matplotlib 示例
示例1
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']
#用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Simhei']
#用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
t = np.arange(1,10, 0.05)
x = np.sin(t)
y = np.cos(t)
# 绘制一个圆形散点图的示例
#定义一个图像窗口
plt.figure(figsize=(6,5))
#绘制一条线
plt.plot(x,y,'r-.')
#使坐标轴相等
plt.axis('equal')
plt.xlabel('正弦')
plt.ylabel('余弦')
plt.title('一个圆形')
#显示图像
plt.show()
示例2
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ##subplot()绘制多个子图 #生成X x1 = np.linspace(0.0, 5.0) x2 = np.linspace(0.0, 2.0) #生成Y y1 = np.cos(2*np.pi*x1) * np.exp(-x1) y2 = np.cos(2*np.pi*x2) ##绘制第一个子图 plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.plot(x1, y1,'y-o') plt.title('A Tale of 2 Subplots') plt.ylabel('Damped oscillation') ##绘制第二个子图 plt.subplot(2,1, 2) plt.plot(x2,y2,'r-o') plt.xlabel('time(s)') plt.ylabel('Undamped') plt.show()
示例3
#直方图 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import stats #example data mu = 100 #分布的均值 sigma = 15 #分布的标准差 x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(10000) #直方图的条数 num_bins = 50 #绘制直方图 n,bins,patches=plt.hist(x,num_bins,density=1, color='g',alpha=0.5) #添加一个最佳拟合和曲线 y = stats.norm.pdf(bins, mu, sigma) #返回关于数据的 pdf 数值(概率密度函数) plt.plot(bins,y,'r--') plt.xlabel('Smarts') plt.ylabel('Probability') #在图中添加公式需要使用 latex 的语法($$) plt.title('Histogram of IQ : $\mu=100$ , $\sigma=15$') #调整图像的间距,防止 轴数值与 label 重合 plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.15) plt.show() print("Bind:\n",bins)
坑:plt.hist中原来的normed没有了,替换成了density,否则画不出来。
示例4
#matplotlib 绘制三维图像 import numpy as np from matplotlib import cm import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D #生成数据 delta = 0.2 x = np.arange(-3,3, delta) y = np.arange(-3,3, delta) X, Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) Z = X**2 + Y**2 x = X.flatten() #返回一维的数组,但该函数只能适用于 numpy 对象( array 或者 mat) y = Y.flatten() z = Z.flatten() fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,6)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121 , projection='3d') ax1.plot_trisurf(x,y,z, cmap=cm.jet , linewidth=0.01) #cmap 指颜色,默认绘制为 RGB(A )颜色空间, jet 表示”蓝 红”颜色 plt.title("3D") ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122) cs= ax2.contour(X, Y, Z, 15 , cmap='jet') #注意这里是大写 X,Y,Z 15 代表的是显示等高线的密集程度,数值越大,画的等 #高线数就越多 ax2.clabel(cs,inline=True,fontsize=10,fmt='%1.1f') plt.title('Contour') plt.show()
示例5
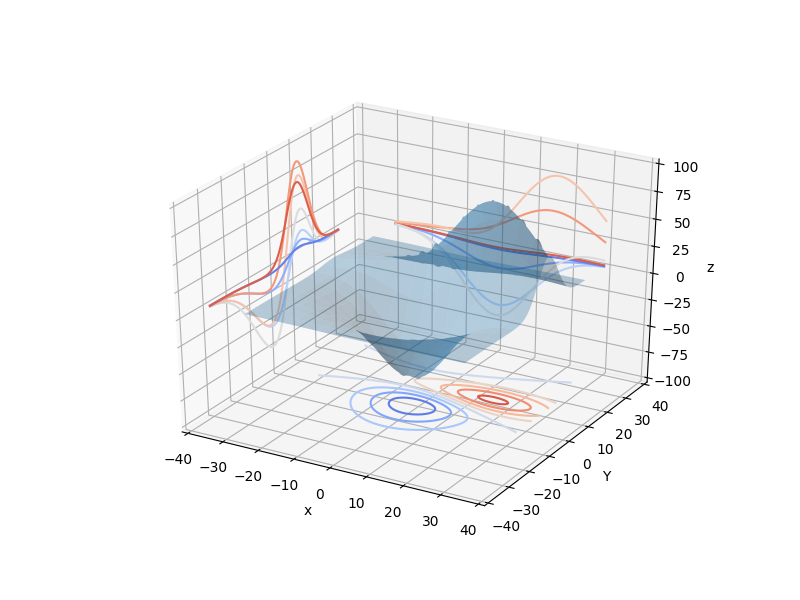
#三维图像+各个轴的投影等高线 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm fig= plt.figure (figsize=(8 , 6)) ax= fig.gca(projection='3d') #生成 维测试数据 X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=8, cstride=8, alpha=0.3) cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-100 , cmap=cm.coolwarm) cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='x', offset=-40 , cmap=cm.coolwarm) cset=ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir= 'y',offset=40 , cmap=cm.coolwarm) ax.set_xlabel('x') ax.set_xlim (-40 , 40) ax.set_ylabel ('Y') ax.set_ylim(-40 , 40) ax.set_zlabel ('z') ax.set_zlim (-100 , 100) plt.show()
示例6
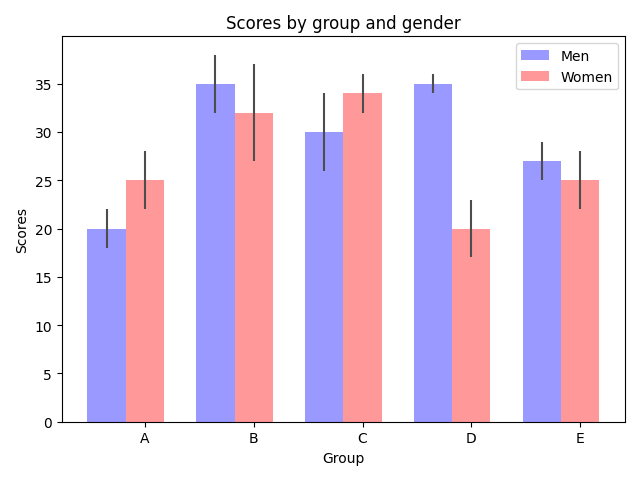
import numpy as np import matplotlib . pyplot as plt #生成数据 n_groups = 5 #组数 #平均分和标准差 means_men = (20 , 35 , 30 , 35 , 27) std_men = (2 , 3 ,4 ,1 , 2) means_women = (25 , 32 , 34 , 20 , 25) std_women = (3 , 5 , 2 , 3 , 3) #条形图 fig , ax= plt.subplots() #生成 0, 1. 2, 3 , .. index= np.arange (n_groups) bar_width = 0.35 #条的宽度 opacity= 0.4 error_config = {'ecolor': '0.3'} #条形图中的第一类条 rectsl = plt.bar(index , means_men , bar_width, alpha = opacity, color ='b', yerr = std_men, error_kw = error_config, label = 'Men') #条形图中的第二类条 rects2 = plt.bar(index +bar_width , means_women , bar_width, alpha = opacity, color = 'r', yerr = std_women, error_kw = error_config, label = 'Women') plt.xlabel('Group') plt.ylabel('Scores') plt. title('Scores by group and gender') plt.xticks(index + bar_width, ('A','B','C','D','E')) plt.legend() #自动调整 subplot 的参数给指定的填充区 plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
示例7
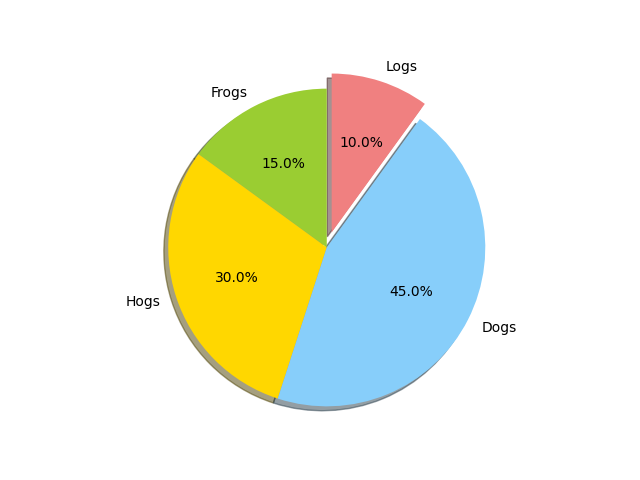
#饼图 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #切片将按顺时针方向排列并绘制 labels = 'Frogs','Hogs','Dogs','Logs' #标注 sizes = [15 , 30 , 45 , 10] #大小 colors = ['yellowgreen','gold','lightskyblue','lightcoral'] #颜色 # 0.1代表第二个块从圆中分离出来 explode = (0 ,0, 0, 0.1) #绘制饼图 plt.pie(sizes, explode=explode , labels=labels, colors=colors, autopct = '%1.1f%%', shadow=True , startangle=90) plt.axis('equal') plt.show()
示例8
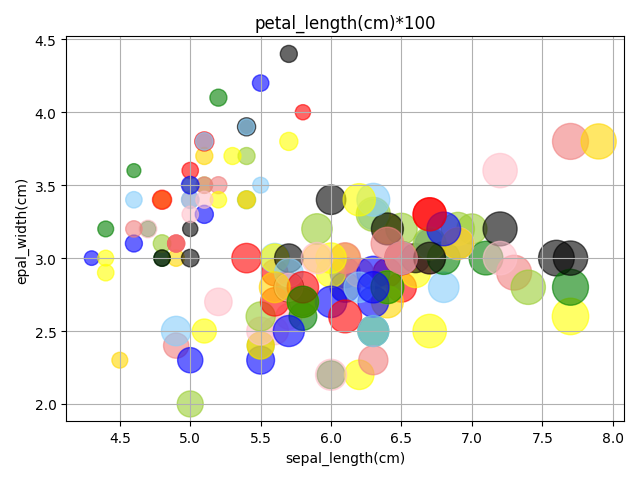
#气泡图(散点图〉 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd #导入数据 df_data= pd.read_csv("https://github.com/sileixinhua/Python_data_science_by_iris/ blob/master/iris.csv") print(df_data.head()) #作图 fig , ax = plt.subplots() #设置气泡图颜色 colors =15* ["yellowgreen","gold","green","blue","red","black", 'lightskyblue','lightcoral','yellow','pink'] #创建气泡图 SepalLength x, SepalWidth ,同时设置 PetalLength 为气 #泡大 ,并设置颜色透明度等 ax.scatter(df_data['sepal_length'],df_data['sepal_width'],s= df_data['petal_length']*100,color = colors,alpha = 0.6) #第三个变 表明根据[ PetalLength ]门 00 数据显示气泡的大小 ax.set_xlabel ('sepal_length(cm)') ax.set_ylabel ('epal_width(cm)') ax.set_title ('petal_length(cm)*100') #显示网格 ax.grid(True) fig.tight_layout() plt.show()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号