Lab5: 面向功能程序构造方法及创新应用 (基础)
1、构造两数交换的函数,并验证各种参数形式
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 交换两个整数的值
void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// 交换两个浮点数的值
void swap(double &a, double &b)
{
double temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// 交换两个字符的值
void swap(char &a, char &b)
{
char temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main()
{
int x = 1, y = 2;
double d1 = 1.5, d2 = 2.5;
char c1 = 'A', c2 = 'B';
// 测试交换整数
swap(x, y);
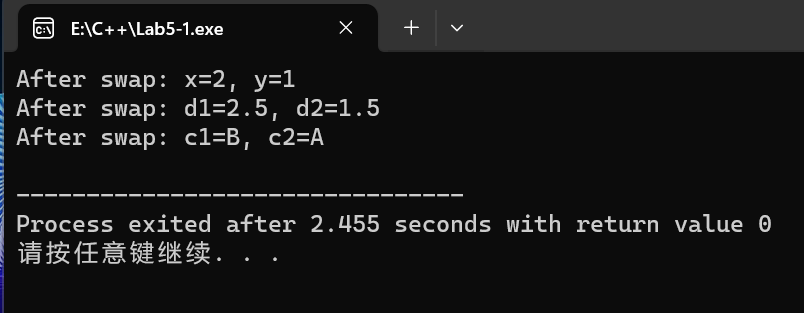
cout << "After swap: x=" << x << ", y=" << y << endl;
// 测试交换浮点数
swap(d1, d2);
cout << "After swap: d1=" << d1 << ", d2=" << d2 << endl;
// 测试交换字符
swap(c1, c2);
cout << "After swap: c1=" << c1 << ", c2=" << c2 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
2、函数及函数指针
-
将 Lab4 的两种排序分别包装为函数并验证
-
进一步构造一个排序函数,其参数包含一个函数指针,通过该函数实现两种排序的统一使用方式。
操作1就是把排序写成函数,没什么难的。
操作2函数指针学到了,传入一个类型为函数指针的参数,也好理解,把代码单独截出来:
void sortArray(int nums[], int length, void (*sortFunc)(int[], int))
{
sortFunc(nums, length);
}
对于操作2的一点思考
以上代码中的sortArray函数中的函数指针参数如果改成普通的函数,会有什么区别?
因为当我把把代码中的函数指针前面的 *去掉之后,代码的运行结果没有改变
查询资料后结论如下:
当你在将函数指针参数改为普通函数参数时,实际上是将函数指针所指向的函数直接作为参数传递进去了。这样做的话,结果可能没有变化是因为函数名本身就是函数指针,所以去掉 * 之后,传入的函数名会被自动转换为函数指针,从而和原来的函数指针参数传入的效果是一样的。
在调用sortArray函数时,你仍然可以传入一个函数名,比如compareFunction,然后这个函数名会被隐式地转换为函数指针,所以运行结果没有改变。
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 选择排序
void selectionSort(int nums[], int length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++)
{
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++)
{
if (nums[j] < nums[minIndex])
minIndex = j;
}
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[minIndex];
nums[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
// 冒泡排序
void bubbleSort(int nums[], int length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < length - i - 1; j++)
{
if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1])
{
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
nums[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 排序函数,参数为数组和排序算法的函数指针
//注意此处函数指针的写法!!
void sortArray(int nums[], int length, void (*sortFunc)(int[], int)) {
sortFunc(nums, length);
}
int main() {
int nums[] = {5, 3, 7, 2, 8, 4, 6, 1};
//int length = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(int);
int length = 8;
// 使用选择排序
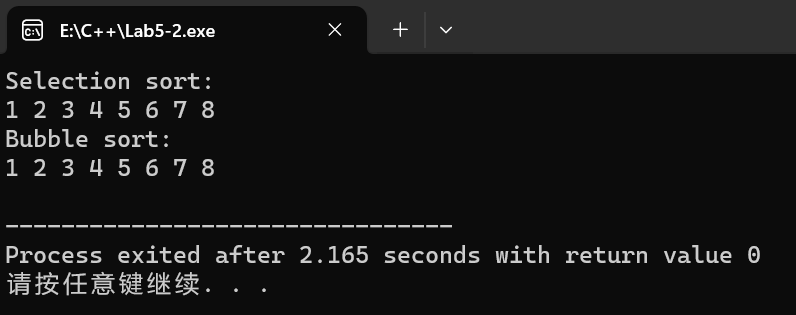
cout << "Selection sort:" << endl;
sortArray(nums, length, selectionSort);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 使用冒泡排序
cout << "Bubble sort:" << endl;
sortArray(nums, length, bubbleSort);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
3 库函数使用
1) 利用随机数库函数,实现一个猜数小游戏。
先获取当前时间作为时间种子,再用rand()函数获取随机数
细节注释在代码里面了
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> //srand,rand 函数
#include <ctime> //time函数
using namespace std;
int main() {
//srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(time(0))); 和下面一行等价
srand((unsigned int)(time(0)));
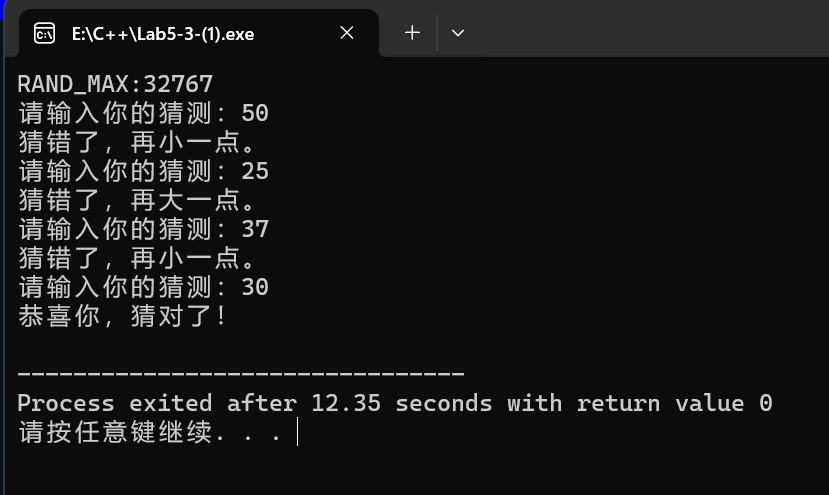
cout<<"RAND_MAX:"<<(long long)RAND_MAX<<endl;
int secretNumber = rand() % 100 + 1;
int guess = 0;
while (guess != secretNumber)
{
cout << "请输入你的猜测:";
cin >> guess;
if (guess == secretNumber)
cout << "恭喜你,猜对了!" << endl;
else if (guess < secretNumber)
cout << "猜错了,再大一点。" << endl;
else cout << "猜错了,再小一点。" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
2) 利用字符串函数 strtok0,分别统计一段文字中的单词出现次数,并按照次数排序输出。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main() {
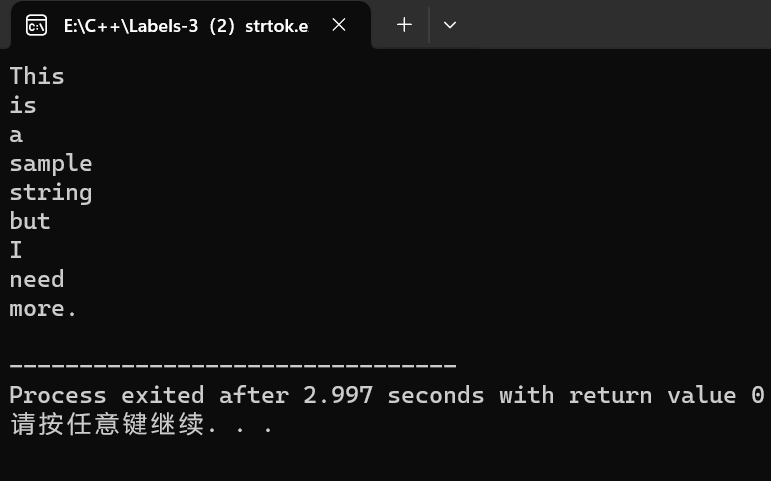
char str[] = "This is a sample string,but I need_more.";
char* token = strtok(str, " "); // 第一次调用,分割空格
while (token != NULL)
{
cout << token << endl; // 输出子字符串
token = strtok(NULL, " , _"); // 继续分割空格,注意参数 NULL
}
return 0;
}
输出
3) 构建一个字符串数组,并按字符串大小进行排序
使用了 strcpy 和 strcmp 函数
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 5;
int main()
{
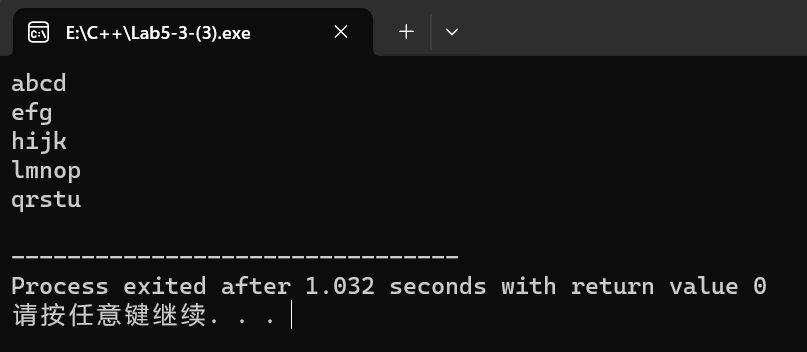
char str[SIZE][SIZE+1] = {"abcd", "efg", "hijk", "lmnop", "qrstu"};
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < SIZE; j++)
{
if (strcmp(str[i], str[j]) > 0)
{
char temp[SIZE+1];
strcpy(temp, str[i]);
strcpy(str[i], str[j]);
strcpy(str[j], temp);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
cout << str[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
4、递归及应用
1) 通过递归方法实现数字拆分
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void work(int x)
{
if(!x) return;
work(x/10);
cout<<x%10<<' ';
}
int main()
{
int a;
cin>>a;
work(a);
return 0;
}
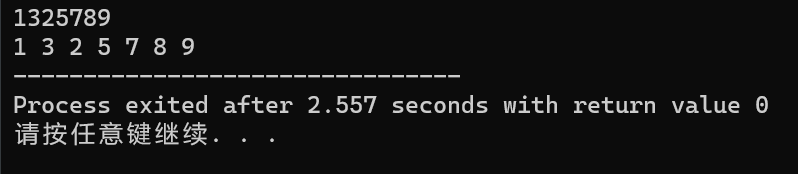
输出
2) 通过递归方法实现选择排序
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
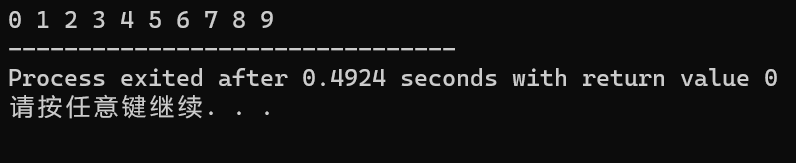
int a[10]={0,2,1,3,5,4,6,7,9,8};
void select_sort(int now)
{
if(now==9) return;
int Index=now;
for(int j=now+1;j<10;j++)
if(a[j]<a[Index]) Index=j;
swap(a[now],a[Index]);
select_sort(now+1);
}
int main()
{
select_sort(0);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) cout<<a[i]<<' ';
return 0;
}
输出



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号