Steps for creating JDBC Application
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity
JDBC API is a Java API that can access any kind of tabular data, especially data stored in a Relational Database.
The JDBC library includes APIs for each of the tasks mentioned below that are commonly associated with database usage
1. Making a Connection to a Database
2. Creaing SQL or MySQL statements
3. Executing SQL or MySQL queries in the Database
4. Viewing Or Modifying the result records.
And here below is an example on how to create a simple JDBC application.
It will show how to open a database connection, execute a SQL query, and display the results
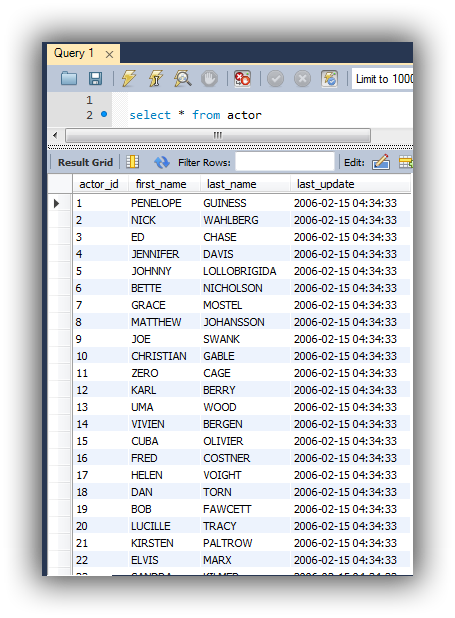
As shown below, we have already some data in table actor stored.
the DB name is 'sakila'
Important steps explained.
1. Import the needed packages : import java.sql.*
2. Register JDBC Driver: Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
3. Open a Connection
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(Url, UserName, Password);
4. Create a Statement.
stmt = conn.CreateStatement();
5. Excute a Query and return the result to ResultSet
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL);
1 //Step 1, import the needed packages 2 import java.sql.*; 3 4 public class Mysql { 5 6 // JDBC driver name and database URL 7 static final String JDBC_Driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; 8 static final String url = 9 10 "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sakila?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"; 11 12 // Credtials , Password and Username 13 14 static final String UserName = "root"; 15 static final String Password = "3792354"; 16 static final String SQL = "Select * from actor"; 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 20 Connection conn = null; 21 Statement stmt = null; 22 23 24 try { 25 26 System.out.println("Connecting to Database..."); 27 Class.forName(JDBC_Driver); 28 29 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, UserName, Password); 30 31 System.out.println("Connected to Databse..."); 32 33 System.out.println("Creating Statement..."); 34 35 stmt = conn.createStatement(); 36 37 System.out.println("Executing the Query..."); 38 39 ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL); 40 41 System.out.println("fetching the result..."); 42 43 while(rs.next()) { 44 45 int id = rs.getInt("actor_id"); 46 47 String name = rs.getString("first_name")+ " "+ rs.getString("last_name"); 48 49 System.out.println(id + " "+ name); 50 51 } 52 53 } 54 55 catch(SQLException se){ 56 //Handle errors for JDBC 57 se.printStackTrace(); 58 }catch(Exception e){ 59 //Handle errors for Class.forName 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 }finally{ 62 //finally block used to close resources 63 try{ 64 if(stmt!=null) 65 stmt.close(); 66 }catch(SQLException se2){ 67 }// nothing we can do 68 try{ 69 if(conn!=null) 70 conn.close(); 71 }catch(SQLException se){ 72 se.printStackTrace(); 73 }//end finally try 74 }//end try 75 76 } 77 78 }
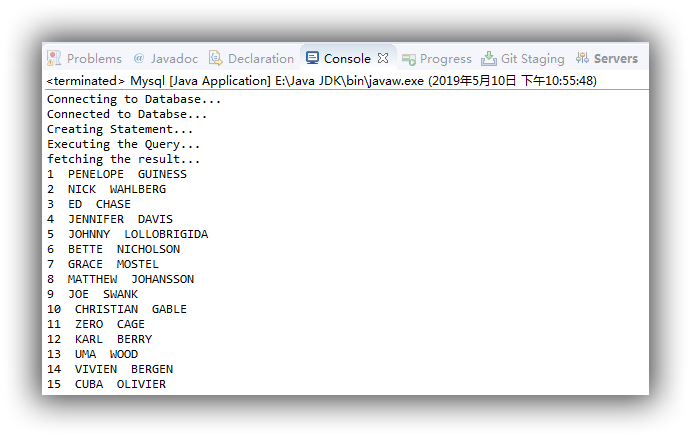
Result shown as below. As could see the data in Database has been successfully fetched.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号