: 2
console.log(buf.indexOf('is'));
// Prints: 8
console.log(buf.indexOf(Buffer.from('a buffer')));
// Prints: 8
// (97 is the decimal ASCII value for 'a')
console.log(buf.indexOf(97));
// Prints: -1
console.log(buf.indexOf(Buffer.from('a buffer example')));
// Prints: 8
console.log(buf.indexOf(Buffer.from('a buffer example').slice(0, 8)));
const utf16Buffer = Buffer.from('\u039a\u0391\u03a3\u03a3\u0395', 'ucs2');
// Prints: 4
console.log(utf16Buffer.indexOf('\u03a3', 0, 'ucs2'));
// Prints: 6
console.log(utf16Buffer.indexOf('\u03a3', -4, 'ucs2'));
buf.lastIndexOf(value[, byteOffset][, encoding])
从后向前查找指定的数据内容,可字符串的lastIndexOf特性一样。
- value: 可以接收 字符串、Buffer对象、整数类型。
- byteOffset: 指定查找的起始位置,默认buf.length - 1。
- encoding: 如果参数是字符串,可以指定其编码类型,默认utf8。
const buf = Buffer.from('this buffer is a buffer');
// Prints: 0
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf('this'));
// Prints: 17
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf('buffer'));
// Prints: 17
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf(Buffer.from('buffer')));
// Prints: 15
// (97 is the decimal ASCII value for 'a')
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf(97));
// Prints: -1
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf(Buffer.from('yolo')));
// Prints: 5
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf('buffer', 5));
// Prints: -1
console.log(buf.lastIndexOf('buffer', 4));
const utf16Buffer = Buffer.from('\u039a\u0391\u03a3\u03a3\u0395', 'ucs2');
// Prints: 6
console.log(utf16Buffer.lastIndexOf('\u03a3', undefined, 'ucs2'));
// Prints: 4
console.log(utf16Buffer.lastIndexOf('\u03a3', -5, 'ucs2'));
buf.includes(value[, byteOffset][, encoding])
与indexOf功能类似,用来查找指定数据,返回布尔值。
- value: 可以接收 字符串、Buffer对象、整数类型。
- byteOffset: 指定查找的起始位置,默认0。
- encoding: 如果参数是字符串,可以指定其编码类型,默认utf8。
const buf = Buffer.from('this is a buffer');
// Prints: true
console.log(buf.includes('this'));
// Prints: true
console.log(buf.includes('is'));
// Prints: true
console.log(buf.includes(Buffer.from('a buffer')));
// Prints: true
// (97 is the decimal ASCII value for 'a')
console.log(buf.includes(97));
// Prints: false
console.log(buf.includes(Buffer.from('a buffer example')));
// Prints: true
console.log(buf.includes(Buffer.from('a buffer example').slice(0, 8)));
// Prints: false
console.log(buf.includes('this', 4));
buf.keys()
创建并返回 Buffer 对象的 iterator 的 key。
const buf = Buffer.from('buffer');
// Prints:
// 0
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
for (const key of buf.keys()) {
console.log(key);
}
buf.values()
创建并返回 Buffer 对象的 iterator 的 value。
const buf = Buffer.from('buffer');
// Prints:
// 98
// 117
// 102
// 102
// 101
// 114
for (const value of buf.values()) {
console.log(value);
}
// Prints:
// 98
// 117
// 102
// 102
// 101
// 114
for (const value of buf) {
console.log(value);
}
buf.toJSON()
将Buffer转为JSON对象并返回,也可以隐式的使用JSON.stringify来代替此方法。
const buf = Buffer.from([0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4, 0x5]);
const json = JSON.stringify(buf);
// Prints: {"type":"Buffer","data":[1,2,3,4,5]}
console.log(json);
// Prints: { type: 'Buffer', data: [ 98, 117, 102, 102, 101, 114 ] }
console.log(buf.toJSON());
const copy = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
return value && value.type === 'Buffer'
? Buffer.from(value.data)
: value;
});
// Prints: <Buffer 01 02 03 04 05>
console.log(copy);
源码:
Buffer.prototype.toJSON = function() {
return {
type: 'Buffer',
data: Array.prototype.slice.call(this, 0)
};
};
buf.write(string[, offset[, length]][, encoding])
在指定的位置以指定的编码将字符串写入Buffer对象,如果写入的字符串的字节数大于Buffer对象的大小,那么就会被截取。另外如果指定的字符编码不支持是无法写入的。
- string: 字符串类型的参数。
- offset: 指定写入的起始位置,默认是0。
- length: 要写入到Buffer对象的长度,默认是buf.length -- length。
- encoding: 指定字符的编码格式,默认utf8。
const buf = Buffer.allocUnsafe(256);
const len = buf.write('\u00bd + \u00bc = \u00be', 0);
// Prints: 12 bytes: ½ + ¼ = ¾
console.log(`${len} bytes: ${buf.toString('utf8', 0, len)}`);
还有一些不常用的API,请自行参阅英文文档。
https://nodejs.org/dist/latest-v7.x/docs/api/buffer.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号