线程的六种状态
线程的六种状态:
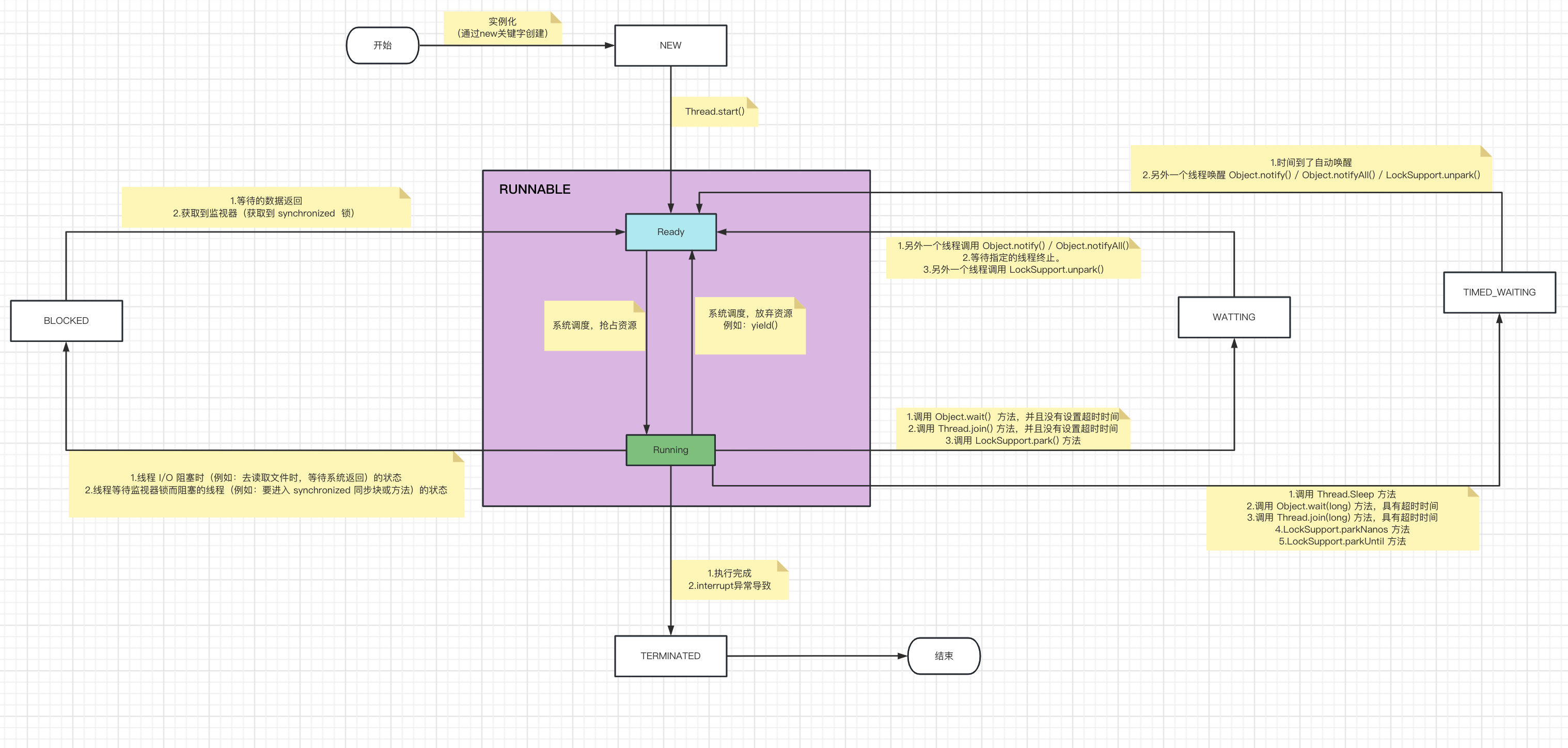
实际是五种状态,但是一般把RUNNABLE 分为: Ready 和 Running ,所以也可以称为线程的六种状态
一、源码
Thead.State 枚举类
public enum State {
/**
* Thread state for a thread which has not yet started.
* 通过 new 关键字创建,但是还未调用 start 方法。这时的状态称为: NEW
*/
NEW,
/**
* Thread state for a runnable thread. A thread in the runnable
* state is executing in the Java virtual machine but it may
* be waiting for other resources from the operating system
* such as processor.
*
* RUNNABLE (可运行)状态:
* 可分为: Ready 、 Running 两种状态
* 1.Ready: 线程已准备好,正在等待来自操作系统的其他资源,例如处理器(例如:线程调用了start方法、通过 notify/notifyAll 唤醒的线程 )
* 2.Running: 系统调度,当前线程抢占到资源,这时的状态称为:Running
*
*/
RUNNABLE,
/**
* Thread state for a thread blocked waiting for a monitor lock.
* A thread in the blocked state is waiting for a monitor lock
* to enter a synchronized block/method or
* reenter a synchronized block/method after calling
* {@link Object#wait() Object.wait}.
*
* BLOCKED (阻塞)状态:
* 1.线程 I/O 阻塞时(例如:去读取文件时,等待系统返回)的状态
* 2.线程等待监视器锁而阻塞的线程(例如:要进入 synchronized 同步块或方法)的状态
*
*/
BLOCKED,
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread.
* A thread is in the waiting state due to calling one of the
* following methods:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link Object#wait() Object.wait} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join() Thread.join} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#park() LockSupport.park}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>A thread in the waiting state is waiting for another thread to
* perform a particular action.
*
* For example, a thread that has called <tt>Object.wait()</tt>
* on an object is waiting for another thread to call
* <tt>Object.notify()</tt> or <tt>Object.notifyAll()</tt> on
* that object. A thread that has called <tt>Thread.join()</tt>
* is waiting for a specified thread to terminate.
*
* WAITING (等待)状态:
* 由于调用以下方法之一,线程处于 WAITING 状态:
* 1.调用 Object.wait() 方法,并且没有设置超时时间
* 2.调用 Thread.join() 方法,并且没有设置超时时间
* 3.调用 LockSupport.park() 方法
*
* 处于等待状态的线程正在等待另一个线程执行特定操作(进行唤醒)。
* 例如:
* 1.调用 Object.wait() 方法的线程,等待另外一个线程调用 Object.notify() / Object.notifyAll()
* 2.调用 Thread.join() 方法的线程,等待指定的线程终止。
* 3.调用 LockSupport.park() 方法的线程,等待另外一个线程调用 LockSupport.unpark()
*/
WAITING,
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread with a specified waiting time.
* A thread is in the timed waiting state due to calling one of
* the following methods with a specified positive waiting time:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link #sleep Thread.sleep}</li>
* <li>{@link Object#wait(long) Object.wait} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join(long) Thread.join} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkNanos LockSupport.parkNanos}</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkUntil LockSupport.parkUntil}</li>
* </ul>
*
* TIMED_WAITING (具有指定等待时间的等待线程的线程状态)状态:
* 由于调用以下方法之一,线程处于 TIMED_WAITING 状态:
* 1.调用 Thread.Sleep 方法
* 2.调用 Object.wait(long) 方法,具有超时时间
* 3.调用 Thread.join(long) 方法,具有超时时间
* 4.LockSupport.parkNanos 方法
* 5.LockSupport.parkUntil 方法
*
* 超过设置的时间之后自动唤醒,进入 RUNNABLE 状态
*
*/
TIMED_WAITING,
/**
* Thread state for a terminated thread.
* The thread has completed execution.
*
* TERMINATED (完成)状态:
* 终止线程的线程状态。线程已完成执行。
*/
TERMINATED;
}
二、线程状态的切换
三、输出线程的几种状态:
代码:
/**
* 线程的六种状态:
* NEW:通过 new 关键字创建
* RUNNABLE:调用 start()
* BLOCKED:被阻塞等待监视器锁定的线程处于此状态
* WAITING:正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作的线程处于此状态。
* TIMED_WAITING:正在等待另一个线程执行动作达到指定等待时间的线程处于此状态。
* TERMINATED:已退出的线程处于此状态。
*
* @author: BlackSoil
* @date: 2022-11-18 09:43
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class T01_State {
public static void m() {
LockSupport.park();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static synchronized void n() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> m(),"线程1");
// thread 线程执行了 new ,观察 NEW 状态
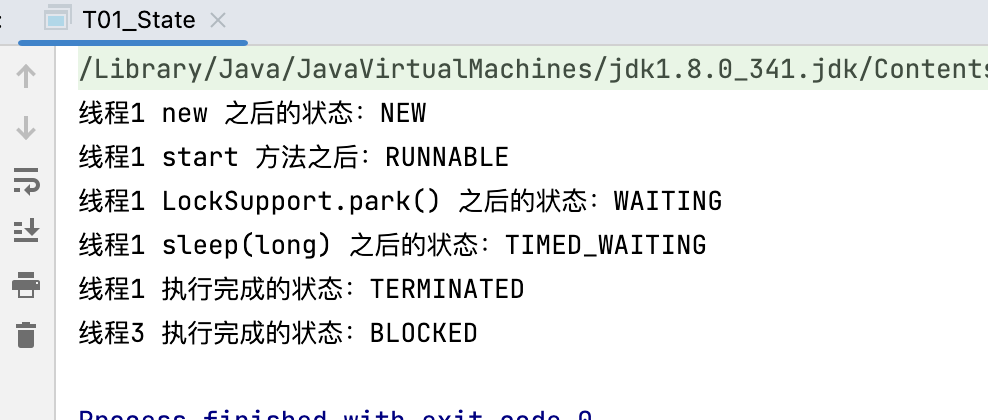
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" new 之后的状态:"+thread.getState());
// thread 线程执行了 start ,观察 RUNNABLE 状态
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" start 方法之后:"+thread.getState());
// thread 线程执行了 LockSupport.park() ,观察 WAITING 状态
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" LockSupport.park() 之后的状态:"+thread.getState());
LockSupport.unpark(thread); //唤醒线程
// thread 线程执行了 sleep(long) ,观察 TIMED_WAITING 状态
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" sleep(long) 之后的状态:"+thread.getState());
// thread 执行结束 ,观察 TERMINATED 状态
thread.join();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" 执行完成的状态:"+thread.getState());
//测试 BLOCKED 状态
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> n(),"线程2");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> n(),"线程3");
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(500);// 让 thread2 先执行
thread3.start();
Thread.sleep(500); //保证 thread 已经执行
System.out.println(thread3.getName()+" 执行完成的状态:"+thread3.getState());
}
}
结果:
分类:
Java线程基础





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!