Tomcat的Session管理(三)
摘要:PersistentManager与StandardManager的异同。
之前两篇关于session的文章主要讨论了session相关的创建、查询、过期处理。而我们查看源码的时候都是默认实现是StandardManager类,实际上实现也可以是PersistentManager类,下面我们就查看下该类的相关方法。
我们都知道PersistentManager代表的是持久化session的管理器。在PersistentManager类定义中有个变量org.apache.catalina.Store,该变量表示session管理器持久化session的方式,具体类图如下:
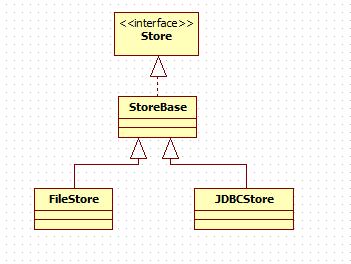
Store
持久化存储方式的抽象类,定义了一些基本方法,例如save(),load(),keys(),clear()等。save()用来将session持久化到持久性介质中。load()方法从持久化介质中读取到内存中,keys()则返回所有的sessionId数组。clear()则清除所有的session。
StoreBase
抽象类,对Store作了基本实现。
FileStore
该类会将session对象存储到某个文件中,文件名会使用session对象的标识符再加上一个后缀.session构成。文件位于临时目录下,也可以调用FileStore类的setDirectroy()方法修改目录。
JDBCStore
该类将session对象通过jdbc存入数据库,因此使用该类需要使用jdbc链接。
鉴于save(),load()源码都很简单这里就不一一查看了。
我们继续讨论PersistentManager类相关方法。
在Request的doGetSession()方法中,我们之前默认manager实现类是StandardManager,如果tomcat中配置的是PersistentManager,那么manager.findSession(requestedSessionId)会略有不同,我们查看下源码(在PersistentManagerBase类中):
@Override
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {
//调用父类的findSession() 也就是ManagerBase类中的findSession,从现有内存中查找是否有指定的session
Session session = super.findSession(id);
// OK, at this point, we're not sure if another thread is trying to
// remove the session or not so the only way around this is to lock it
// (or attempt to) and then try to get it by this session id again. If
// the other code ran swapOut, then we should get a null back during
// this run, and if not, we lock it out so we can access the session
// safely.
//翻译下 英文注释
// 代码运行到这里,因为我们不确定是否有别的线程要移除这个session,所以最保险的办法就是加锁再次尝试获取该session
// 如果有其他代码正在执行 swapOut(将内存session持久化到介质中),那么我们应该返回null,如果没有的话,那么我们就可以安全的访问这个session
if(session != null) {
synchronized(session){
session = super.findSession(session.getIdInternal());
if(session != null){
// To keep any external calling code from messing up the
// concurrency.
session.access();
session.endAccess();
}
}
}
// 再次判断
if (session != null)
return session;
// See if the Session is in the Store
//从持久化介质中查找 session是否存在
session = swapIn(id);
return session;
}
查看 swapIn()方法:
/**
* Look for a session in the Store and, if found, restore
* it in the Manager's list of active sessions if appropriate.
* The session will be removed from the Store after swapping
* in, but will not be added to the active session list if it
* is invalid or past its expiration.
*
* @return restored session, or {@code null}, if none is found
*/
/**
* 在Store(存储介质)中查找session,如果发现将把session恢复到该Manager的活跃session集合中。
* 这个session将会从Store中移除,但是如果session过期或者无效将不会添加到活跃集合。
*/
protected Session swapIn(String id) throws IOException {
if (store == null)
return null;
Object swapInLock = null;
/*
* The purpose of this sync and these locks is to make sure that a
* session is only loaded once. It doesn't matter if the lock is removed
* and then another thread enters this method and tries to load the same
* session. That thread will re-create a swapIn lock for that session,
* quickly find that the session is already in sessions, use it and
* carry on.
*/
synchronized (this) {
swapInLock = sessionSwapInLocks.get(id);
if (swapInLock == null) {
swapInLock = new Object();
sessionSwapInLocks.put(id, swapInLock);
}
}
Session session = null;
synchronized (swapInLock) {
// First check to see if another thread has loaded the session into
// the manager
session = sessions.get(id);
if (session == null) {
try {
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
try {
session = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedStoreLoad(id));
} catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
Exception e = ex.getException();
log.error(sm.getString(
"persistentManager.swapInException", id),
e);
if (e instanceof IOException){
throw (IOException)e;
} else if (e instanceof ClassNotFoundException) {
throw (ClassNotFoundException)e;
}
}
} else {
//加载session
//1111111
session = store.load(id);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
String msg = sm.getString(
"persistentManager.deserializeError", id);
log.error(msg, e);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg, e);
}
if (session != null && !session.isValid()) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"persistentManager.swapInInvalid", id));
session.expire();
removeSession(id);
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString("persistentManager.swapIn", id));
session.setManager(this);
// make sure the listeners know about it.
((StandardSession)session).tellNew();
add(session);
((StandardSession)session).activate();
// endAccess() to ensure timeouts happen correctly.
// access() to keep access count correct or it will end up
// negative
session.access();
session.endAccess();
}
}
}
// Make sure the lock is removed
synchronized (this) {
sessionSwapInLocks.remove(id);
}
return session;
}
可以看到主要的核心代码就是标注1的地方,Store.load(id),而这个源码配合Store.save(session)不管是FileStore还是JDBCStore都是很简单的,所以就不查看了。
除了getSession()方法有不同的地方,周期性任务的方法也略有不同。
在ManagerBase的backgroundProcess()方法中:
@Override
public void backgroundProcess() {
count = (count + 1) % processExpiresFrequency;
if (count == 0)
processExpires();
}
因为processExpires()方法PersitentManagerBase中有复写的方法,所以会调用子类的方法。
@Override
public void processExpires() {
//111111111
long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
Session sessions[] = findSessions();
int expireHere = 0 ;
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Start expire sessions " + getName() + " at " + timeNow + " sessioncount " + sessions.length);
for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++) {
if (!sessions[i].isValid()) {
expiredSessions.incrementAndGet();
expireHere++;
}
}
//222222
processPersistenceChecks();
if ((getStore() != null) && (getStore() instanceof StoreBase)) {
((StoreBase) getStore()).processExpires();
}
long timeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("End expire sessions " + getName() + " processingTime " + (timeEnd - timeNow) + " expired sessions: " + expireHere);
processingTime += (timeEnd - timeNow);
}
在标注1到标注2之间的代码和之前查看的并无区别,基本就是将内存中的session一个个过期检查下。接着调用了processPersistenceChecks()方法。
public void processPersistenceChecks() {
//空闲时间超出一定的存储到存储器中
processMaxIdleSwaps();
//活跃session超出一定比例的存储到存储器中
processMaxActiveSwaps();
//空闲时间超出一定时间的进行备份
processMaxIdleBackups();
}
因为三个方法都相差不大,就着了其中一个来查看下
/**
* Swap idle sessions out to Store if they are idle too long.
*/
protected void processMaxIdleSwaps() {
if (!getState().isAvailable() || maxIdleSwap < 0)
return;
//获取所有的session
Session sessions[] = findSessions();
long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Swap out all sessions idle longer than maxIdleSwap
//一个变量,在server.xml里可以配置,session的最大空闲时间,超出session会被保存到存储器中,如果是负数,那么永远不保存
if (maxIdleSwap >= 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++) {
StandardSession session = (StandardSession) sessions[i];
synchronized (session) {
if (!session.isValid())
continue;
int timeIdle;
if (StandardSession.LAST_ACCESS_AT_START) {
timeIdle = (int) ((timeNow - session.getLastAccessedTimeInternal()) / 1000L);
} else {
timeIdle = (int) ((timeNow - session.getThisAccessedTimeInternal()) / 1000L);
}
if (timeIdle >= maxIdleSwap && timeIdle >= minIdleSwap) {
if (session.accessCount != null &&
session.accessCount.get() > 0) {
// Session is currently being accessed - skip it
continue;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString
("persistentManager.swapMaxIdle",
session.getIdInternal(),
Integer.valueOf(timeIdle)));
try {
//11111
swapOut(session);
} catch (IOException e) {
// This is logged in writeSession()
}
}
}
}
}
}
查看标注1 的 swapOut(session)
protected void swapOut(Session session) throws IOException {
if (store == null || !session.isValid()) {
return;
}
((StandardSession)session).passivate();
//222
//写入到存储器中
writeSession(session);
//从活跃session名单中移除,也就是内存中移除
super.remove(session, true);
//回收session对象
session.recycle();
}
查看标注2的writeSession()
protected void writeSession(Session session) throws IOException {
if (store == null || !session.isValid()) {
return;
}
try {
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
try{
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedStoreSave(session));
}catch(PrivilegedActionException ex){
Exception exception = ex.getException();
if (exception instanceof IOException) {
throw (IOException) exception;
}
log.error("Exception in the Store during writeSession: "
+ exception, exception);
}
} else {
//3333333
store.save(session);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(sm.getString
("persistentManager.serializeError", session.getIdInternal(), e));
throw e;
}
}
可以看出最后还是调用的store.save(session)方法,就不再查看了,其他的processMaxActiveSwaps(),processMaxIdleBackups()方法都很类似,就留给读者自行查看了。
总的来说PersistentManager与StandardManager区别在于,PersistentManager在StandardManager的基础上额外增加了存储的功能,不管查找,删除,还是保存都需要在内存和存储器中同时进行。
总结:本文讨论了session管理器,该组件用来管理session管理中的session对象,解释了不同管理器的区别,以及session管理器如何把内存中session持久化到存储器中
最后附上相关配置:
在web.xml中配置 session 的过期时间,默认30min
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
在server.xml中配置 session管理器,默认StandardManager可以不配置,如果需要配置全局的session manager,可以在conf/context.xml中配置
StandardManager
当Tomcat服务器关闭或重启,或者Web应用被重新加载时,会对在内存中的HttpSession对象进行持久化, 并把它们保存到文件系统中,默认的文件为$CATALINA_HOME/work/Catalina/hostname/applicationname/SESSIONS.ser
在<Context></Context>标签内配置<Manager></Manager>标签
<Manager className="org.apache.catalina.session.StandardManager" maxInactiveInterval="-1" />
备注:如果服务器异常关闭则所有会话都会丢失,StandardManager没有机会进行存盘处理
PersistentManager
<Manager className="org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManager"
saveOnRestart="true"
maxActiveSessions="-1"
minIdleSwap="60"
maxIdleSwap="60"
maxIdleBackup="60"
>
<!--<Store className="org.apache.catalina.session.FileStore" directory="../session" />-->
<Store
className="org.apache.catalina.session.JDBCStore"
driverName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://url?user=user&password=psd"
sessionTable="tomcat_session"
sessionIdCol="session_id"
sessionDataCol="session_data"
sessionValidCol="session_valid"
sessionMaxInactiveCol="max_inactive"
sessionLastAccessedCol="last_access"
sessionAppCol="app_name"
/>
</Manager>
saveOnRestart:是否在重启的时候加载保存sessionmaxActiveSessions:最大允许session数量,-1 不限制minIdleSwap:最小空闲时间,超出将会被转存到存储器中maxIdleSwap:最大空闲时间,超出将会被转存到存储器中
Store相关:
directory:采用FileStore的时候指存储session的目录sessionTable:存储session的表名sessionIdCol:sessionid列名sessionDataCol:sessionData列名sessionValidCol:session是否有效列名sessionMaxInactiveCol:session最大闲置时间列名sessionLastAccessedCol:session上次访问时间列名sessionAppCol:session归属的应用名称列名
(完)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号