Java正则表达式
一、简述
在字符串比较时,简单的操作可以使用一些算法来查找或匹配,如要判断一个端口地址地址是否合法,可以简单的判断其是否在0-65536之间。
但是,有一些字符匹配操作使用这种方法非常复杂,如匹配一个QQ号:
- 首先先检测该QQ号的长度是否大于等于5位并且小于等于11位;
- 然后还需判断第一位是否为0,是0则不合法;
- 若合法,还得检测其是否全为数字。
这个过程用java可以这样写:
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String qq = bfr.readLine();
//1.判断QQ位数是否合法
if(qq.length() >= 5 && qq.length() <= 11) {
//2.判断是否非0开头
if(!qq.startsWith("0")) {
//3. 判断是否非数字
try {
long nqq = Long.parseLong(qq);
System.out.println("qq:" + nqq);
}catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("包含非法字符!");
}
}else {
System.out.println("QQ号不能以0开头。");
}
}else {
System.out.println("QQ位数必须为<5,11>。");
}
}
}
虽然也可以搞定,但是用正则表达式我们可以这样写:
String regex = "[1-9]\\d{4,11}";
boolean flag = qq.matches(regex);
System.out.println(flag ? "qq:" + qq : "不合法!");
是不是超级方便呢?所以,对于字符串的复杂操作,我们应该使用正则表达式。
正则表达式优点:简化对字符串的复杂操作。缺点:当符号定义的越来越长时,阅读性极差。
二、匹配
在String,有一个matches方法。
boolean matches(String regex);
match在英文中有匹配的意思,它需要传入匹配规则,只要有一处不匹配,就匹配结束,返回false。
如:
System.out.println("-1234".matches("-?\\d+"));
System.out.println("5678".matches("-?\\d+"));
System.out.println("+100".matches("-?\\d+"));
System.out.println("+100".matches("(-|\\+)?\\d+"));
将输出为:
true
true
false
true
三、切割
在String中,有两个split方法用来切割字符串。
String[] split(String regex); //根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串
String[] split(String regex, int limit); //根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串
传入相应的规则,便可按此规则将字符串分离开来,结果保存在String数组中。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Splitting {
public static String knights =
"Then, when you have found the shrubbery, you must " +
"cut down the mightiest tree in the forest... " +
"with... a herring!";
public static void split(String regex) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(knights.split(regex)));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
split(" "); //按空格划分字符串
split("\\W+"); //非单词字符
split("n\\W+"); //n加非单词字符
}
}
输出将为:
[Then,, when, you, have, found, the, shrubbery,, you, must, cut, down, the, mightiest, tree, in, the, forest..., with..., a, herring!]
[Then, when, you, have, found, the, shrubbery, you, must, cut, down, the, mightiest, tree, in, the, forest, with, a, herring]
[The, whe, you have found the shrubbery, you must cut dow, the mightiest tree i, the forest... with... a herring!]
四、替换
对于规则,java中也封装的有相应的对象,这个类是Pattern。通过查看文档可以发现这个类没有构造函数,意味着不能对其进行实例化。它的方法如下:
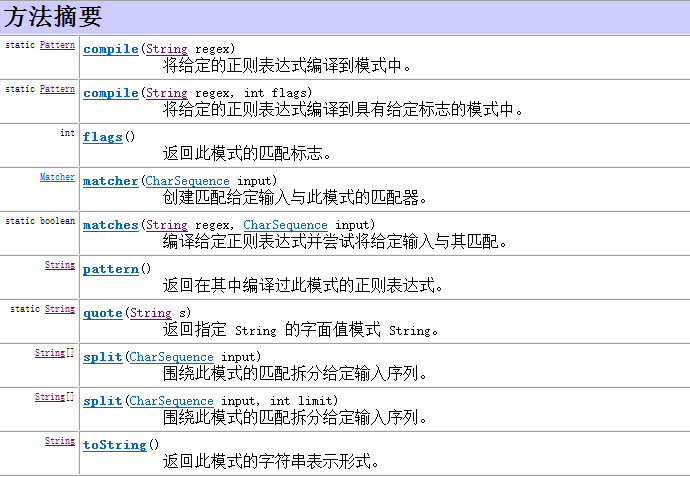
通过compaile()方法可以将规则封装成对象,通过matcher()来将正则对象和要作用的字符串相关联,获取匹配对象。Matcher类用来表示正则对象。
public static void getDemo() {
String str = "hello today is saturday";
String reg = "\\b[a-z]{5}\\b";
//将规则封装成对象
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(reg);
//让正则对象和要作用的字符串相关联,获取匹配对象
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);
//将规则作用到字符串上,并进行符合规则的子串查找
while(m.find()) {
System.out.println(m.group());
}
}
匹配到的将为:
hello
today
五、获取
获取的步骤为:
1、将正则封装成对象
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(reg);
2、 让正则和要操作的字符串相关联
Marcher m = p.macher(str);
3、 关联后,获得正则匹配引擎
4、 通过引擎对符合规则的子串进行操作
可以发现在String类中也有matches方法。其实它用的就是Pattern和Matcher对象来完成的。String将其封装起来,使用变得简单了,但是功能相对就比较单一了。
public static void getDemo()
{
String str = "ming tian jiu yao fang jia le ,da jia。";
System.out.println(str);
String reg = "\\b[a-z]{4}\\b";
//将规则封装成对象。
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(reg);
//让正则对象和要作用的字符串相关联。获取匹配器对象。
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);
while(m.find()) //将规则作用到字符串上,并进行符合规则的子串查找。
{
System.out.println(m.group()); //用于获取匹配后的结果
System.out.println(m.start()+"...."+m.end());
}
}
输出如下:
ming tian jiu yao fang jia le ,da jia。
ming
0....4
tian
5....9
fang
18....22
六、练习
1、去掉重复及多余字符
有这样的一个字符串:我我...我我...我要....要要..要要...学学学..编编编.程.程程..程.程。第一步去掉其多余的点号,输出;第二步去掉重复的汉字使只保留一个并输出。
String str = "我我...我我...我要....要要..要要...学学学..编编编.程.程程..程.程";
str = str.replaceAll("\\.+", ""); //出现一次或多次".",替换为空
System.out.println(str);
str = str.replaceAll("(.)\\1+", "$1"); //任意字符出现一次或多次,替换为1次
System.out.println(str);
输出为:
我我我我我要要要要要学学学编编编程程程程程
我要学编程
2、匹配IP
有这样一串IP地址,192.68.1.254 102.49.23.013 10.10.10.10 2.2.2.2 8.109.90.30,要求:取出其中的IP地址,并按地址段顺序输出IP地址。
public static void ipSort() {
String ip = "192.68.1.254 102.49.23.013 10.10.10.10 2.2.2.2 8.109.90.30";
ip = ip.replaceAll("(\\d+)", "00$1"); //位数对齐,先对所有数将加两个0,使这些数的位数都大于等于3位
System.out.println(ip);
ip = ip.replaceAll("0*(\\d{3})", "$1"); //有0的去掉0
System.out.println(ip);
String[] arr = ip.split(" ");
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<String>();
for(String s : arr) {
ts.add(s); //装入TreeSet中,可以自动排序
}
for(String s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.replaceAll("0*(\\d+)", "$1")); //去掉多余的0
}
}
输出为:
00192.0068.001.00254 00102.0049.0023.00013 0010.0010.0010.0010 002.002.002.002 008.00109.0090.0030
192.068.001.254 102.049.023.013 010.010.010.010 002.002.002.002 008.109.090.030
2.2.2.2
8.109.90.30
10.10.10.10
102.49.23.13
192.68.1.254
3、匹配邮箱地址
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String mail = bfr.readLine();
//较为精确的匹配
String reg = "[a-zA-z0-9_]+@[a-zA-z0-9]+(\\.[a-zA-z]+){1,3}";
System.out.println(mail.matches(reg));
//相对不太精确的匹配
reg = "\\w+@\\w+(\\.\\w+)+";
System.out.println(mail.matches(reg));
输出为:
//Input 1
coolcpp@outlook.com
true
true
//Input 2
123@qq.com.cn
true
true
//Input 3
1@1.1
false
true



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号