【GCC编译器】计算支配树信息 Part1 - 求CFG的深度为主搜索树
- 深度为主生成树:将图中所有的结点和那些构成深度为主次序的边表示为树的形式,并将其他的边(这些边不是深度为主次序的一部分)用一种有别于树的方式来表示(我们用虚线而不是实线表示它们)
- 属于深度为主生成树的边称为树边(tree edge)
- 不属于深度为主生成树的那些边分为三类:
- 前向边(forward edge):从一个结点到一个直接后裔并且不是树边的边(用F标识),主编号由小到大
- 后向边(back edge):从一个结点到树中它的一个祖先的边(用B标识),主编号由大到小
- 横向边(cross edge):连接两个在树中互不是祖先的结点的边(用C标识),主编号由大到小
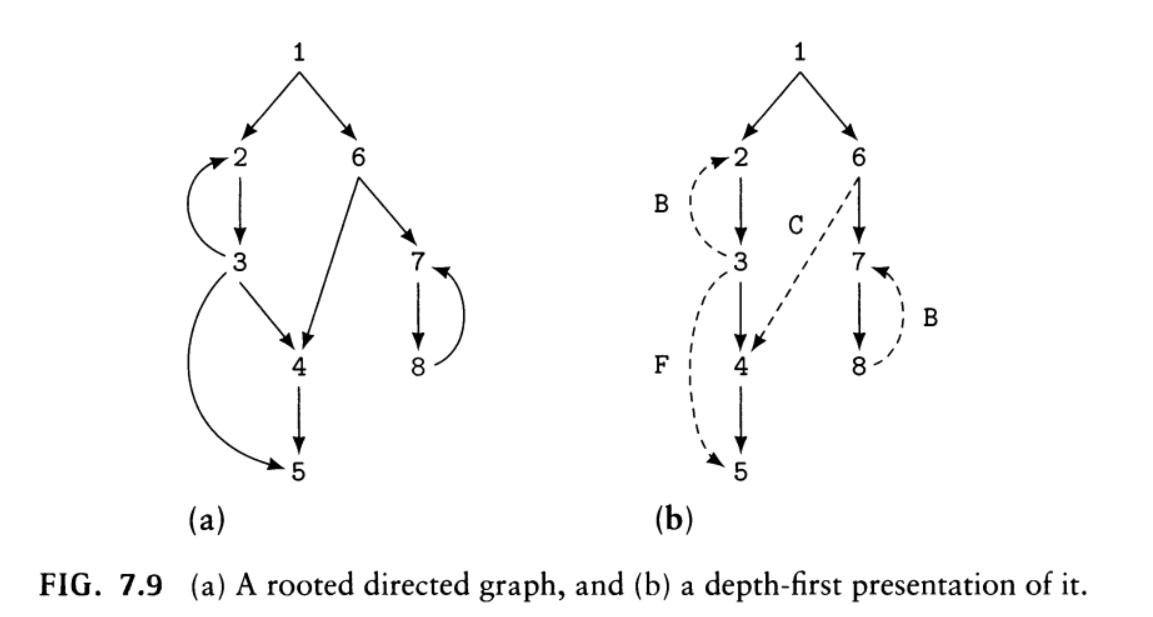
- GCC在计算深度为主搜索树时,使用的是非递归算法。利用stack先入后出的特点,完成树的深度优先遍历。为了使得代码逻辑更清晰,删除了CDI_POST_DOMINATORS模式相关的代码。
- 遍历过程中一共生成3张映射表:
- bb的index --> bb的深度为主编号:保存在映射表m_dfs_order
- bb的深度为主编号 --> bb的index:保存在映射表m_dfs_to_bb
- bb的深度为主编号 --> 在深度为主生成树中,bb的父节点的深度为主编号:保存在m_dfs_parent
/* The nonrecursive variant of creating a DFS tree. BB is the starting basic
block for this tree and m_reverse is true, if predecessors should be visited
instead of successors of a node. After this is done all nodes reachable
from BB were visited, have assigned their dfs number and are linked together
to form a tree. */
void
dom_info::calc_dfs_tree_nonrec (basic_block bb)
{
edge_iterator *stack = new edge_iterator[m_n_basic_blocks + 1];
int sp = 0;
unsigned d_i = dom_convert_dir_to_idx (CDI_DOMINATORS);
/* Initialize the first edge. */
edge_iterator ei = ei_start (bb->succs);
/* When the stack is empty we break out of this loop. */
while (1)
{
basic_block bn;
edge_iterator einext;
/* This loop traverses edges e in depth first manner, and fills the
stack. */
while (!ei_end_p (ei))
{
edge e = ei_edge (ei);
/* Deduce from E the current and the next block (BB and BN), and the
next edge. */
bb = e->src;
bn = e->dest;
/* 三种情况下跳过当前节点:
1. BN是end block,对于CDI_DOMINATORS模式来说,即exit block.
2. 没有给BN分配保存dominance information的空间.
3. 已经被访问过的节点. */
if (bn == m_end_block || bn->dom[d_i] == NULL
|| m_dfs_order[bn->index])
{
ei_next (&ei);
continue;
}
/* 深度优先,遍历BN的后继节点. */
einext = ei_start (bn->succs);
gcc_assert (bn != m_start_block);
/* Fill the DFS tree info calculatable _before_ recursing. */
/* my_i 是BB的深度为主编号.
child_i 是BN的深度为主编号. */
TBB my_i;
if (bb != m_start_block)
my_i = m_dfs_order[bb->index];
else
my_i = *m_dfs_last;
/* 将BN和child_i的映射关系存入表m_dfs_order. */
TBB child_i = m_dfs_order[bn->index] = m_dfsnum++;
/* 将child_i和BN的映射关系存入表m_dfs_to_bb. */
m_dfs_to_bb[child_i] = bn;
/* 将BB和BN的父子节点关系写入表m_dfs_parent. */
m_dfs_parent[child_i] = my_i;
/* Save the current point in the CFG on the stack, and recurse. */
stack[sp++] = ei;
ei = einext;
}
if (!sp)
break;
ei = stack[--sp];
/* OK. The edge-list was exhausted, meaning normally we would
end the recursion. After returning from the recursive call,
there were (may be) other statements which were run after a
child node was completely considered by DFS. Here is the
point to do it in the non-recursive variant.
E.g. The block just completed is in e->dest for forward DFS,
the block not yet completed (the parent of the one above)
in e->src. This could be used e.g. for computing the number of
descendants or the tree depth. */
ei_next (&ei);
}
delete[] stack;
}posted on 2021-08-07 00:00 Save-Reset 阅读(300) 评论(0) 收藏 举报

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号