ThreadLocal源码阅读
一、前言
-
在线程安全问题中,会使用synchronized关键字,只允许一个线程进入锁定的方法或代码块,这样可以保证原子性,即"以时间换空间"。但在并发量较大时,会存在大量线程等待同一个对象锁,导致系统性能下降。
-
考虑到synchronized的弊端,于是出现了volatile和ThreadLocal等解决线程安全的思路。volatile所修饰的变量不保存拷贝,直接访问主内存,主要用于"一写多读"的场景。ThreadLocal会为每一个线程创建一个副本,保证每个线程访问的都是自己的副本,线程之间相互隔离,即"以空间换时间"。
二、ThreadLocal概要
1.ThreadLocal如何使用
在使用ThreadLocal之前,先看一个示例1(线程不安全场景)
/** * 示例1:线程不安全场景 */ public class MyThread { private int count = 0; public void incrementCount() { count++; } public int getCount() { return count; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new ThreadA(i, myThread).start(); } Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println("主线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", finalCount:" + myThread.getCount()); } } class ThreadA extends Thread { private int i; private MyThread myThread; public ThreadA(int i, MyThread myThread) { this.i = i; this.myThread = myThread; } @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } myThread.incrementCount(); System.out.println("子线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===>i:" + i + ",count:" + myThread.getCount()); } }
运行结果:
子线程名称:Thread-1===>i:1,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-0===>i:0,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-2===>i:2,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-3===>i:3,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-5===>i:5,count:4 子线程名称:Thread-4===>i:4,count:5 子线程名称:Thread-8===>i:8,count:5 子线程名称:Thread-9===>i:9,count:4 子线程名称:Thread-6===>i:6,count:4 子线程名称:Thread-7===>i:7,count:4 主线程名称:main, finalCount:5
可以看到:finalCount最终输出错误,预计的结果应为10,实际却为5,即出现了线程安全问题。
把示例1改成使用ThreadLocal,如示例2(使用ThreadLocal)
/** * 示例2:使用ThreadLocal */ public class MyThreadLocal { private ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); public void incrementCount() { threadLocal.set(getCount() + 1); } public int getCount() { return threadLocal.get() == null ? 0 : threadLocal.get(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThreadLocal myThreadLocal = new MyThreadLocal(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { new ThreadB(i, myThreadLocal).start(); } Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println("主线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", finalCount:" + myThreadLocal.getCount()); } } class ThreadB extends Thread { private int i; private MyThreadLocal myThreadLocal; public ThreadB(int i, MyThreadLocal myThreadLocal) { this.i = i; this.myThreadLocal = myThreadLocal; } @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } myThreadLocal.incrementCount(); System.out.println("子线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===>i:" + i + ",count:" + myThreadLocal.getCount()); } }
运行结果:
子线程名称:Thread-6===>i:6,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-3===>i:3,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-7===>i:7,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-9===>i:9,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-4===>i:4,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-1===>i:1,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-2===>i:2,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-8===>i:8,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-5===>i:5,count:1 子线程名称:Thread-0===>i:0,count:1 主线程名称:main, finalCount:0
可以看到:
-
finalCount为0。因为主线程中会创建一个threadLocal副本,即第一次调用threadLocal.get()为null,则返回结果值0。
-
count全部为1。因为每个子线程中都会创建一个属于自己的threadLocal副本,在执行myThreadLocal.incrementCount()代码后,count会加1,则返回结果值1。
2.ThreadLocal工作原理
示例1解读:
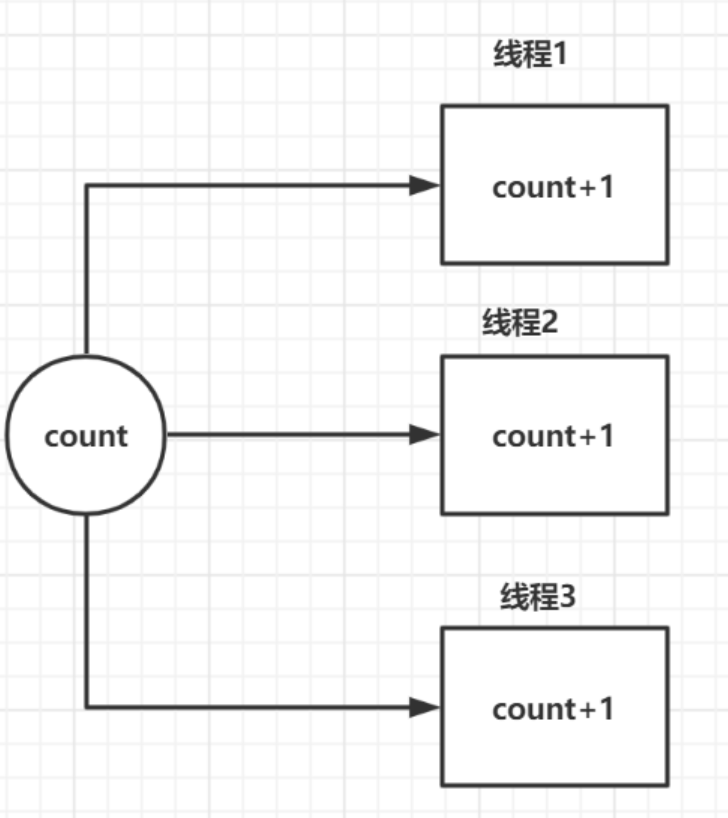
可以看到,多个线程同时访问共享变量count,当某个线程执行count++时,可能其它线程也正在执行count++,但由于变量没有使用volatile关键字,即在多个线程中变量count不可见性,会导致其它线程拿到的是旧的count值+1,就会出现示例1运行结果的问题。
示例2解读:
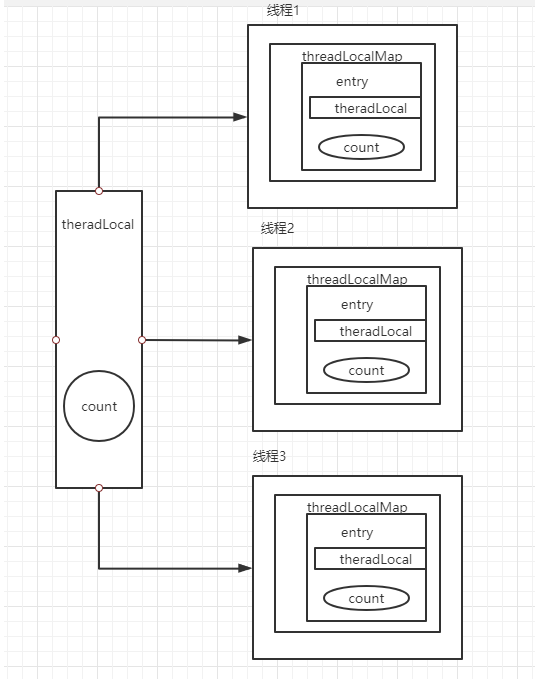
可以看到,ThreadLocal会给每个线程都创建变量的副本,保证每个线程访问的都是自己的副本,线程之间相互隔离。每个线程内部都有一个threadLocalMap,每个threadLocalMap中都包含了一个entry数组,而entry数组是由threadLocal和数据组成键值对的。
3.ThreadLocal源码解析
在Thread类中,定义了threadLocals成员变量
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
它的类型是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,可以看出ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的内部类;
ThreadLocalMap内部类源码:
static class ThreadLocalMap { static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } } /** * The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two. */ private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /** * The table, resized as necessary. * table.length MUST always be a power of two. */ private Entry[] table; /** * The number of entries in the table. */ private int size = 0; /** * The next size value at which to resize. */ private int threshold; // Default to 0 ......代码省略 }
可以看到:
-
ThreadLocalMap类中定义了一个数组table,类型为Entry,Entry是WeakReference(弱引用)的子类;
-
Entry包含了ThreadLocal变量和值value,其中ThreadLocal变量为WeakReference的referent;
在ThreadLocal类中,常用的四个方法:get()、initialValue()、set(T value)、remove()
3.1 get方法源码
public T get() { // 获取当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程中的ThreadLocalMap对象 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { // 获取ThreadLocalMap中的Entry对象 ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // 获取entry中的值 T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } // 调用初始化方法 return setInitialValue(); }
getMap方法源码:
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; }
返回当前线程的成员变量threadLocals。
getEntry方法源码:
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) { // threadLocalHashCode对table.length - 1的取余操作, // 这样可以保证数组的下表在0到table.length - 1之间。 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); // 获取下标对应的entry Entry e = table[i]; if (e != null && e.get() == key) // 返回entry return e; else // 如果entry为空,或者e.get()为空,或者额。get()与当前key不一致,则清理数据 return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); }
entry是WeakReference(弱引用)的子类,e.get()会调用:
public T get() { return this.referent; }
返回的是一个引用,是构造器传入的threadLocal对象
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { // threadLocal传递 super(k); value = v; } }
getEntryAfterMiss方法源码:
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; while (e != null) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == key) return e; if (k == null) expungeStaleEntry(i); else i = nextIndex(i, len); e = tab[i]; } return null; }
getEntryAfterMiss方法中会调用expungeStaleEntry方法,源码:
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; // expunge entry at staleSlot // 将下标staleSlot对应的entry中的value设置为null,有助于垃圾回收,避免内存泄漏 tab[staleSlot].value = null; // 将下表staleSlot对应的entry设置为null,有助于垃圾回收,避免内存泄漏 tab[staleSlot] = null; // 数组大小-1 size--; // Rehash until we encounter null Entry e; int i; // 变量staleSlot之后的entry不为空的数据 for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) { // 当前位置的entry中对应的threadLocal ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == null) { // value设置为null,有助于垃圾回收,避免内存泄漏 e.value = null; // entry设置为null,有助于垃圾回收,避免内存泄漏 tab[i] = null; // 数组大小-1 size--; } else { // 重新计算下标位置 int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); if (h != i) { tab[i] = null; // Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until // null because multiple entries could have been stale. // 如果h和i不相等,则说明存在hash冲突,它前面的entry被清理,则该entry需向前移动 // 防止下次get()或set()时,再次因散列冲突而查到null值 while (tab[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); tab[h] = e; } } } return i; }
entry中包含了threadLocal和value,threadLocal是WeakReference(弱引用)的referent。每次垃圾回收器触发GC时,会回收WeakFerence中的referent,将referent设置为null。固在table数组中会存在很多threadLocal为null,但value不为null的entry,这种数据是无法通过getEntry方法获取到entry的,因为有判断条件if (e != null && e.get() == key);
如果threadLocal使用强引用,threadLocal不再使用时,但ThreadLocalMap中还存在该引用,那么只要主线程不结束,无法被GC回收,会导致内存泄漏。另在使用线程池时,由于线程不会被销毁,线程会被重复使用,会导致threadLocal无法被释放,也会导致内存泄漏。
3.2 setInitialValue方法源码
private T setInitialValue() { // 初始化值 T value = initialValue(); // 获取当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程中的ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) // 不为空,则覆盖key为当前threadLocal的值 map.set(this, value); else // 为空,则创建新的ThreadLocalMap,进行初始化赋值 createMap(t, value); return value; }
initialValue方法源码:
protected T initialValue() { return null; }
改方法默认返回null,该方法用protected修饰,说明可以被子类重写实现。
createMap方法源码:
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }
为当前线程成员变量threadLocals进行初始化赋值。
3.3 set方法源码
public void set(T value) { // 获取当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) // 不为空,则覆盖key为当前threadLocal的值 map.set(this, value); else // 为空,则创建新的ThreadLocalMap,进行初始化赋值 createMap(t, value); }
set(this, value)源码:
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. // 将table数组赋值给新数组tab Entry[] tab = table; // 数组长度 int len = tab.length; // 计算当前Entry的下标 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { // 获取entry中的ThreadLocal对象 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); // 如果当前threadLocal与当前key相当 if (k == key) { // 覆盖旧值 e.value = value; return; } // 如果当前threadLocal为null if (k == null) { // 创建一个新的entry赋值给当前key replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } // 如果key不存在数组tab中,则创建一个新的entry放到数组tab中 tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); // 数组大小+1 int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); }
在replaceStaleEntry方法中也会调用expungeStaleEntry方法。
3.4 remove方法源码
public void remove() { // 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); // 如果当前threadLocalMap不为空,则清理 if (m != null) m.remove(this); }
m.remove(this)源码:
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) { // 将table数组赋值给新的数组tab Entry[] tab = table; // 数组大小 int len = tab.length; // 计算下标 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); // 循环变量从下表i之后不为空的entry for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { // 如果当前获取到threadLocal与key相等 if (e.get() == key) { // 清空引用 e.clear(); // 处理threadLocal为空,但value不为空的entry expungeStaleEntry(i); return; } } }
e.clear()源码:
public void clear() { this.referent = null; }
直接将引用设置为null,有助于垃圾回收,避免内存泄漏
4.ThreadLocal有哪些坑
1.内存泄漏
ThreadLocal使用了WeakReference(弱引用)也会存在内存泄漏问题,因为entry中的key(即threadLocal)设置成了弱引用,但value没有,还是会存在下面的强依赖:
Thread -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value
2. 线程安全问题
如定义的static变量a,在多线程情况下,threadLocal中的value需要修改并设置a的值,会存在线程安全问题,因为static变量是多个线程共享的,不会再单独保存副本。
三、总结
-
-
entry的key(即threadLocal)为弱引用,可以被垃圾回收器回收
-
ThreadLocal中最常用的四个方法:get()、initialValue()、set(T value)、remove(),除了initialValue方法外,其他方法都会调用expungeStaleEntry方法做key==null的数据清理
-



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号