Java对栈的基本操作
数据结构之基本数据结构---栈:先入后出
百度百科:
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。
向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是
把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
自定义栈:
示例代码:
package stack; /** * @Author YangHe * @Date 2020/4/14 11:27 * 手动实现:栈的基本操作 * 后进先出 LIFO */ public class StackTest { private final int stackSize; //栈可用最大容量 private int base; //栈底指针 private int top; //栈顶指针 private int[] array; //存储使用数组实现 //初始化栈 public StackTest(int stackSize) { this.stackSize = stackSize; this.base=-1; this.top=-1; this.array=new int[stackSize]; } //判断栈是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return base==top; } //判断栈是否满 public boolean isFull(){ return (top-base)>=stackSize; } //获取栈的长度 public int getStackLength(){ return top-base; } //出栈但不删除(指针不移动) public int peek(){ if(!isEmpty()){ return array[top]; }else{ System.out.println("栈为空,返回-1"); return -1; } } //出栈并且删除(指针移动) public int pop(){ if(!isEmpty()){ return array[top--]; }else{ System.out.println("栈为空,返回-1"); return -1; } } //入栈 public void push(int n){ if(!isFull()){ array[++top]=n; }else{ System.out.println(top); System.out.println("栈已满"); } } //销毁栈 public void stackDestroy(){ array=null; top=-1; } public static void main(String[] args) { StackTest stackTest=new StackTest(10); for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ stackTest.push(i); System.out.println("入栈元素"+i+" 栈长度:"+stackTest.getStackLength()); } for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ System.out.println("不删除栈顶元素出栈:"+stackTest.peek()+" 栈长度:"+stackTest.getStackLength()); } for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ System.out.println("删除栈顶元素出栈:"+stackTest.pop()+" 栈长度:"+stackTest.getStackLength()); } stackTest.stackDestroy(); System.out.println("销毁栈之后长度为:"+stackTest.getStackLength()); } }
示例结果:

Stack类:
List接口下Vector类的子类Stack 也可以模拟 “栈”这种数据结构
示例代码:
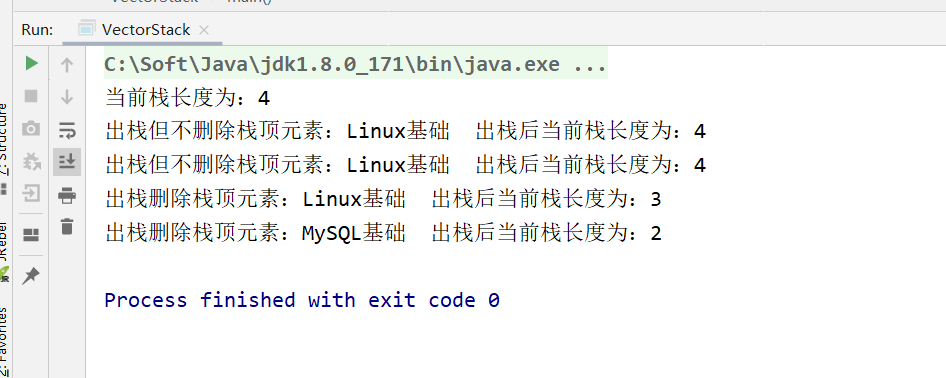
package stack; import java.util.Stack; /** * @Author YangHe * @Date 2020/4/14 16:24 * Vector下的Stack子类: 模拟 “栈”这种数据结构 * 后进先出 LIFO */ public class VectorStack { public static void main(String[] args) { Stack v=new Stack(); //入栈 v.push("Java基础"); v.push("python基础"); v.push("MySQL基础"); v.push("Linux基础"); System.out.println("当前栈长度为:"+v.size()); //出栈 并不删除 System.out.println("出栈但不删除栈顶元素:"+v.peek()+" 出栈后当前栈长度为:"+v.size()); System.out.println("出栈但不删除栈顶元素:"+v.peek()+" 出栈后当前栈长度为:"+v.size()); //出栈 删除元素 System.out.println("出栈删除栈顶元素:"+v.pop()+" 出栈后当前栈长度为:"+v.size()); System.out.println("出栈删除栈顶元素:"+v.pop()+" 出栈后当前栈长度为:"+v.size()); } }
示例结果:
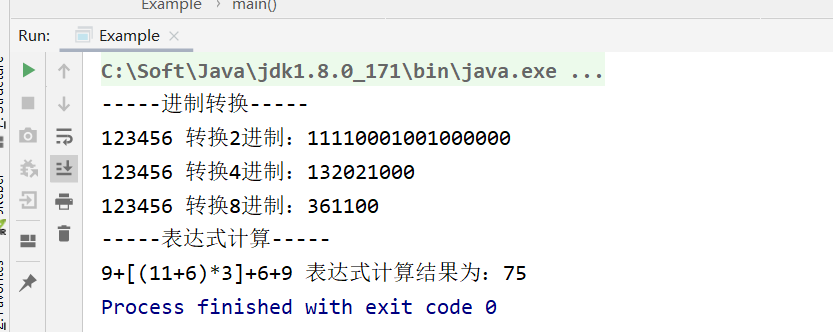
以下为我写的两个栈的应用(进制转换,表达式计算):
示例代码:
package stack; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /** * @Author YangHe * @Date 2020/4/16 14:34 * 使用栈的实例 */ public class Example { /** * 进制转换 * @param parameter 要转换的十进制数 * @param scale 进制数 * @return */ public static long hexConversion(int parameter,int scale){ StackTest stackTest=new StackTest(Integer.class,50); while(true){ //进行计算入栈 if(parameter>=scale){ int a=parameter/scale; int b=parameter%scale; stackTest.push(b); parameter=a; }else{ stackTest.push(parameter); break; } } long result=stackTestToIntTool(stackTest); //将获取的栈数据转化成long类型进行展示 return result; } /** * 表达式运算 暂未实现运算符优先级 * @param expression * @return */ public static StackTest<String> compute(String expression){ StackTest stackTest=new StackTest(String.class,50); Pattern p; Matcher m; p = Pattern.compile("\\+|\\-|\\*|\\/|\\(|\\)|\\[|\\]|[1-9]\\d*\\.?\\d*"); m = p.matcher(expression); while(m.find()){ String str=m.group(); if(str.equals(")")){ int result=0; while(!stackTest.peek().equals("(")){ Integer a=Integer.valueOf(stackTest.pop().toString()); String x=stackTest.pop().toString(); Integer b=Integer.valueOf(stackTest.pop().toString()); result=calculate(a,x,b); } stackTest.pop(); stackTest.push(String.valueOf(result)); }else if(str.equals("]")){ int result=0; while(!stackTest.peek().equals("[")){ Integer a=Integer.valueOf(stackTest.pop().toString()); String x=stackTest.pop().toString(); Integer b=Integer.valueOf(stackTest.pop().toString()); result=calculate(a,x,b); } stackTest.pop(); stackTest.push(String.valueOf(result)); }else{ stackTest.push(str); } } while(stackTest.getStackLength()>1){ Integer a=Integer.valueOf(stackTest.pop().toString()); String x=stackTest.pop().toString(); Integer b=Integer.valueOf(stackTest.pop().toString()); stackTest.push(String.valueOf(calculate(a,x,b))); } return stackTest; } /** * stackTest转化为long类型数 * @param stackTest * @return */ public static long stackTestToIntTool(StackTest stackTest){ String str=""; while(!stackTest.isEmpty()){ str+=stackTest.pop(); } return Long.valueOf(str); } /** * 进行计算 * @param a * @param x * @param b * @return */ public static int calculate(int a,String x,int b){ if(x.equals("+")){ return a+b; }else if(x.equals("-")){ return b-a; }else if(x.equals("*")){ return a*b; }else if(x.equals("/")){ return b/a; } return 0; } /** * 打印栈 * @param stringStackTest */ public static void print(StackTest<String> stringStackTest){ while(stringStackTest.isEmpty()){ System.out.println(stringStackTest.pop()); } } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("-----进制转换-----"); System.out.println("123456 转换2进制:"+hexConversion(123456,2)); System.out.println("123456 转换4进制:"+hexConversion(123456,4)); System.out.println("123456 转换8进制:"+hexConversion(123456,8)); System.out.println("-----表达式计算-----"); String str="9+[(11+6)*3]+6+9"; StackTest<String> stringStackTest=compute(str); System.out.print(str+" 表达式计算结果为:"); while(!stringStackTest.isEmpty()){ System.out.print(stringStackTest.pop()); } } }
示例结果: